Preparation method of meso-porous titanium dioxide/activated carbon in-situ composite material
An in-situ composite material and mesoporous titanium dioxide technology, applied in the direction of catalyst activation/preparation, chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, complicated preparation process, high experimental cost, etc., and achieve low cost, The effect of simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Add 0.4 g of sugar and stir and emulsify 160 ml of 6.5 g / L glycolipid-based microbial surfactant aqueous solution of coccilipid sophorolipid at room temperature for 30 minutes to obtain emulsion A. Then, add 50 ml of 0.5 mol / L TiCl 4 Solution was added dropwise in the emulsion A at a speed of 15 drops per minute, and continued magnetic stirring for 30 minutes, allowing Ti 4+ It can be fully adsorbed in the nanovesicle structure of coccidia cells. Slowly add 1 mol / L ammonia water dropwise at a rate of 10 drops per minute until pH = 7, continue magnetic stirring for 2 hours, let the cell structure part mineralize and deposit, then let stand for 2 hours, high-speed centrifuge, wash twice with water, wash once with alcohol, remove Cl - and NH 4 + and H 2 O. Finally, the precipitate was dried in a drying oven at 100 °C for 24 h, and then heat-treated and carbonized at 400 °C for 3 h at a heating rate of 15 °C / min to obtain mesoporous TiO 2 / Activated carbon in situ co...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2: 160ml of 6.5g / L glycolipid-based microbial surfactant coccidiolipid sophorolipid aqueous solution was added at room temperature with 0.4g of sugar and stirred and emulsified for 30 minutes to obtain emulsion A. Then, 60ml of 0.3mol / LTi(SO 4 ) 2 Solution, drop in the emulsion A with the speed of 16 drops per minute, continue magnetic stirring for 30 minutes, let Ti 4+ It can be fully adsorbed in the nanovesicle structure of coccidia cells. Slowly add 1 mol / L ammonia water dropwise at a rate of 10 drops per minute until pH = 7, continue magnetic stirring for 2 hours, let the cell structure part mineralize and deposit, then let stand for 2 hours, high-speed centrifuge, wash twice with water, wash once with alcohol, remove SO 4 2- and NH 4 + and H 2 O. Finally, the precipitate was dried in a drying oven at 100°C for 24 hours, then heated to 400°C at a heating rate of 15°C / min, and then heat-treated and carbonized at 400°C for 3 hours to obtain mesopor...
Embodiment 3
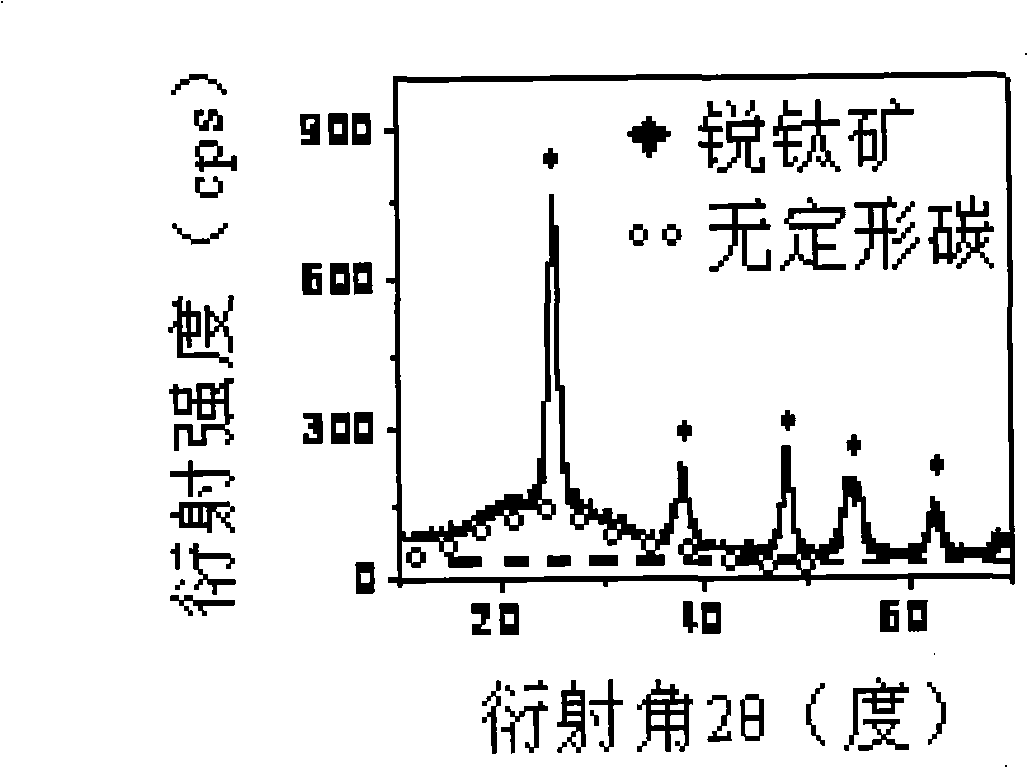
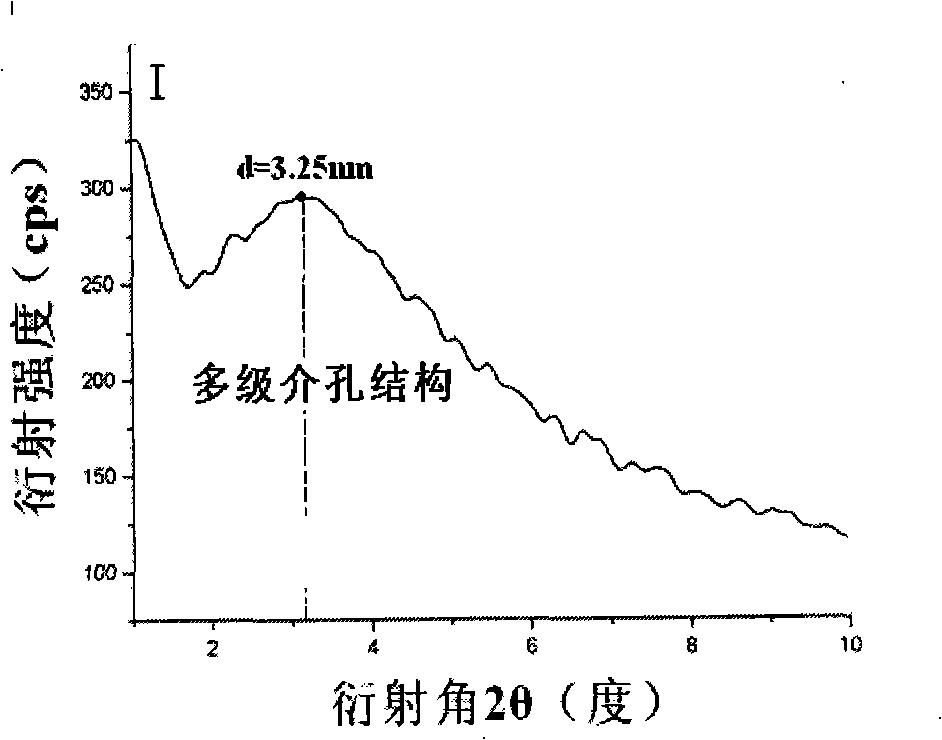
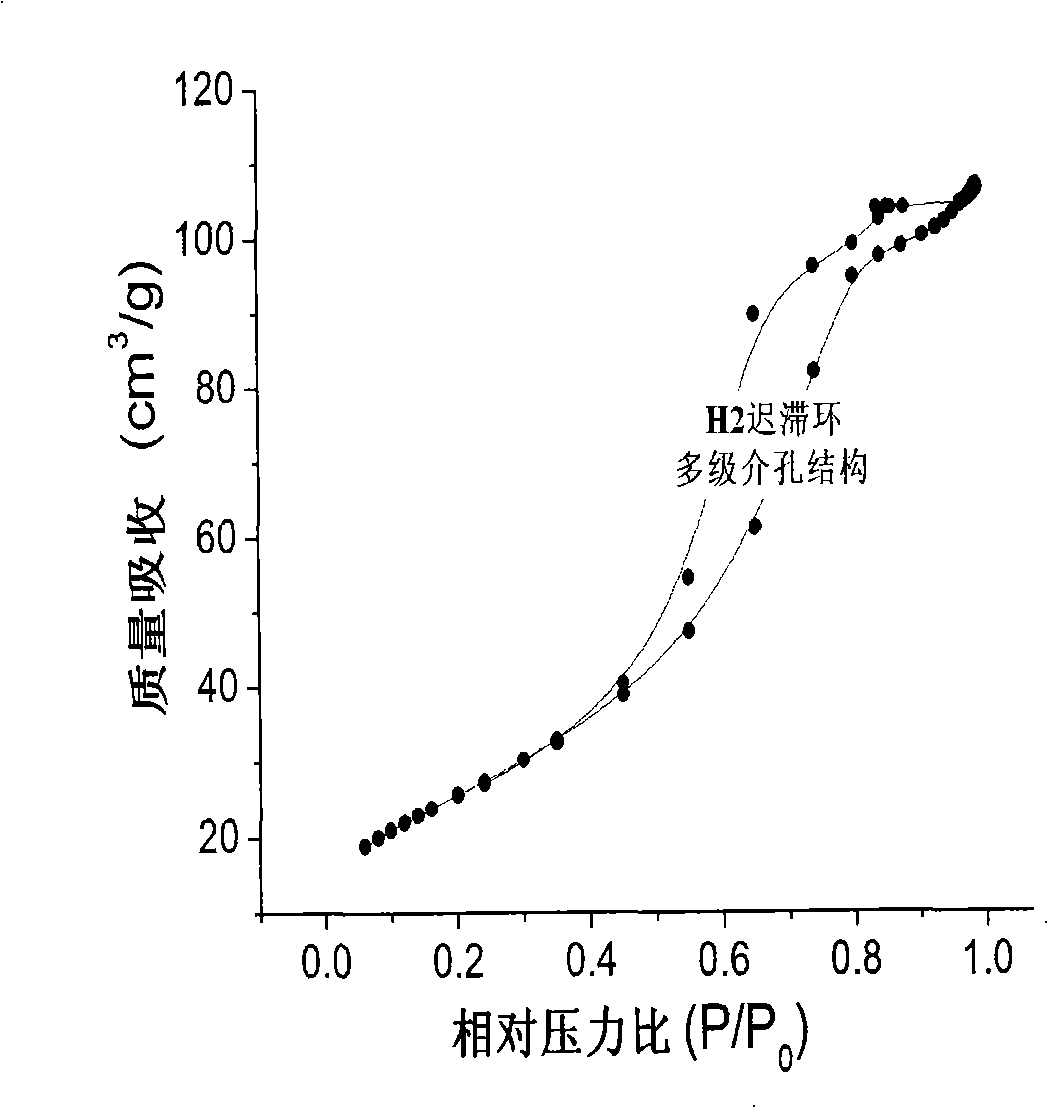
[0036] Embodiment 3. As described in Embodiment 1, the difference is that the heating rate of the heat treatment is 10° C. / min, the temperature is raised to 420° C., and the carbonization is carried out for 4 hours. Mesoporous TiO 2 / The particle size of the activated carbon in situ composite material is 36-49nm, and there are open worm-like ordered structural pores between the particles. The mesopore diameter distribution is 4-33nm, the atomic ratio of Ti / C is 1.01, and the specific surface area is 285m 2 / g.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com