Root nodule azotobacter strain BDYD1 and uses thereof
A slow rhizobium, nitrogen fixation technology, applied in the application, bacteria, biocide and other directions to achieve the effect of improving nitrogen nutrition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 Isolation and purification of nitrogen-fixing bacteria strain BDYD1
[0038] Take fresh root nodules, rinse them with water, and dry the surface moisture with filter paper. Put it in 95% ethanol for 3 minutes, take it out and wash it with sterile water for 5-6 times, then put it in 0.2% HgCl 2 Sterilize for 5 minutes, take out and rinse with sterile water 5-6 times. Then cut in half on a flame sterilized glass slide, clamp the half tumor with sterile tweezers, mark the incision facing the surface of the YMA (Table 1) medium, incubate at 28°C after inversion.
[0039] After the thalli grow out, select the rhizobia-like colony from the plate and streak on the plate for culture. After 3 days, observe the colony situation, and observe until 15 days, because Bradyrhizobium needs 7 to 15 days to appear colonies. According to the following two aspects, it can be preliminarily judged whether it is rhizobia: ①Colony shape: the colony of rhizobia is round, milky whit...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2 Sequencing of the 16S rDNA sequence of Azotobacter tumefaciens strain BDYD1
[0043] The total DNA of the strain was extracted and subjected to PCR-specific amplification. After the PCR amplification product was checked on 1.0% agarose gel electrophoresis, it was sent to Yingjun Company for sequence determination. The sequencing result is shown in SEQ ID NO:1.
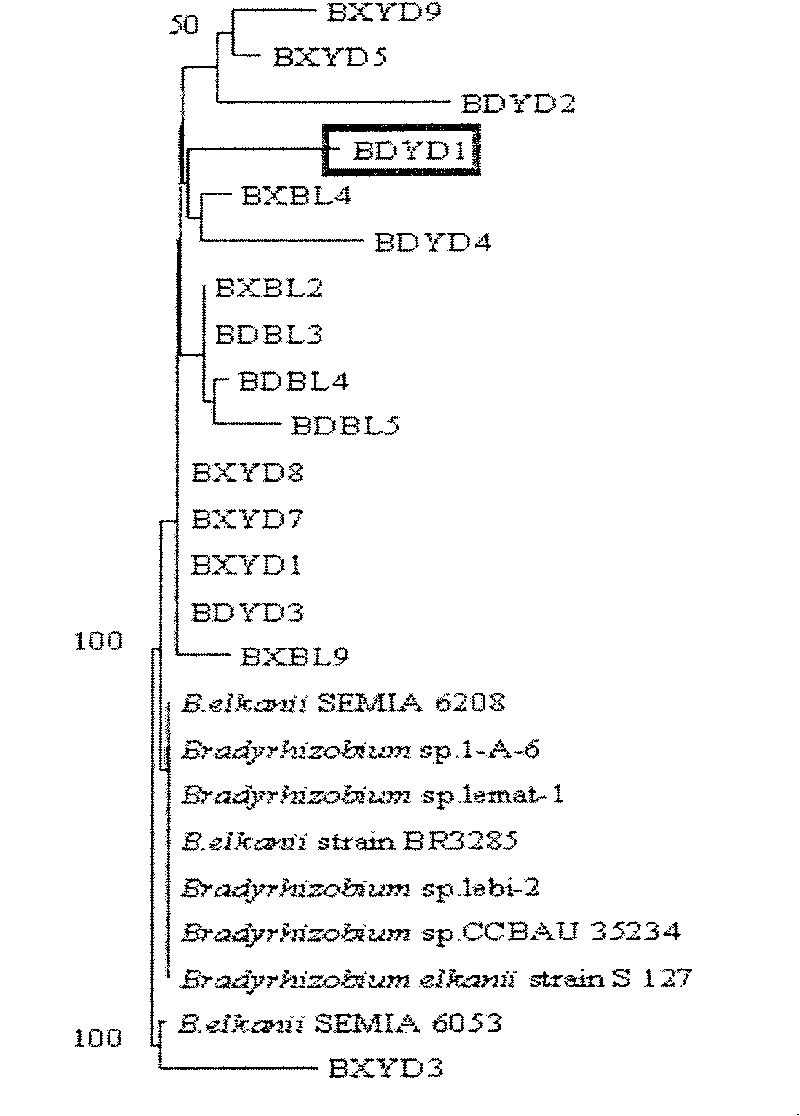
[0044] Eight reference strains were obtained from the GenBank database, and the 16S rDNA partial sequences of the isolated strains and reference strains were analyzed using the software GeneDoc and TREECONW, and a phylogenetic relationship diagram between the isolated strains and the standard strains was constructed, as shown in image 3 shown. Therefore, it was determined that the isolated nitrogen-fixing bacteria strain BDYD1 was a new strain of Bradyrhizobium, and it was named Huagu No.1.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3 tie-back test
[0046] The recertification of the tie-back test adopts the above-mentioned large test tube paper culture device ( Figure 4 ), soybean seed treatment is also as described above.
[0047] Bacterial liquid culture: use an inoculation loop to pick a ring of rhizobia in the test tube and put it into the TY liquid medium. The formula of the TY liquid medium is shown in Table 2. After plugging it with a cotton plug, seal it with kraft paper and put it on the shaker Cultivate until the logarithmic growth phase (about 4 to 6 days), and the culture temperature is 28°C.
[0048] Table 2 TY liquid medium ( / L)
[0049]
[0050] Inoculation treatment: Put the germinated seeds in a petri dish and soak them in the bacterial solution for 15 minutes, plant the seedlings between the filter paper and the tube wall with tweezers, add 1-2mL of the bacterial solution to each seedling to ensure that each seedling The inoculation amount of seedlings reached 1.0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com