A moldable biomaterial for bone regeneration
A biomaterial and biodegradation technology, applied in the field of biomaterials, can solve problems such as high cost, achieve the effect of reducing polymer content, reducing burden, and increasing porosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0266] Example 1: Preparation of solid particle porous material coated with active agent
[0267] This example uses β-TCP coated particles as the solid porous material and rhGDF-5 as the active agent. Alternatives can be prepared similarly.
[0268] Raw materials must be sterilized in an appropriate manner. Initially 500 mg of β-TCP (500-1000 μm particle size) was placed in dry form in a 2R-glass. The rhGDF-5 stock solution (3.4 mg / ml in 10 mM HCl) was diluted to 0.54 μg / ml with the corresponding coating buffer. 475 µl of the rhGDF-5 solution obtained by the above method was pipetted onto β-TCP with a pipette and absorbed. The wet pellet was incubated at 25°C for 1 hour and then lyophilized. Other examples of coating β-TCP are described in WO03 / 043673 and PCT / EP2005 / 006204.
Embodiment 2
[0269] Example 2: Preparation of biodegradable paste material
[0270] Initial polymer (RG502H; PLGA; polymer composition: 48-52mol% D, L-lactide and 48-51mol% glycolide; intrinsic viscosity: 0.16-0.24dl / g, 25°C, 0.1% in CHCl 3 Medium; Boehringer, Ingelheim) was added to the necessary amount of organic solvent (PEG400) in a porcelain crucible. The two components are homogenized and heated at about 60°C until the polymer is completely dissolved in the organic solvent. Subsequently, an inorganic filler (beta-tricalcium phosphate powder) and optionally other excipients (eg, a degradation regulator such as carboxymethylcellulose sodium salt) are dispersed into the polymer solution.
Embodiment 3
[0271] Example 3: Moldable biomaterials hardened in situ comprising porous calcium-containing ceramics
[0272] The coated beta-tricalcium phosphate particles of Example 1 and the biodegradable paste material of Example 2 are mixed gently in a crucible, for example, with a sterile spoon, to form a viscous, moldable Material. Preparation of implant materials with different ratios (wt% / wt%) of β-TCP particles and polymer paste: a) β-TCP:polymer paste ratio of 1:1.3; b ) the ratio of β-TCP:polymer paste is 1:1.4; c) the ratio of β-TCP:polymer paste is 1:1.5; and d) the ratio of β-TCP:polymer paste is 1:1.7.
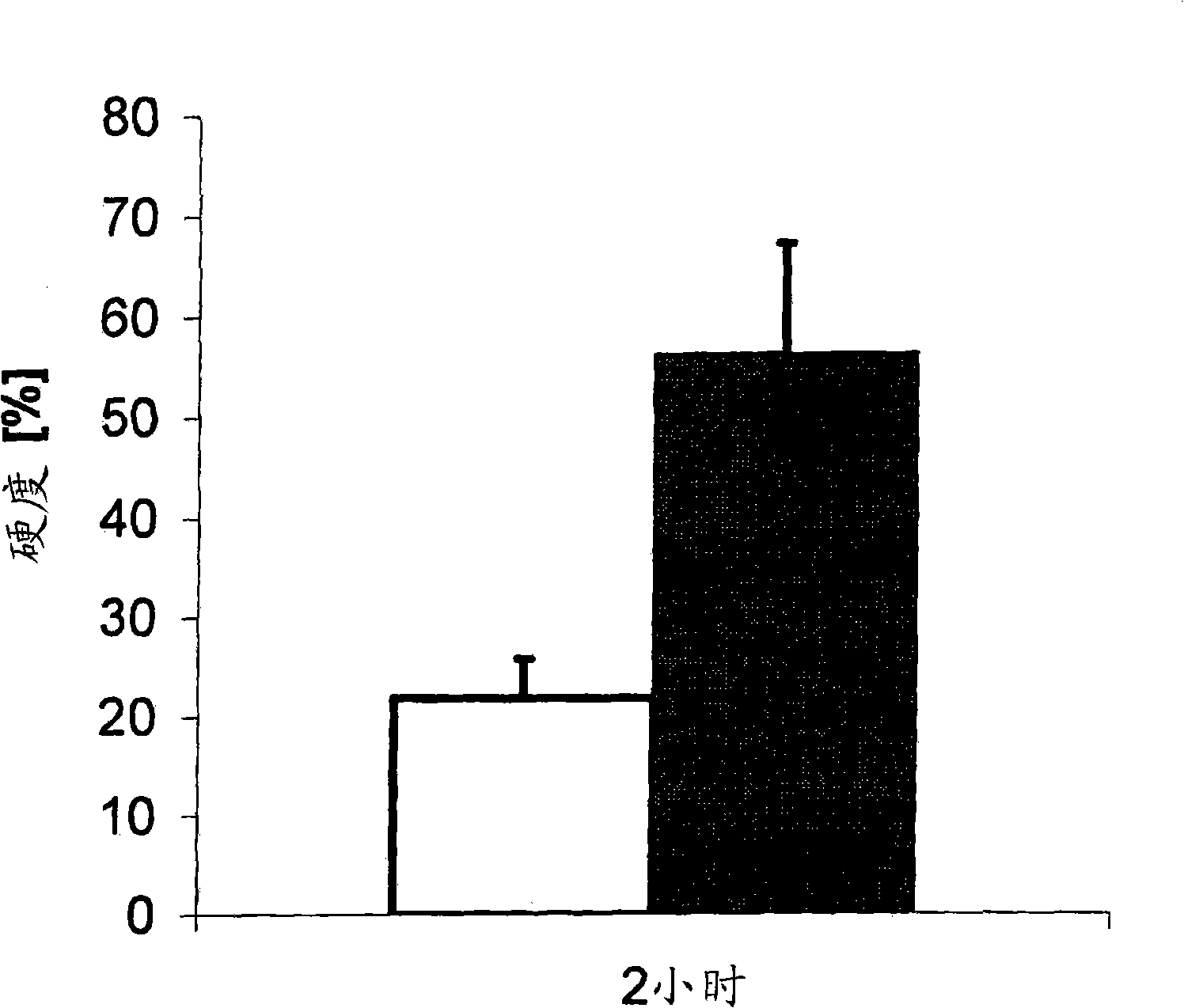
[0273] For all experiments requiring biodegradable paste material or moldable biomaterial in its post-hardened shape, the material was transferred to wells of a 48-well plate (250-300 mg per well). The well plates were then incubated in a bath containing PBS-buffer, where the temperature was fixed at 37°C. The bath takes 150min -1 The frequency is constantly vibrating. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com