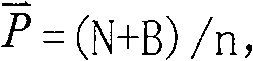Method for determining coagulant optimal addition quantity and optimal pH in water treatment
A coagulant dosage technology, applied in the field of environmental engineering, can solve the problems of water treatment coagulant dosage and dosage conditions that have not yet been applied, and achieve considerable economic and social benefits, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] A method for determining the optimal dosage of coagulant and the optimal pH value in water treatment, comprising the steps of:
[0057] (1) Find the boundary condition of the coagulant dosage, determine the range of the molar ratio of the metal ion in the coagulant to the total phosphorus in the water to be treated:
[0058] The water used in this experiment is the secondary effluent of a sewage treatment plant, and the water quality is shown in Table 1.
[0059] Table 1 Water quality indicators of secondary effluent
[0060]
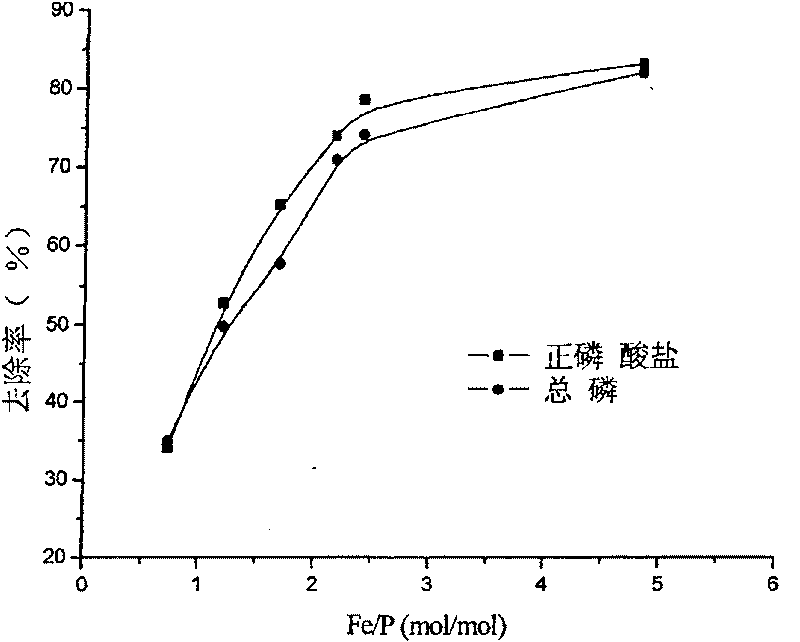
[0061] Take 400mL water samples and place them in six 500mL beakers, add ferric sulfate (see Table 2) to make the Fe / P molar ratio (see Table 2), stir at 200r / min for 1min, and stir at 30r / min 30min, then let it settle for 30min, take the liquid at 3cm below the liquid surface, and measure the concentration of orthophosphate and total phosphorus. The results are shown in Table 2, see figure 1 .
[0062] Table 2 Experimental effect of ferri...
Embodiment 2
[0081] The coagulant takes aluminum sulfate as an example:
[0082] (1) Find the boundary condition of the coagulant dosage, determine the scope of the molar ratio of the metal ion in the coagulant and the total phosphorus in the water to be treated;
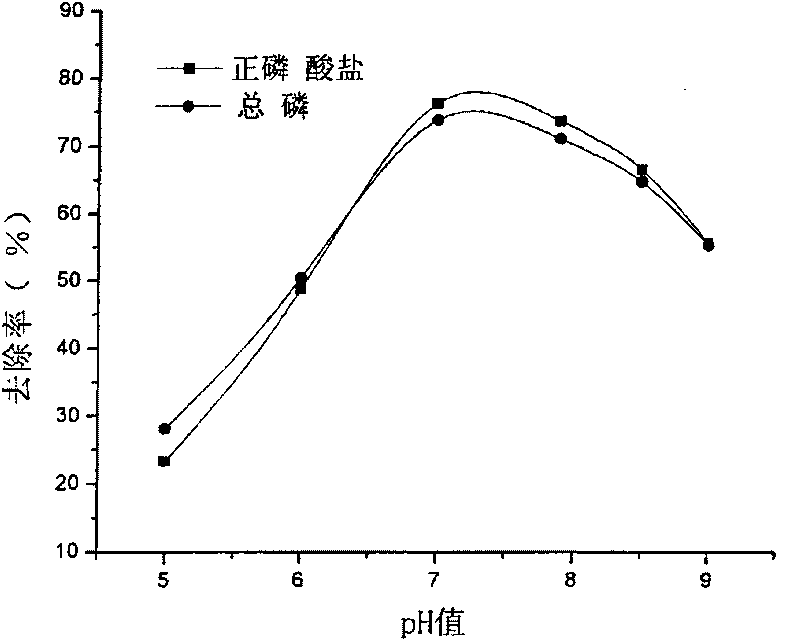
[0083] (2) Find the boundary conditions of the pH value and determine the range of the pH value;
[0084] (3) Simplex optimization test: (method with reference to Example 1) The boundary conditions determined by experiments are respectively that the dosage Al / P (mol / mol) is between 1-5.0: 1, and the pH value is between 5.0-8.5 between. Choose three points (i.e. points 1, 2, 3) in this area to start the simplex experiment. When the dosage is 4.13 (Al / P, mol / mol) and the pH value is 6.3, the removal efficiency of aluminum sulfate At this time, the removal rate of total phosphorus is 95.60%, and the residual concentration of total phosphorus is 0.12mg / L, reaching the standard of "Urban Sewage Recycling-Water Quality for Landscape...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Take the coagulant polyaluminum chloride as an example:
[0087] (1) Find the boundary condition of the coagulant dosage, determine the scope of the molar ratio of the metal ion in the coagulant and the total phosphorus in the water to be treated;
[0088] (2) Find the boundary conditions of the pH value and determine the range of the pH value;
[0089] (3) Simplex optimization test: (method with reference to Example 1) The boundary conditions determined by experiments are respectively that the dosage Al / P (mol / mol) is between 1-5.5: 1, and the pH value is between 5.0-8.5 between. Choose three points (namely, points 1, 2, and 3) in this area to start the simplex experiment. When the dosage is 4.37 (Al / P, mol / mol) and the pH value is 5.4, the removal efficiency of polyaluminium chloride is the largest, and the removal rate of total phosphorus is 93.97% at this time, and the residual concentration of total phosphorus is 0.16 mg / L, reaching the standard (GB / T18921-2002)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com