Method for preparing polyvinylidene fluoride microporous filtering film
A technology of polyvinylidene fluoride and microporous membrane, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, membrane technology, semi-permeable membrane separation, etc., can solve the problem of low performance and mechanical strength, uneven pore structure in the membrane, uneven With the separation membrane structure and other problems, it can reduce the harm to the environment and human body, have good penetration and high pure water flux.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
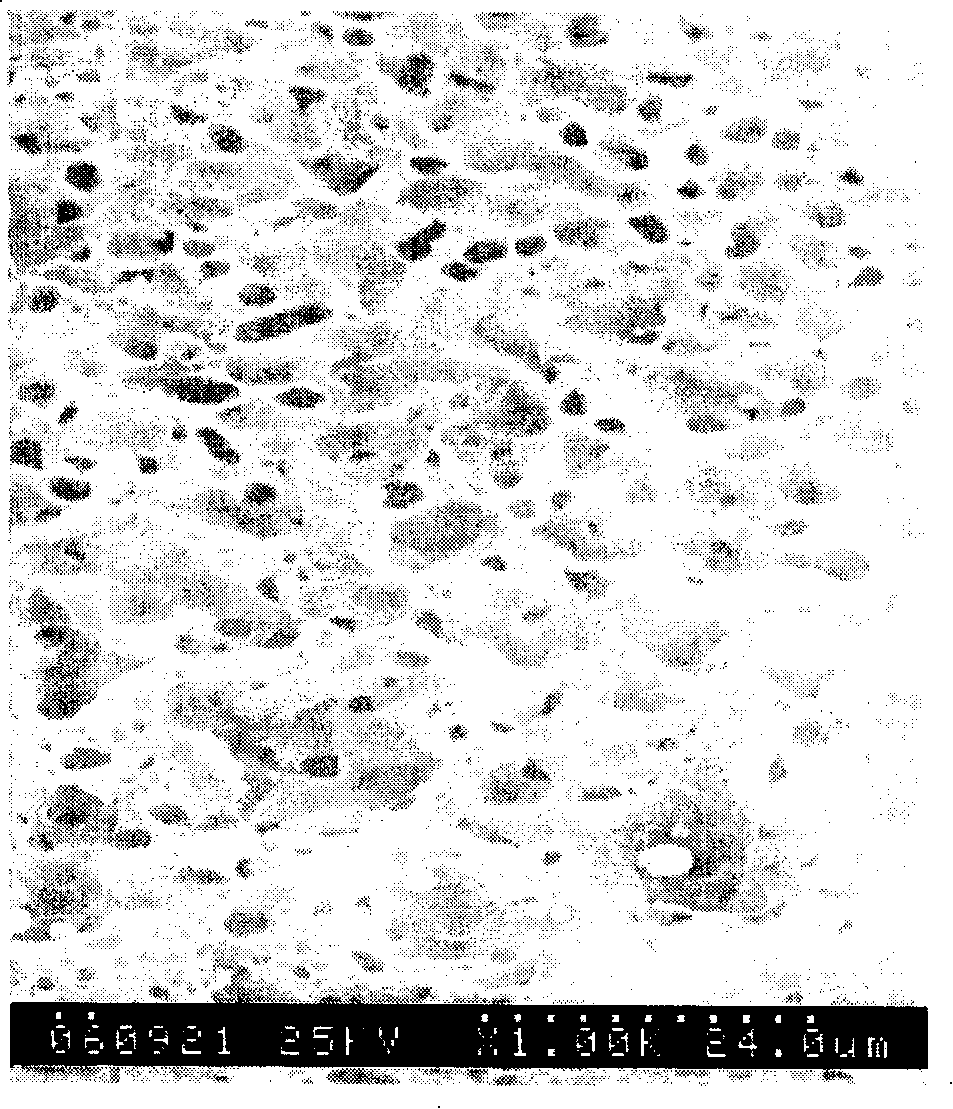
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0025] The preparation method of the polyvinylidene fluoride microporous filter membrane of the present invention is carried out according to the following steps:
[0026] (1) Mix the polyvinylidene fluoride resin with the diluent. The content of the polyvinylidene fluoride resin in the mixture is 10-60% by weight, preferably 20-40% by weight; the above-mentioned mixture is sealed in a stirring container filled with nitrogen, Raise the temperature to 140~220℃ (below the boiling point of the diluent), mechanically stir or use twin-screw shear stirring to form a homogeneous polymer solution;
[0027] (2) Spread the homogeneous polymer solution obtained above uniformly on a mold for casting (with a scraper if necessary), and cool down naturally in the air or put it in a certain medium directly to quench it, so that the film-forming liquid will have phases. Separation and solidification of polyvinylidene fluoride;
[0028] (4) Use water as the extractant to extract the diluent in the ...
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1. Preparation of Microporous Membrane by Polyvinylidene Fluoride and Ethylene Glycol Ether Acetate System
[0034] Mix the polyvinylidene fluoride resin (weight average molecular weight 226,000) with a mass percentage of 20% and ethylene glycol ethyl ether acetate with a mass percentage of 80%, and then add polyvinylidene fluoride with a mass percentage of 3%. Ethylene glycol (molecular weight 400) into the above mixture; then, the mixture was sealed in a stirring container filled with nitrogen, heated to 140 ℃, fully dissolved to a homogeneous solution; 6 hours later, stand at a constant temperature, degassing, The obtained homogeneous polymer solution is uniformly spread on a mold at the same temperature for molding. Naturally cool to 25°C. After cooling, put the mold into water to extract ethylene glycol ethyl ether acetate and polyethylene glycol. Change the water every 12 hours for a total of 3 to 4 times. After that, the formed membrane is taken out of the mo...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2: Preparation of microporous filter membrane by polyvinylidene fluoride and ethylene glycol ethyl ether acetate system
[0037] Mix 30% by mass polyvinylidene fluoride (weight average molecular weight 226,000) and 70% by mass ethylene glycol ethyl ether acetate, and then add 3% polyvinylidene fluoride by mass. Diol (molecular weight 400) was added to the above mixture; then, the mixture was sealed in a stirring vessel filled with nitrogen, and the temperature was raised to 140° C. to fully dissolve to a homogeneous solution. After 6 hours, let it stand at a constant temperature and defoam, and spread the obtained homogeneous polymer solution evenly on a mold at the same temperature for molding. Quench in water to 25°C to solidify and form, and extract ethylene glycol ethyl ether acetate and polyethylene glycol. Change the water every 12 hours for a total of 3 to 4 times. After that, the formed membrane is taken out of the mold, and soaked in absolute ethanol for 2 t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface average pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com