Rain cultivation method of forestation on dry-hot valley dryland hillside fields
A technology for dry and hot valleys and sloping land, which is applied in the fields of land preparation, afforestation, forestry, etc. It can solve the problems of no forest land, poor vegetation coverage, and weak seedlings, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing afforestation costs, strong practicability, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
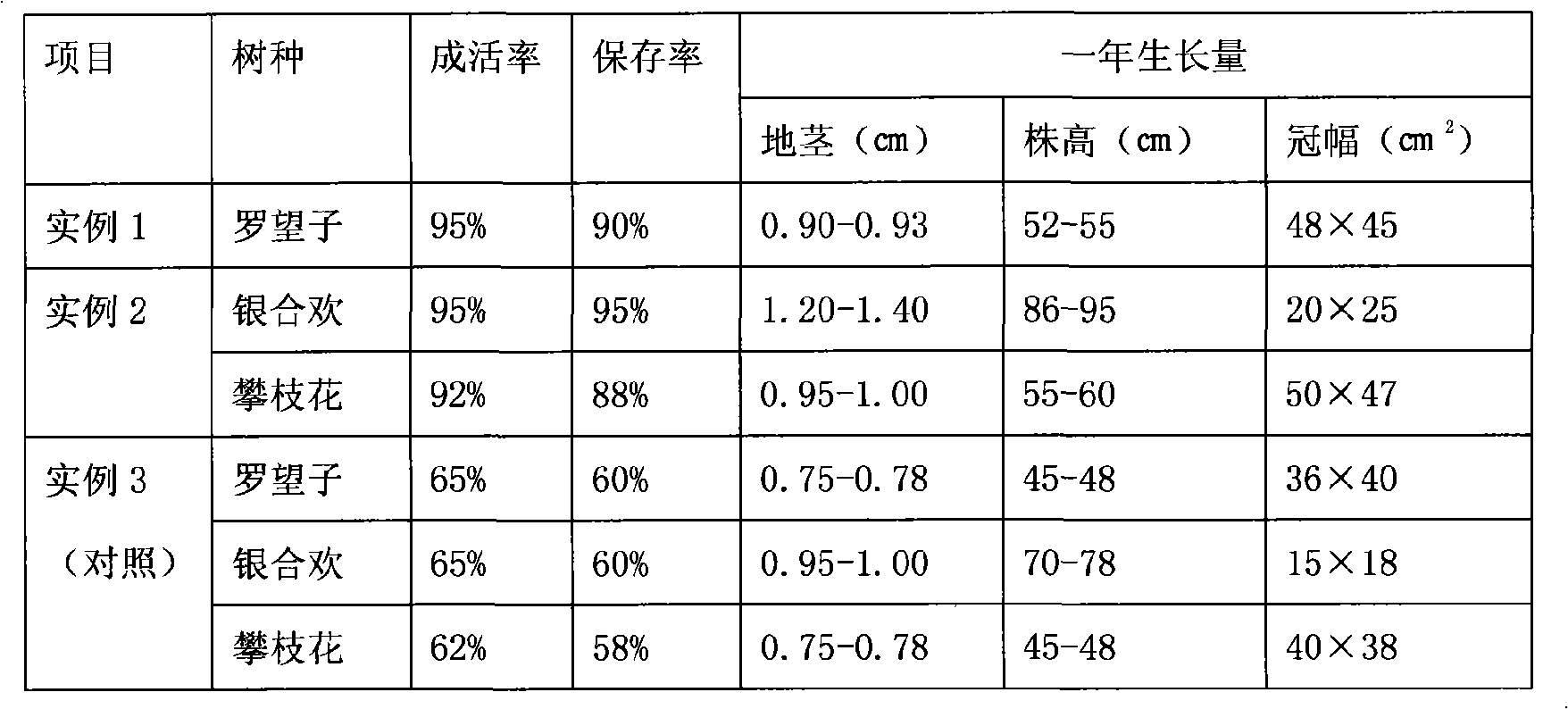
[0019] Project: 1,000 mu rainfed tamarind afforestation project. Afforestation location: Dry and hot valley in Yuanmou County, Yunnan Province
[0020] 1. Excavation of the big pond: When the soil was moist at the end of the rainy season last year, the tamarind seedlings were excavated along the contour line of the afforestation slope and planted in the big pond. The length, width and depth of the big pond are 120cm×80cm×100cm. Separate the excavated topsoil and subsoil. Allow natural sunlight to fully expose the soil to backfill.
[0021] 2. Fertilizer backfill: One month before the rainy season in the year of planting, mix the fully exposed soil with 10kg of organic fertilizer and 4kg of calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer per pond, and then backfill in layers, topsoil backfilling in the lower pond layer, and subsoil backfill in the upper pond layer. The backfill soil is 10cm lower than the planting pond to facilitate the accumulation of rainwater in the big pond. After...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Project: State Forestry Administration's 5,000-mu conversion of farmland to forestry project (Panzhihua and Leucaena), location: Yangkaiwo River Basin in the dry-hot valley of Yuanmou, Yunnan. Except that following measures are different from Example 1, all the other methods are the same as Example 1.
[0029] 1. Excavation of the big pond: the length, width and depth of the big pond of the two tree species are the same as those in Example 1.
[0030] 2. Fertilizer backfill: The backfill fertilizer for Leucaena juniperus is 5kg of organic fertilizer and 2kg of calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer; for Panzhihua colonization, it is 8kg of organic fertilizer and 2.5kg of calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer.
[0031] 3. Cultivate strong seedlings for colonization: The cultivation of Leucaena and Panzhihua seedlings began in the previous year of afforestation. After about one year of management, the bare-root seedlings with developed root systems and thick stems withou...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment 3 (contrast: existing afforestation technology)
[0034] During the implementation process of returning farmland to forests with the participation of farmers in dry and hot valleys in Yuanmou County, they dug planting holes with a length, width, and depth of 40cm×40cm×40cm when the rainy season came that year, and did not make water storage circles (i.e. fish scale pits). , No base fertilizer is applied, just dig and plant, and the tamarind, leucaena and panzhihua seedlings cultivated in the past can be planted in the pond. After the survey at the end of the rainy season, the survival rate of the seedlings was only about 65%. After the drought, the survival rate in the second year was only 60%, and the growth of the seedlings was weak, and the seedlings were dying every year. After that, the seedlings were replenished every year. Greatly increase the cost of afforestation.
[0035] Table: the inventive method and the effect contrast of existing afforestation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com