A method for assigning addresses to nodes in wireless networks
一种无线网络、节点的技术,应用在网络领域,达到低开销的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
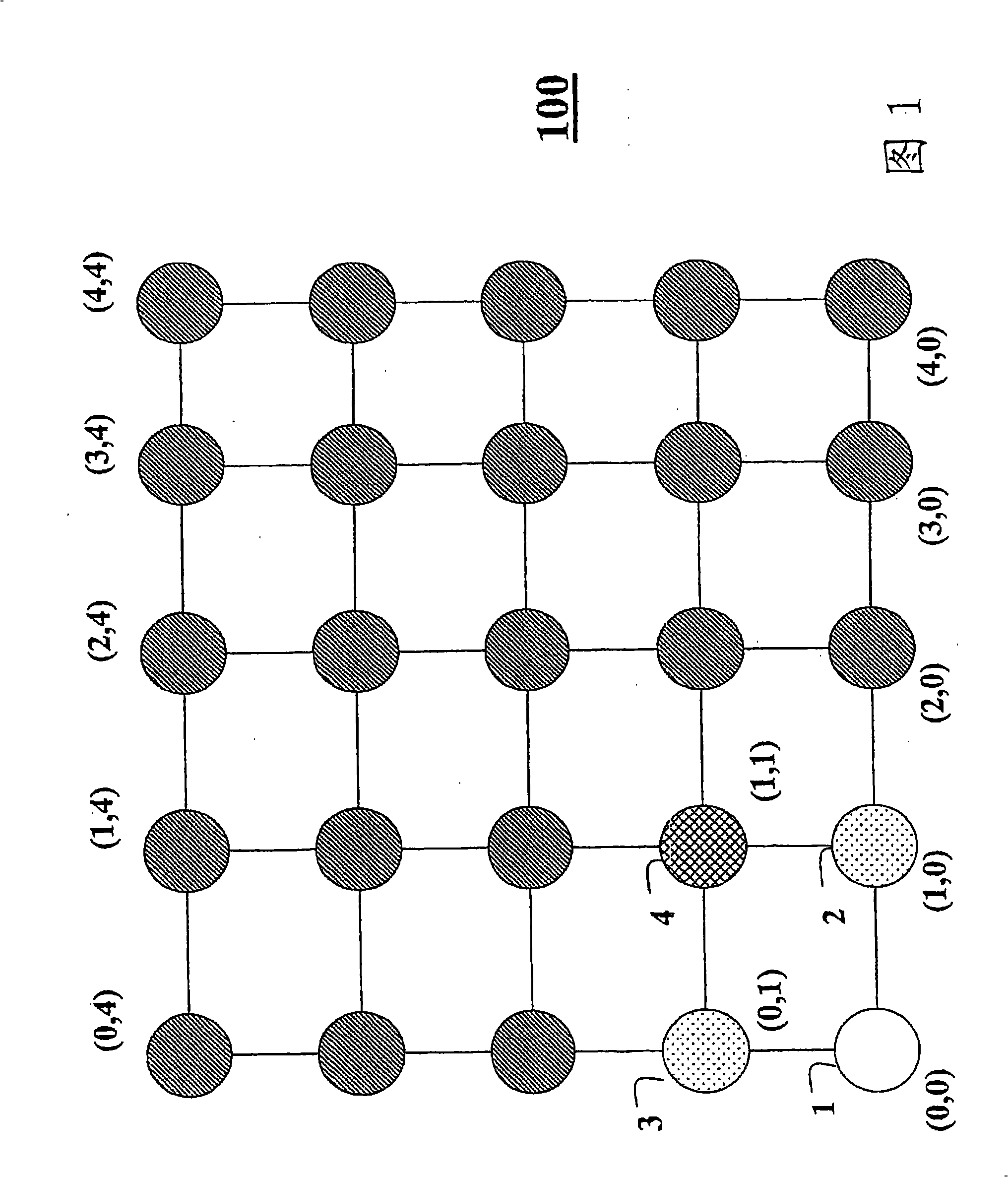
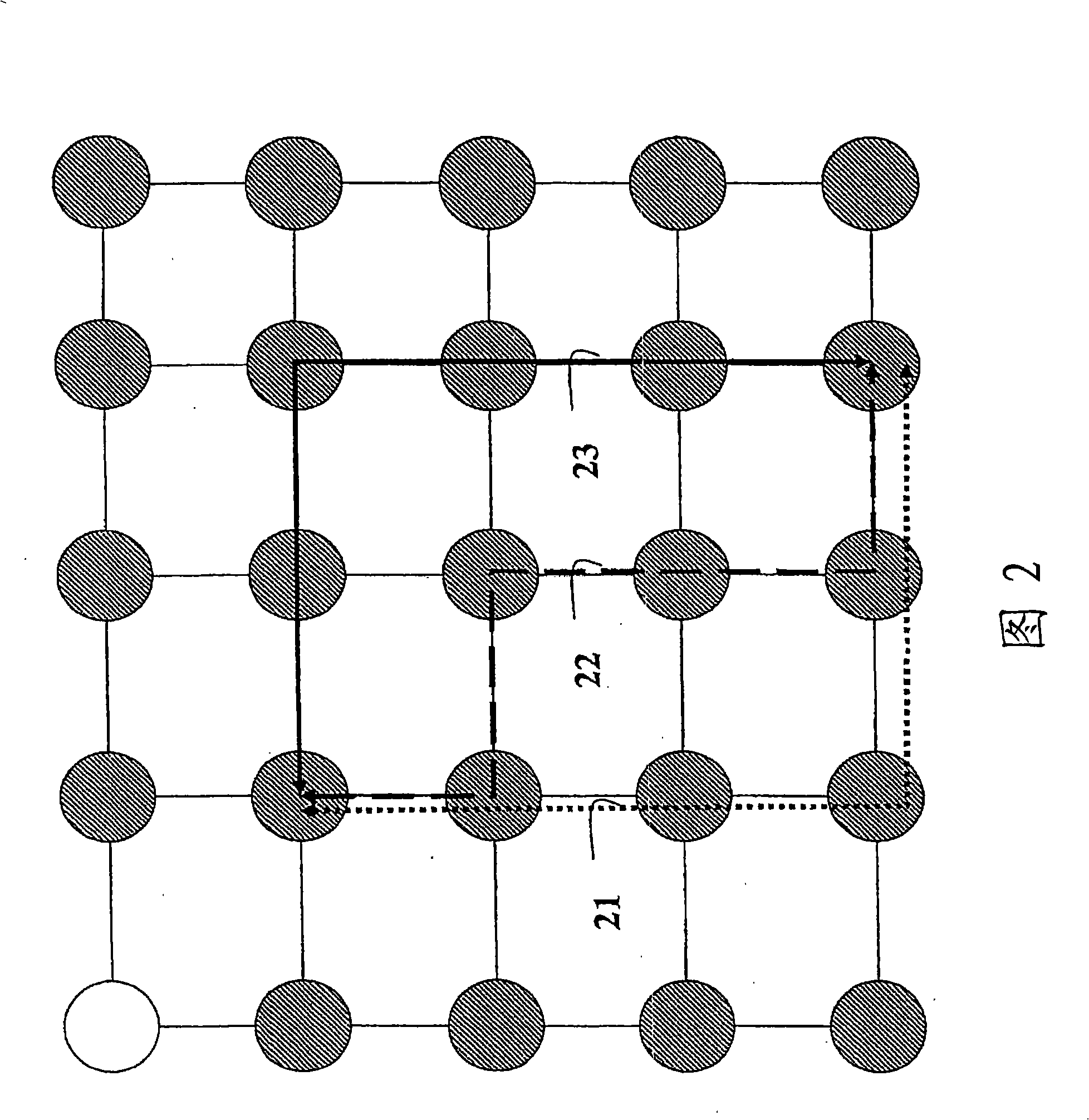
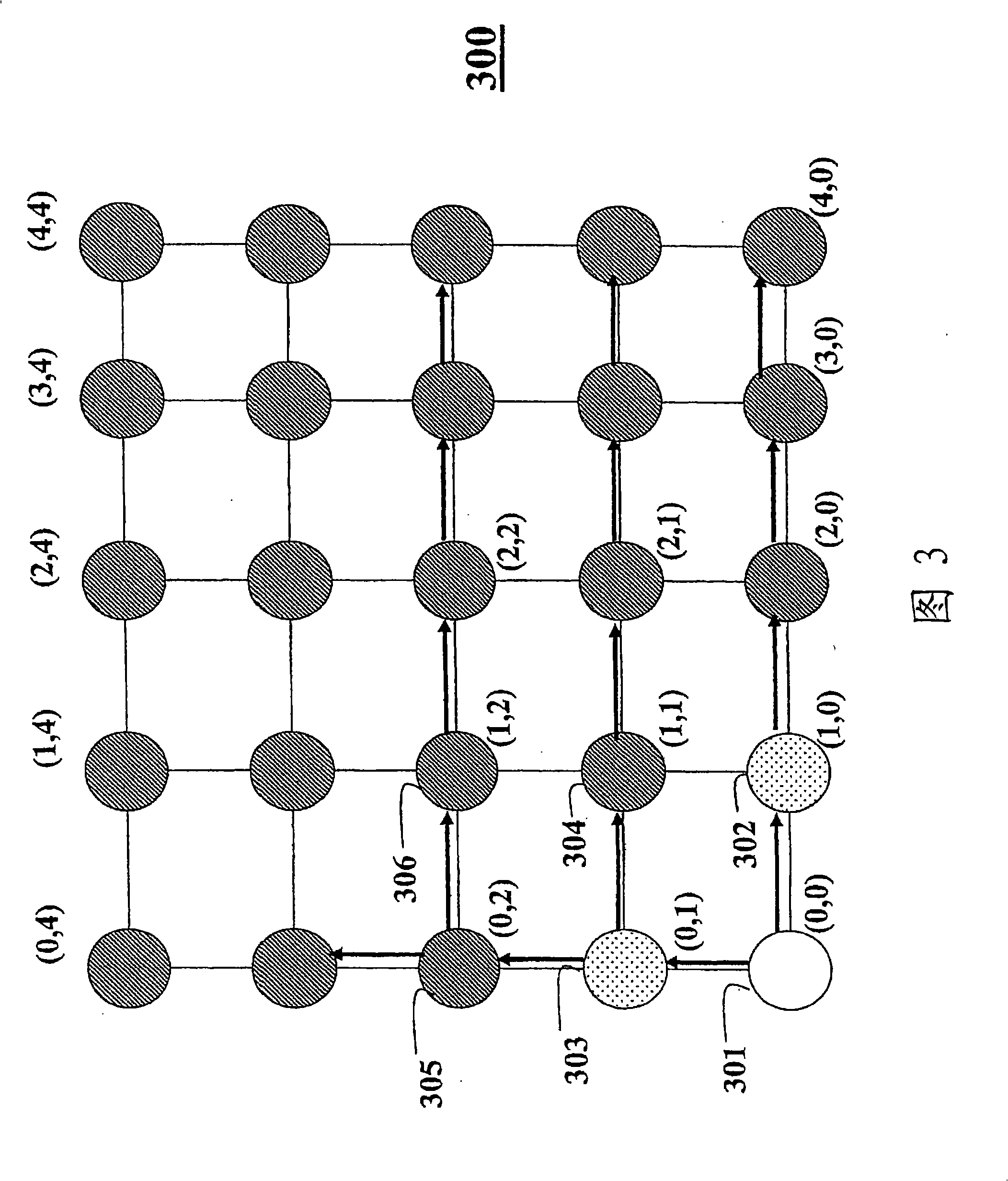
[0017] Fig. 1 shows an example of an n-dimensional grid 100 of nodes in a wireless network according to an embodiment of the present invention, where n is 2. Each intersection point of the grid has Cartesian coordinates, eg (0, 0), (0, 1), ... (4, 4). A node's or n-tuple's coordinates are the logical address of the corresponding node. Coordinates have multiple components, the number of which is equal to the dimensionality of the grid. For example, in two dimensions, each logical address has two components.
[0018] The range of values for each component is expressed in the number of bits assigned to that component. For example, if a full address is specified with 16 bits, then each component can be assigned 8 bits for values in the range [0, 255]. Alternatively, the assignment could be 6 bits and 10 bits, and so on. In other words, the grid can be square, rectangular or higher order parallelepipeds. Additional dimensions can also be used, eg in four dimensions the coo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com