Method for epitaxial generation of gallium antimonide on gallium arsenide substrate
A technology of epitaxial growth and gallium antimonide, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of high dislocation density, low peak intensity, poor crystal quality, etc., and achieve the reduction of density and screw position The effect of reducing the error density and increasing the strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
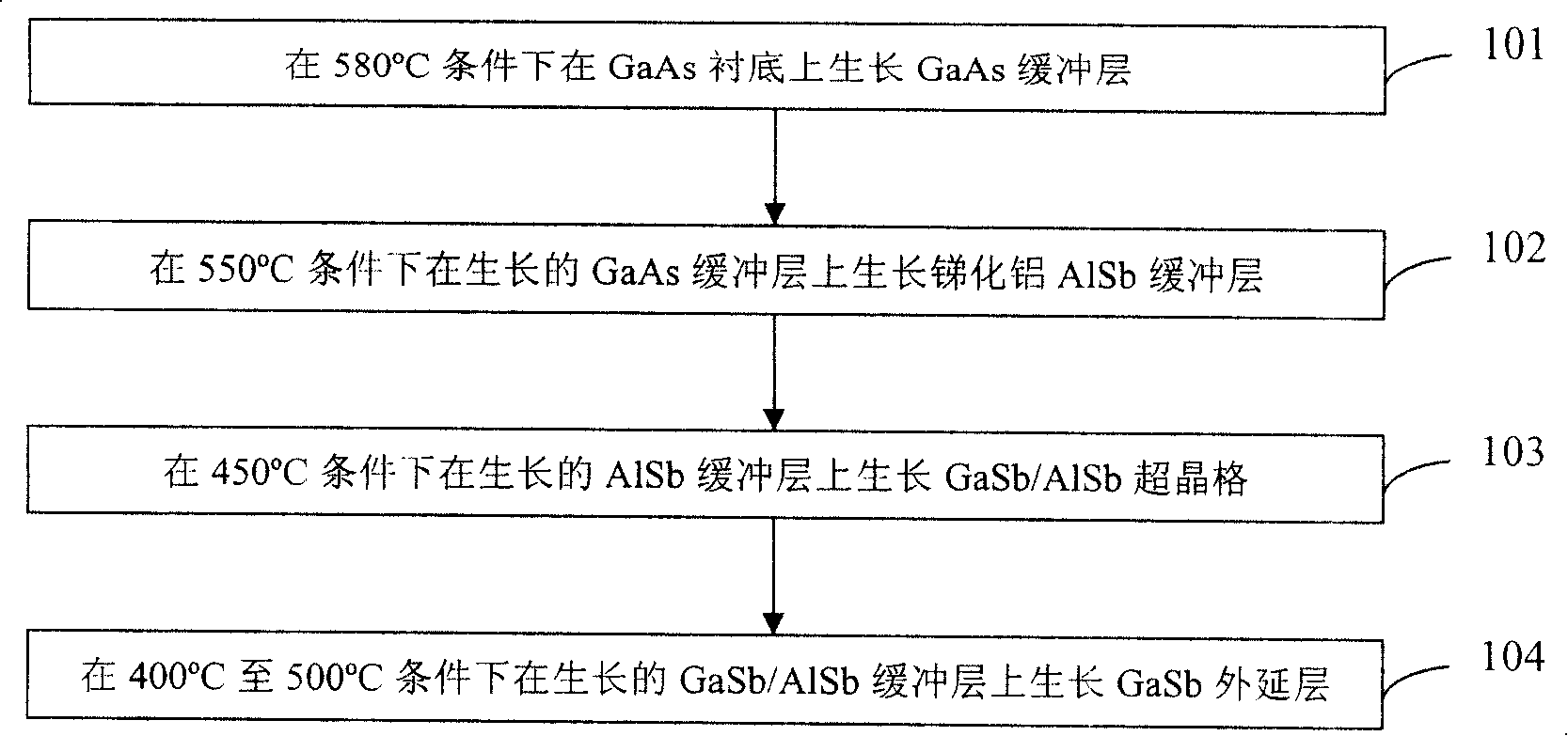
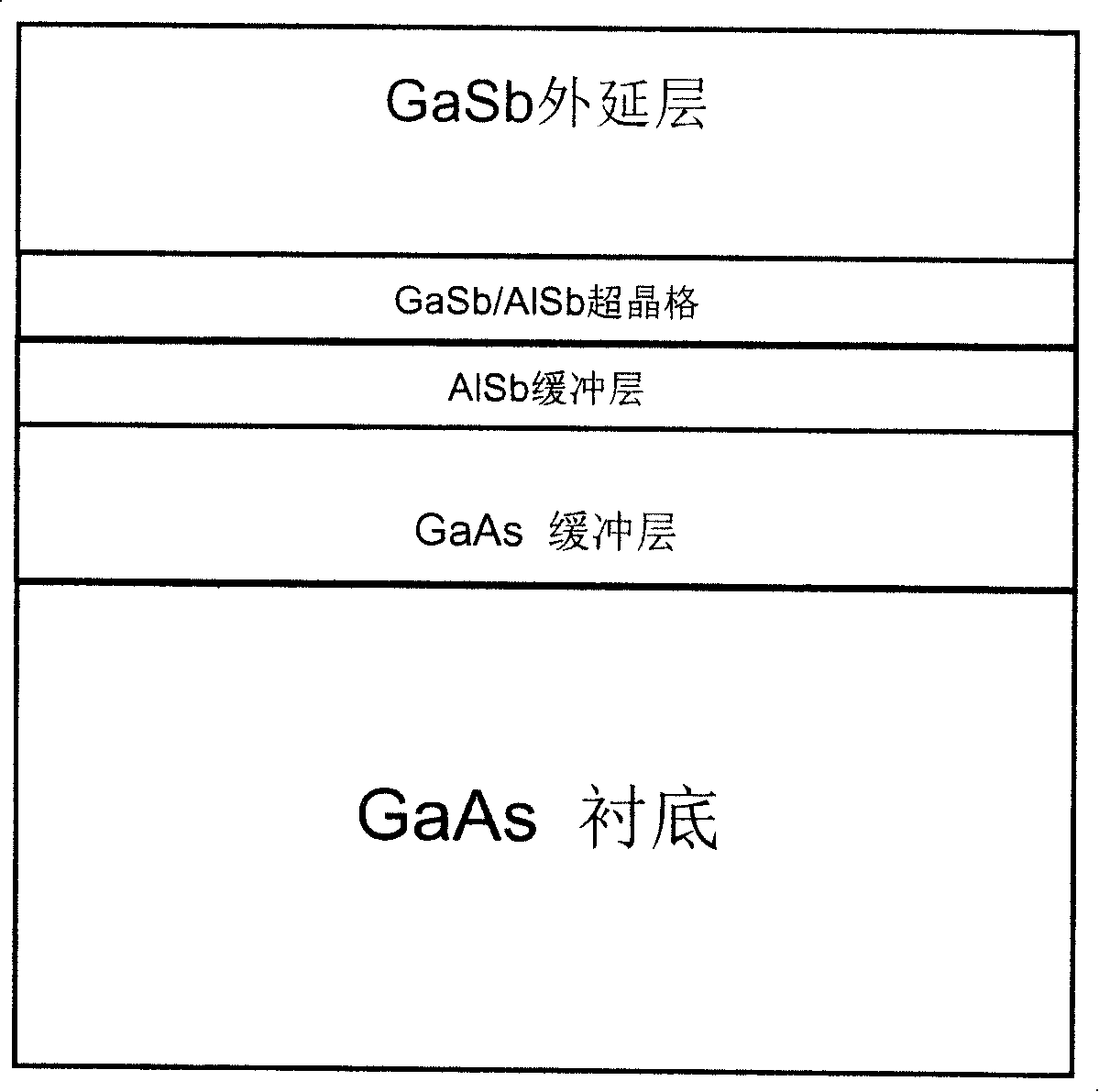
[0069] After high-temperature deoxidation and degassing of the cleaned GaAs substrate, the temperature of the GaAs substrate is lowered to 580°C, the Ga source furnace shutter is opened, the Ga source temperature is 1150°C, and the GaAs high-temperature buffer layer is crystallized on the GaAs substrate grow. The growth time of the GaAs buffer layer is 30 minutes, and the thickness is 0.5 μm. The molecular beam epitaxy growth chamber pressure is 5×10 -9 mbar.
[0070] Then close the Ga source furnace shutter, lower the substrate temperature to about 550°C, close the As source furnace shutter, open the Sb source furnace shutter, open the Al source furnace shutter, the Al source temperature is 1180°C, and grow a low-temperature AlSb buffer on the GaAs buffer layer. layer, the growth time is 12 minutes, and the thickness is about 100nm. The molecular beam epitaxy growth chamber pressure is 5×10 -9 mbar.
[0071] Then close the shutter of the Al source furnace, lower the subs...
Embodiment 2、3
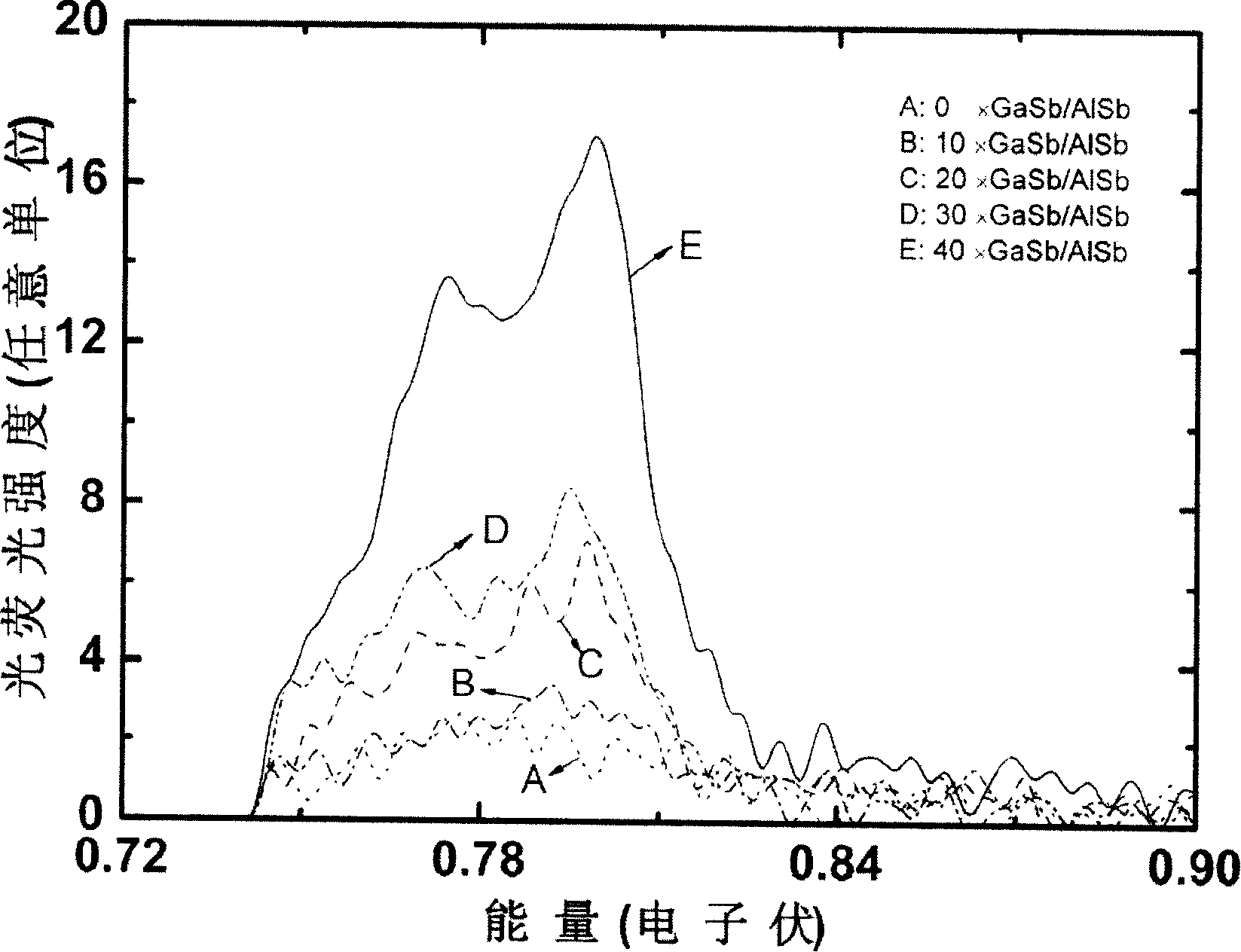
[0074] The GaSb / AlSb superlattices of different period numbers are 20 (C), 30 (D) respectively, all the other are the same as embodiment 1. The PL spectrum measured under 10K is as follows image 3 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com