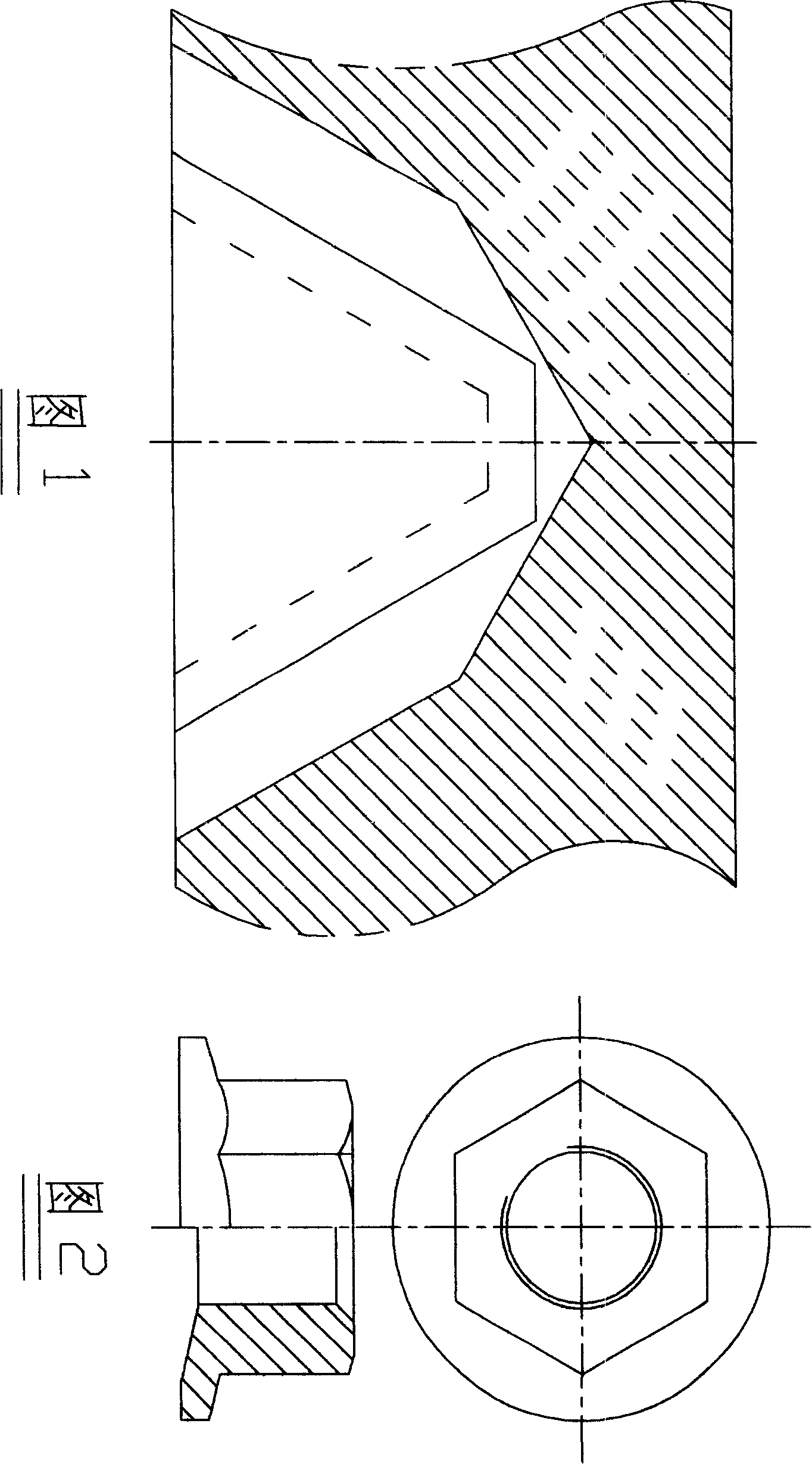
Double tooth variation type double anti-loose nut
A double anti-loosening and nut technology, applied in the direction of nuts, screws, bolts, etc., can solve the problems of non-loosening, difficult to use, and impossible to find when assembling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0005] Ordinary national standard nuts have good connectivity, but are not anti-loosening, and are not suitable for locomotives, vehicles, transportation machinery, power machinery, ships and other moving machinery vehicles. Change the equilateral triangular thread of the national standard nut into a combination of two threads. The basic tooth angle of the nut, that is, the angle between the two waists is 60 degrees, and two anti-loosening slopes are connected to it, and the two anti-loosening slopes form a 30-degree clip with the thread axis. Angle, the angle between the two anti-loosening slopes is 120 degrees, symmetrical, and the crest is the intersection point (line) of the two slopes. For large nuts, the sharp point can be ground into a plane. Make the taps in this way, and use the special taps to process the nuts, and you can get the double-variable tooth type anti-loosening nuts; in August 2004, the anti-loosening performance test was conducted in the Academy of Mechani...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com