Method for forcibly changing rotating position of piston ring and cross-type two-stroke diesel engine
A technology of two-stroke internal combustion engine, rotating position, applied in the direction of piston rings, mechanical equipment, engine components, etc., capable of solving problems such as complex structures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
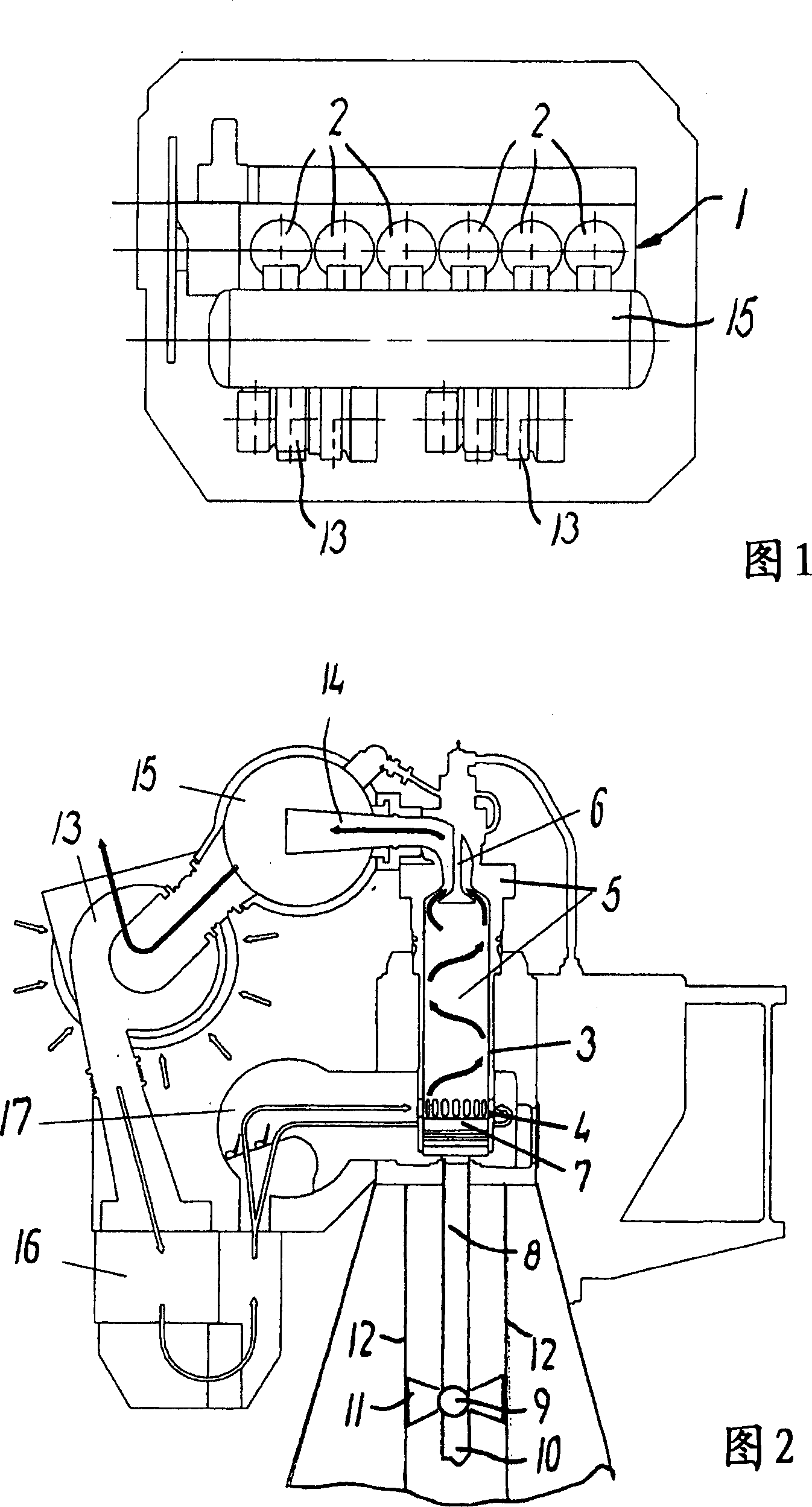
[0030] In the exemplary embodiment of FIG. 1 , a two-stroke internal combustion engine 1 has six cylinders 2 arranged in a single row (tandem engine). The engine may have other numbers of cylinders, for example 4 to 15 cylinders. The engine can be made, for example, from MAN B&W diesels and MC or ME type diesels, or from W_rtsil_ of the Sulzer RT-flex or Sulzer RTA type, or from Mitsubishi. These cylinders may have a bore diameter in the range of eg 25-120 cm, preferably 35-120 cm, more preferably 50-110 cm. The engine has a power range of, for example, 270-8500 kW per cylinder, preferably 1000-7000 kW. Therefore, the engine of the present invention is a large engine.
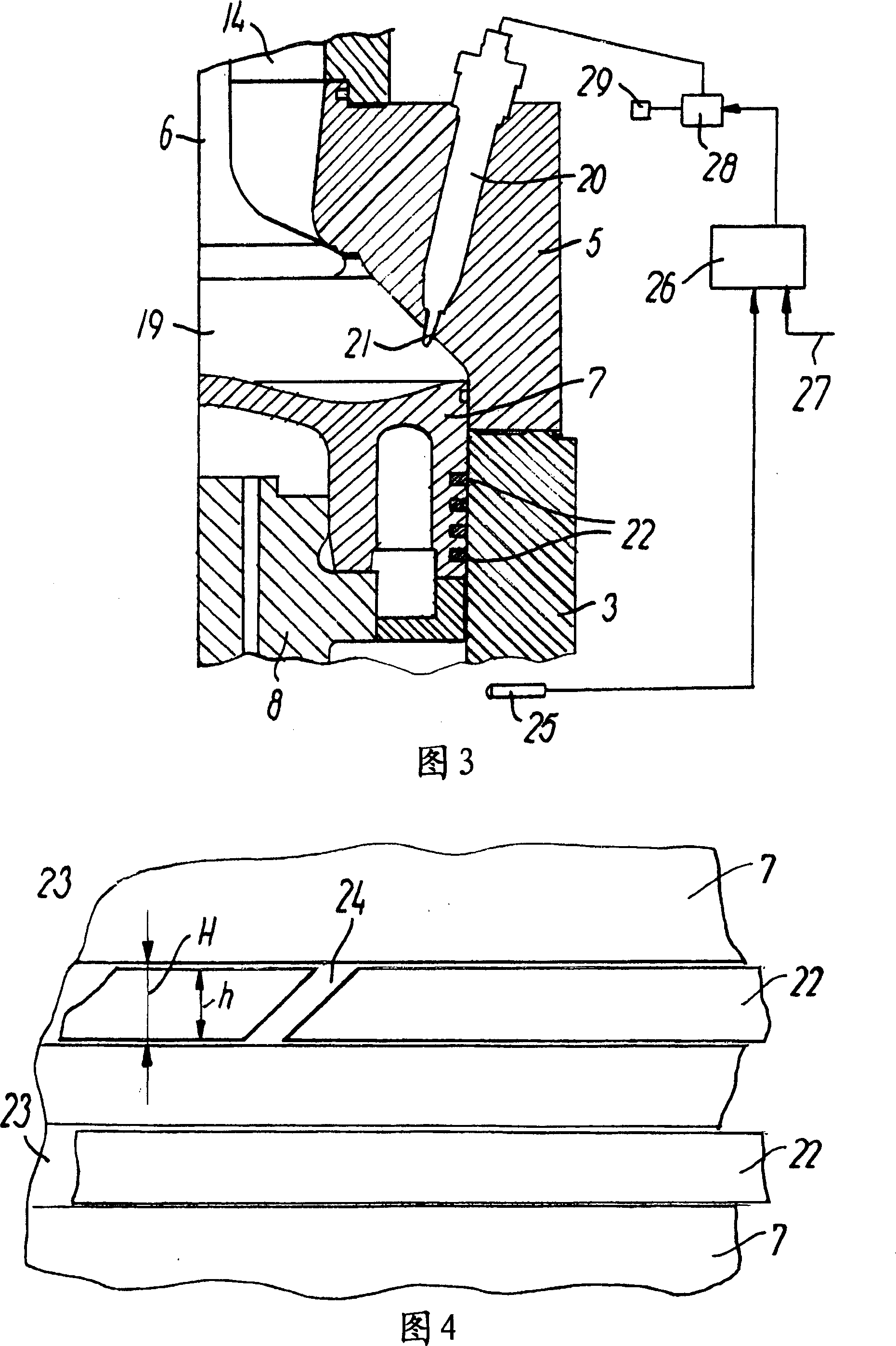
[0031] Each cylinder 2 has a cylinder liner 3 with a row of exhaust holes 4 at its lower end, a cylinder head 5 and an exhaust valve 6 positioned at the upper end of the cylinder liner. The piston 7 is mounted on a piston rod 8 . The piston rod is conventionally connected to a crankpin on a crankshaft (not ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com