Method for detecting hereditary hearing loss relative connexin 26 gene GJB2 mutation and kit for detection
A technology of connexin and hereditary deafness, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as the inability to comprehensively and accurately analyze the relationship between deafness and the inability to accurately determine hereditary deafness, and achieve the effect of facilitating diagnosis and improving the detection rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1 Detection of the GJB2 mutation of the connexin 26 gene in an autosomal recessive family with hereditary deafness
[0024] 1. Test samples
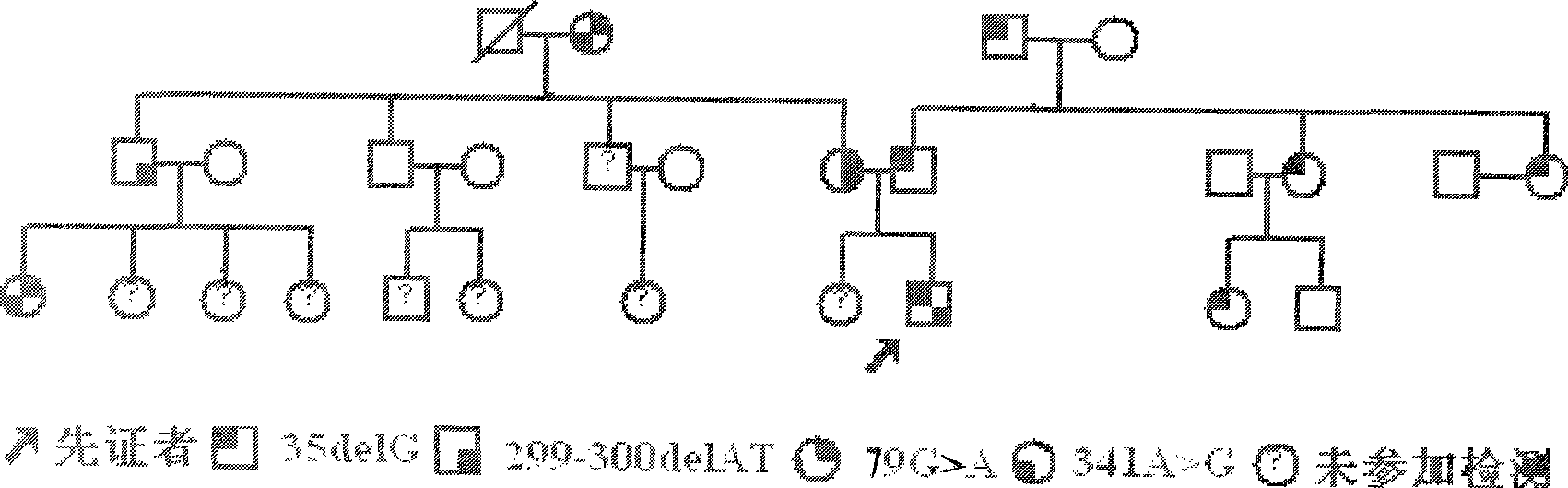
[0025] One deaf family with autosomal recessive inheritance as the transmission characteristic was selected, with a total of 27 people, including 3 deaf patients. Among the subjects, there were 2 deaf patients, and peripheral whole blood DNA was extracted from the subjects (Yuan Huijun et al., Chinese Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, 1998, 33(2): 67-70; Li Weimin et al., Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, 2001, 15 (Supplement): 53-58), as a test sample. For the pedigree of the family, see figure 1 .
[0026] The proband, male, 15 years old, Han nationality, had a full-term vaginal delivery. He was deaf when he was 1 year old, and his medication history was unknown. Physical examination: the general condition is normal, the tympanic membrane is intact, and the temporal bone CT examination excludes inner ear deform...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Example 2 Detection of GJB2 mutation in sporadic cases of hereditary deafness-related connexin 26 gene of unexplained sensorineural deafness
[0089] 1. Test samples
[0090] Select 50 sporadic patients with unexplained sensorineural deafness, and extract peripheral whole blood DNA from the individuals (Yuan Huijun et al., Chinese Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, 1998, 33(2): 67-70; Li Weimin et al., Clinical Otorhinolaryngology Department Journal, 2001, 15 (Supplement): 53-58), as a test sample.
[0091] 2. Primer design 3. PCR amplification reaction 4. Purification and sequence determination of PCR products are the same as in Example 1.
[0092] 5. Results: See Table 1.
[0093] Table 1 Example 2 GJB2 gene detection results
[0094] genotype number of people 9G>A / IVS1+1G>A 1 235delC / 257C>G 1 235delC / 299delAT 2 235delC / wide type 1 235delC / 235delC 1 299delAT / 299delAT 1 176del16 / 139G>T 1 wide type / wide type 42...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Example 3 Type I kit for GJB2 mutation of hereditary deafness-associated connexin 26 gene and its application
[0096] 1. The type I kit (100 copies) suitable for heel blood spots contains the following components:
[0097] (1) Solution I (the main component is 5% Chelex) 25ml;
[0098] (2) PCR amplification reaction reagents, including dNTP, 2×PCR buffer (for exon 1 amplification), 10×PCR buffer (for exon 2 amplification), Mg++, triple distilled water, Taq enzyme 1 (for amplifying exon 1), Taq enzyme 2 (for amplifying exon 2);
[0099] (3) the forward primer F1 of the amplification GJB2 gene basic promoter region, exon 1 and its cut region described in claim 2 and the amplification GJB2 gene basic promoter region, exon 1 and its Reverse primer R1 for the cut region, forward primer F2 for amplifying exon 2 and its cut region, and reverse primer R2 for amplifying exon 2 and its cut region mixed in equal proportions;
[0100] (4) Instruction manual.
[0101] 2. Detect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com