System for adsorbing, separating and detecting ultra-drop target protein
A target protein, ultra-micro-volume technology, applied in material separation, measurement devices, selective adsorption, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient elution of chip microbeads, small amount of modified samples, and affecting the specificity of chip microbeads
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] Embodiment one: the preparation of microbead
[0082] 1. Chitosan Microbeads
[0083] Chitosan (chitosan), chemical name (1,4)-A-amino-A-deoxy-B-D-glucan, is a copolymer of N-deacetylglucosamine, because chitosan and its derivatives are free of Toxicity, biodegradability and good biocompatibility, it is widely used as immobilized carrier of enzymes and cells.
[0084] The following is the preparation process of chitosan microbeads: weigh chitosan 9, dissolve it in 300mL of 2% acetic acid solution, stir continuously for 2 hours to fully dissolve, remove insoluble matter by suction filtration, add Tween-80 10mL, oil Phase dispersion medium, porogen ethyl acetate, emulsifier and polymer surface modifier, fully stirred and reacted at 50°C for 30 minutes, raised the temperature to 60°C, added formaldehyde solution, reacted for 30 minutes, then added 2.0ml of glutaraldehyde, Adjust the pH to 9.0, raise the temperature to 80°C, and react for 60 minutes. Suction filter, wash ...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Embodiment 2: Surface functional group modification of microbeads
[0100] 1. Surface affinity modification process of chitosan microbeads
[0101] Add appropriate amount of deionized water to chitosan microbeads, activate with epichlorohydrin, add EDC and heparin, and stir at 4°C for 24 hours to obtain surface affinity-modified microbeads.
[0102] The long-chain alkyl group of chitosan microbeads is used as the hydrophobic part, and the sulfate group is used as the hydrophilic part to synthesize N-octyl-O-sulfate chitosan (OCS1) to obtain microbeads with surface hydrophilic modification.
[0103] 2. Surface ion exchange modification process of cellulose microbeads
[0104] Add the washed cellulose microbeads to a solution containing 0.1mol / L DEAE hydrochloride and 0.5mol / L NaOH, and keep stirring at 60°C for 10 hours to make it cross-link-DEAE weakly basic anion exchange group group.
[0105] 3. Metal chelation affinity modification of microbeads
[0106] Add micr...
Embodiment 3
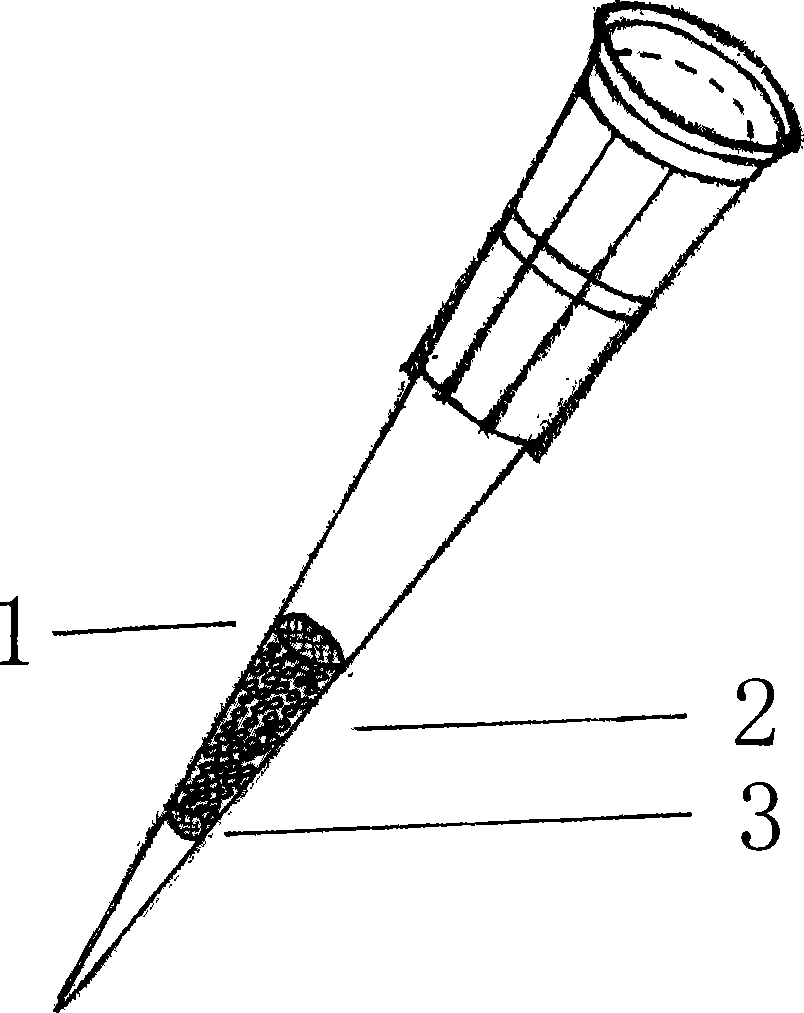
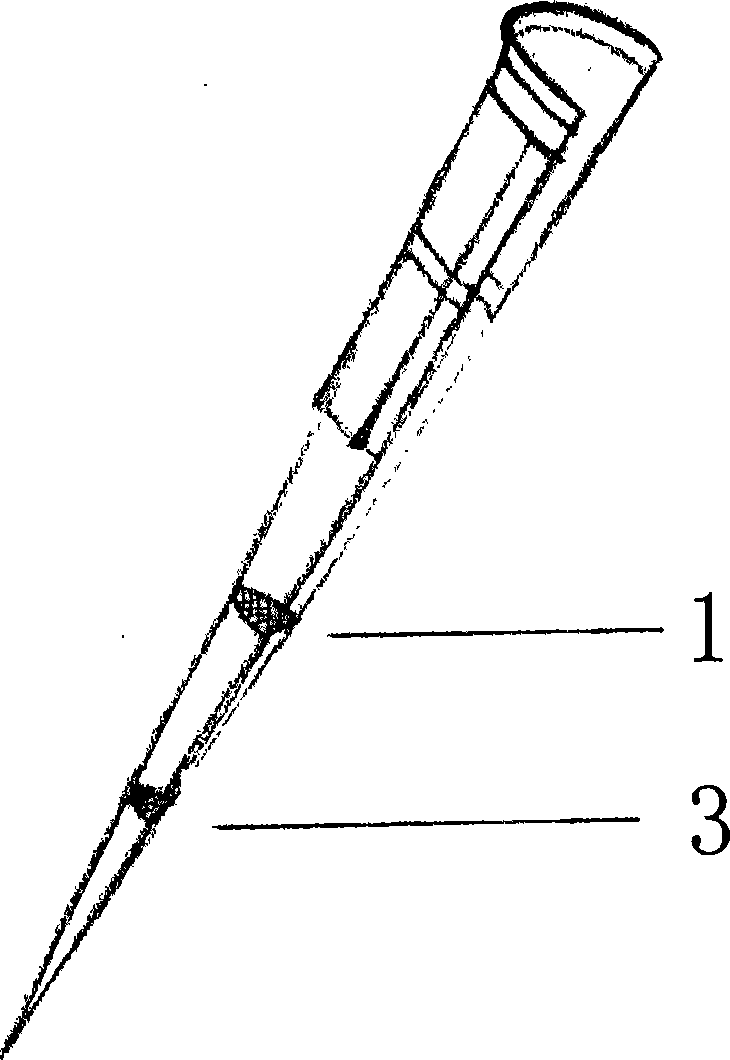
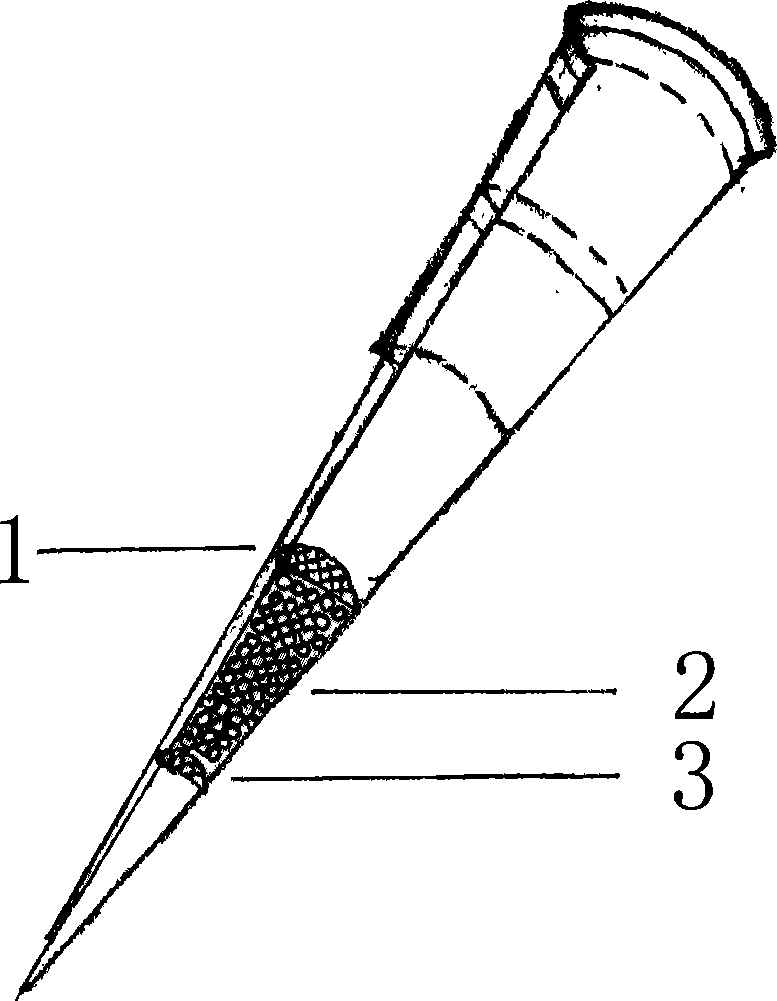
[0107] Embodiment three: the loading of the separation filler in the hollow tube
[0108] Put the fine steel wire mesh or wire mesh with smaller diameter into the upper end hole, and it is located in the middle or lower part of the hollow tube, and then put the separation packing. According to the number of samples to be separated, adjust the density of the separation packing. Finally, a fine steel wire mesh or wire mesh with a larger diameter is installed to fix the separation packing.
[0109] Or, in the process of preparing microbeads, close or plug the upper end hole of the hollow tube until the upper limit position of the separation filler, then insert the hollow tube upside down into the microbead solution, adjust the position of the separation filler in the hollow tube, and the separation filler After being fixed in the hollow tube, the closure or blockage is removed from the upper end of the hollow tube to obtain a hollow tube containing separated packing without a cy...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com