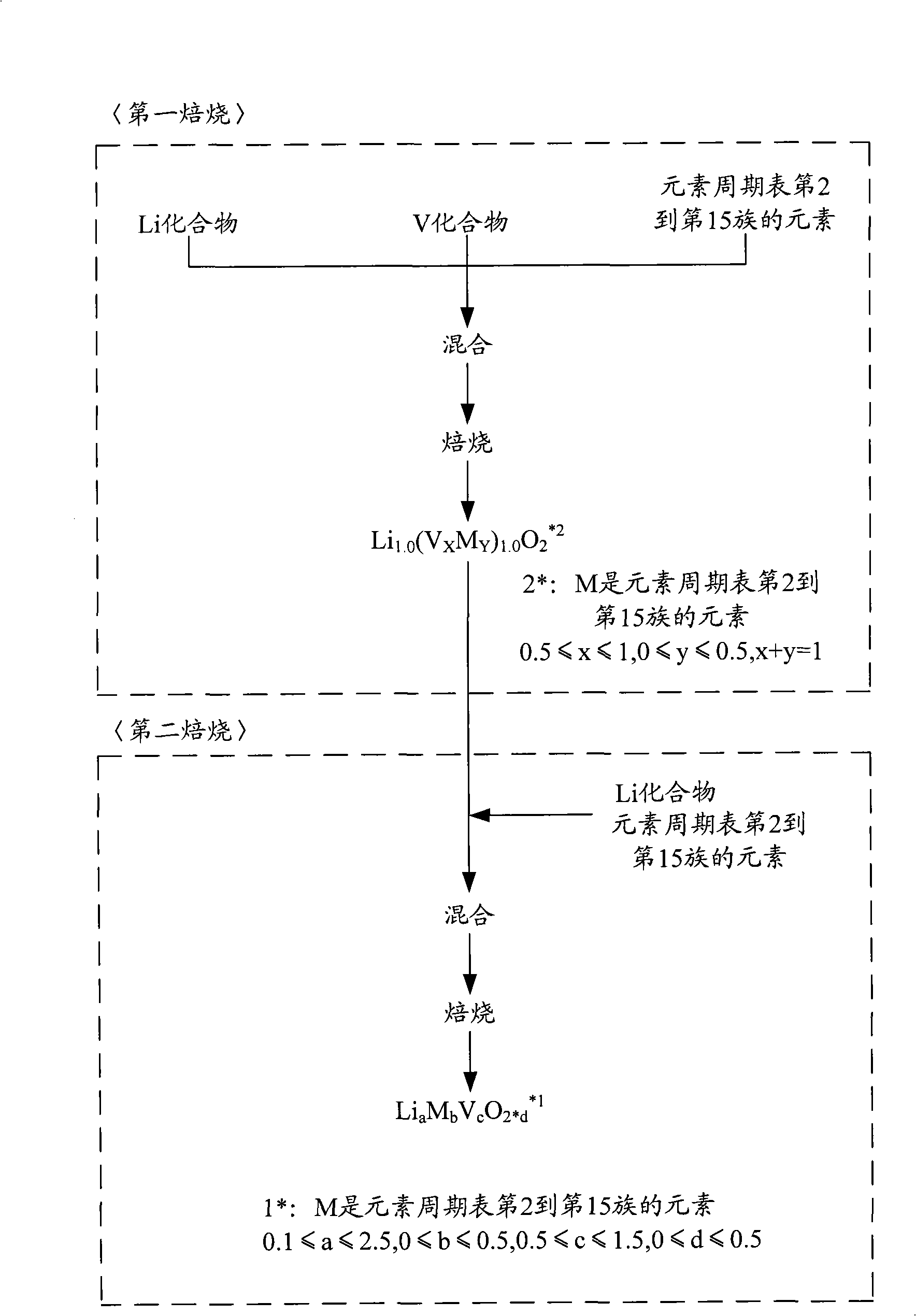
Cathode active material for non-aqueous electrolyte rechargeable battery and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of negative electrode active material and non-aqueous electrolyte, which is applied in the field of negative electrode active material for rechargeable battery with non-aqueous electrolyte and its preparation, can solve the problems such as capacity decline, and achieve the effect of high crystallinity and high capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
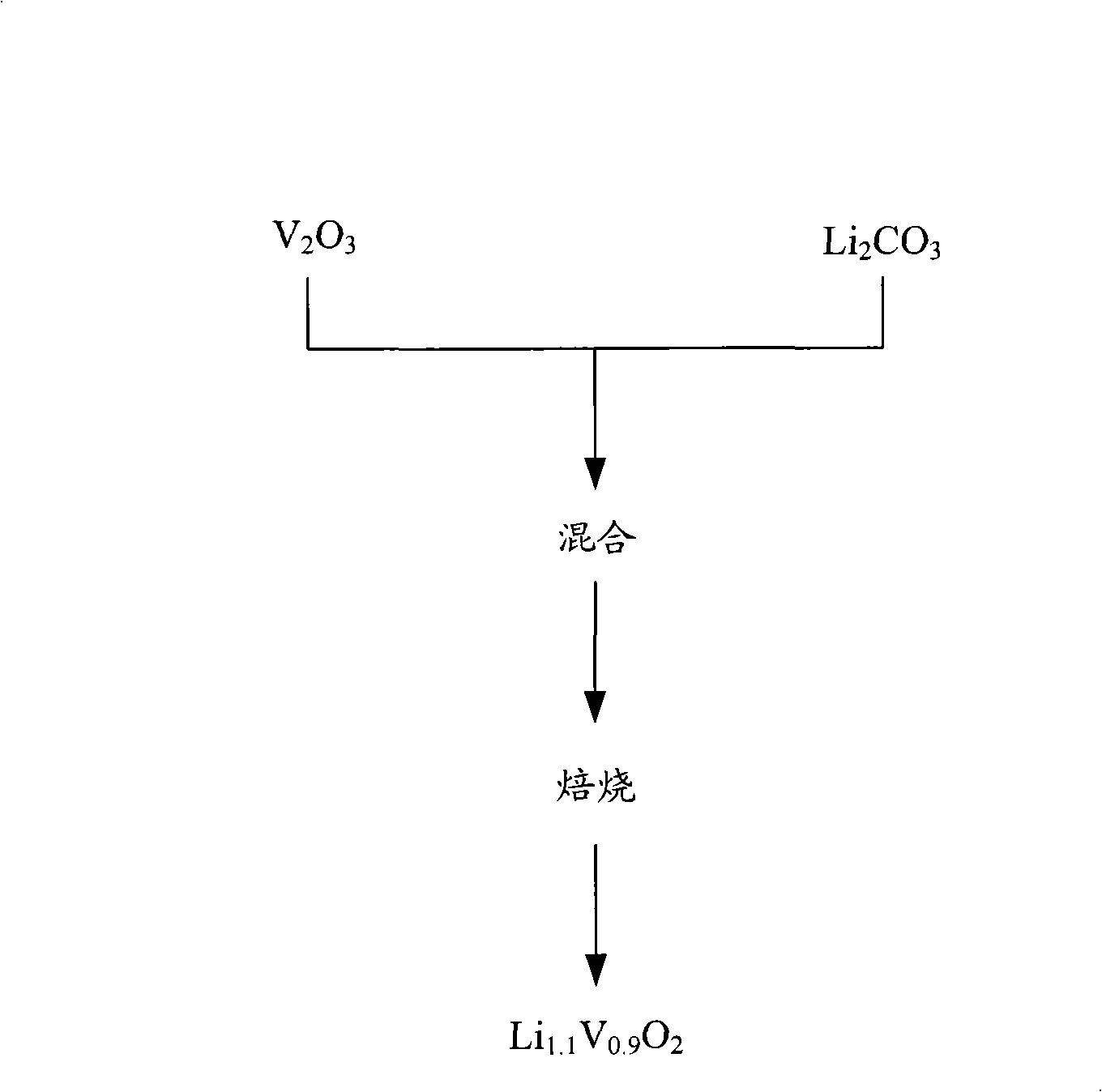
[0054] figure 2 A flowchart of the preparation method of lithium vanadium oxide according to the conventional method.
[0055] refer to figure 2 , due to Li 1.1 V 0.9 o 2 is stoichiometrically unstable, so when the raw materials are mixed simultaneously and subsequently calcined to obtain Li 1.1 V 0.9 o 2 , a crystalline material with lattice vacancy defects in the crystal lattice results. Li ions can intercalate into the lattice vacancies of lithium vanadium oxide during charge and discharge. Properly intercalated lithium can combine with other atoms to fill lattice vacancies, but unintentionally intercalated lithium ions cause lattice defects. When the lattice defects are stabilized, the balance between atomic bonding can be changed, the interlayer distance will be kept at a uniform distance, or the intercalation and dissociation between the layered structures of lithium vanadium oxides cannot occur due to the electrical repulsion between lithium ions. sites for i...
Embodiment 1
[0069] Will Li 2 CO 3 and V 2 o 3 The mixture was mixed at a molar ratio of 1.0:1.0, and then the mixture was calcined at 1100° C. for 5 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere to prepare lithium vanadium oxide having a layered rock-salt structure as a framework.
[0070] Next, the lithium vanadium oxide with layered rock-salt structure and Li 2 CO 3 Mixed at a molar ratio of 0.9:0.1, and then calcined at 1100°C for 5 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain lithium vanadium oxide (Li 1.1 V 0.9 o 2 ).
[0071] The lithium vanadium oxide as the negative electrode active material is subjected to XRD (X-ray diffraction) detection under the following conditions to obtain the full width at half maximum of the (003) plane and the peak intensity ratio of the (003) and (104) planes. The results are shown in Table 1 below.
[0072] XRD detection equipment: Rigaku Rint 2000 (Rigaku company)
[0073] Vacuum tube: CuKα1
[0074] Voltage: 50kV
[0075] Current: 300mA
[0076] Sca...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Will Li 2 CO 3 and V 2 o 3 Mixed at a molar ratio of 1.0:1.0, and then calcined at 1100° C. for 5 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere to prepare lithium vanadium oxide with a layered rock-salt structure as a framework. Next, the lithium vanadium oxide with layered rock-salt structure and Li 2 CO 3 and MgC 2 o 4 2H 2 O was mixed at a molar ratio of 0.87:0.1:0.03, and then calcined at 1100°C for 5 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain lithium vanadium oxide (Li 1.1 Mg 0.03 V 0.87 o 2 ). Then, the battery is prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the lithium vanadium oxide (Li 1.1 Mg 0.03 V 0.87 o 2 ) as the negative electrode active material.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com