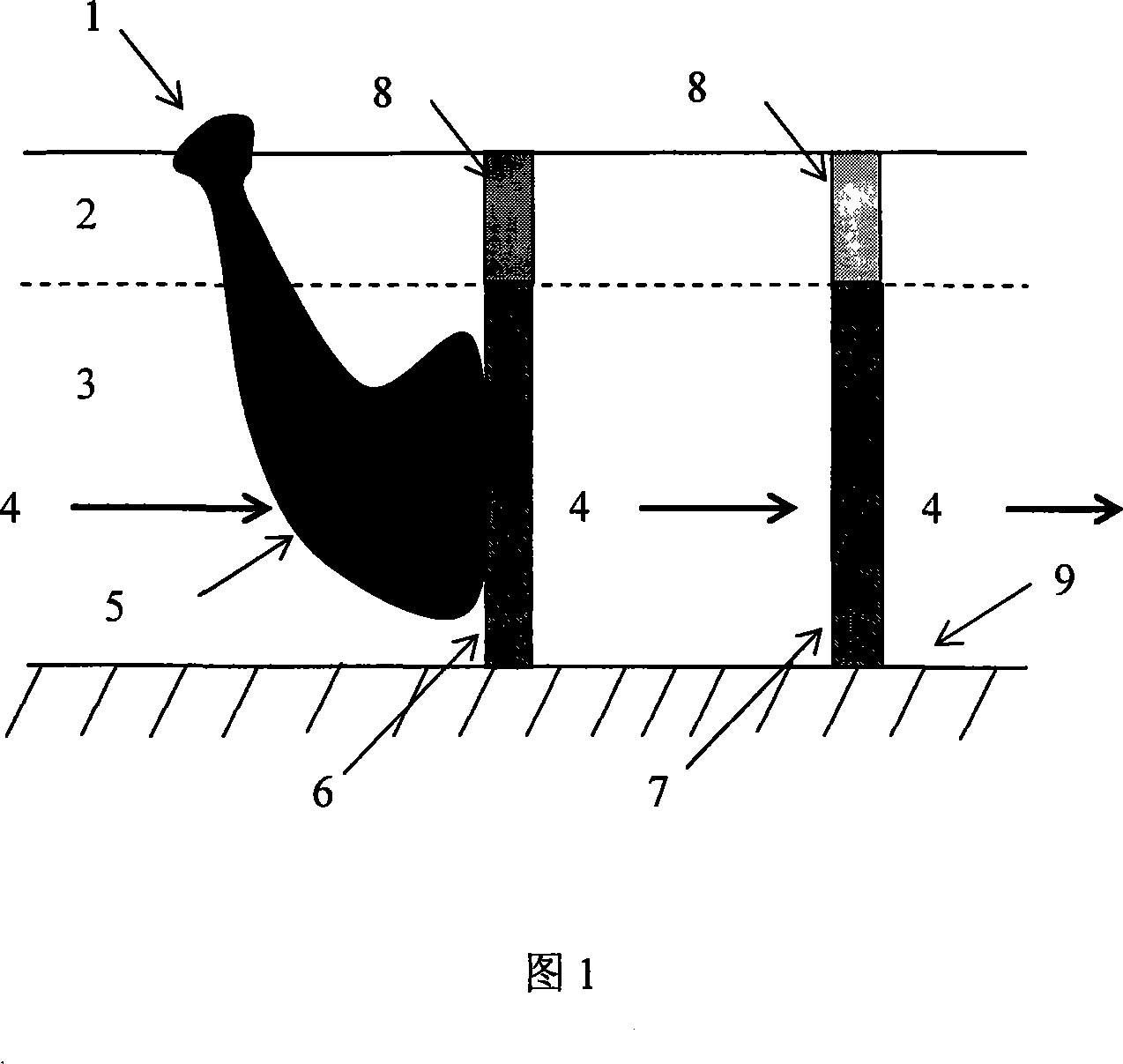
Organism fixing and permeating reaction wall system and stuffing for repairing polluted underground water
A groundwater remediation and osmotic reaction wall technology, which is applied in the direction of contaminated groundwater/leachate treatment, water pollutants, biological water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the effect of groundwater bioremediation, additional microbial loss, and increasing repair costs, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of slowing down the oxygen release rate, increasing biomass, and avoiding loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] 1) The production process of the oxygen-releasing material solid particles is: the CaO 2 , (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 、KH 2 PO 4 , trace elements (by MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 , MnSO 4 ·H 2 O, ZnSO 4 ·H 2 O and NaCl), coarse sand, and cement are mixed evenly, and after adding water, they are sent to a granulator for granulation to obtain solid oxygen-releasing material particles (with a particle size of 1.5 cm). The mass percent of above-mentioned mixture is as follows: CaO 2 5%; (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 40%; KH 2 PO 4 10%; coarse sand 15%; cement 10%; water 15%; trace elements 5% (of which MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O is 1%, Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 1%, MnSO 4 ·H 2 O is 1%, ZnSO 4 ·H 2 O is 1%, NaCl is 1%).
[0027] 2) Immobilization method of microorganisms: Dissolve sodium alginate in water, add activated carbon, and mix with the suspension of Ochrobactrum anthropi, which has the function of degrading aniline, in a volume ratio of 1:1. Pour the mixture into calcium chloride solu...
Embodiment 2
[0030] 1) The production process of the oxygen-releasing material solid particles is: the CaO 2 , (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 、KH 2 PO 4 , trace elements (by MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 , MnSO 4 ·H 2 O, ZnSO 4 ·H 2 O and NaCl), coarse sand, and cement are mixed evenly, and after adding water, they are sent to a granulator for granulation to obtain solid particles of oxygen-releasing material (particle size: 2 cm). The mass percent of above-mentioned mixture is as follows: CaO 2 12%; (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 25%; KH 2 PO 4 25%; coarse sand 8%; cement 13%; water 13%; trace elements 4% (of which MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O is 0.8%, Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 0.8%, MnSO 4 ·H 2 O is 0.8%, ZnSO 4 ·H 2 O is 0.8%, NaCl is 0.8%).
[0031] 2) Immobilization method of microorganisms: Dissolve sodium alginate in water, add activated carbon, and mix with the suspension of white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosprium burdsall, which has the function of degrading organic matter such as chlorinated aromatic co...
Embodiment 3
[0034] 1) The production process of oxygen-releasing material solid particles is: MgO 2 , (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 、KH 2 PO 4 , trace elements (by MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 , MnSO 4 ·H 2 O, ZnSO 4 ·H 2 O and NaCl), coarse sand, and cement are mixed evenly, and after adding water, they are sent to a granulator for granulation to obtain solid oxygen-releasing material particles (with a particle size of 1.5 cm). The mass percent of above-mentioned mixture is as follows: MgO 2 10%; (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 30%; KH 2 PO 4 24%; coarse sand 10%; cement 15%; water 8%; trace elements 3% (of which MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O is 0.6%, Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 0.6%, MnSO 4 ·H 2 O is 0.6%, ZnSO 4 ·H 2 O is 0.6%, NaCl is 0.6%).
[0035] 2) Immobilization method of microorganisms: dissolve polyvinyl alcohol in water, add sodium alginate, and mix evenly with the suspension of Ochrobactrum anthropi which has the function of degrading aniline at a volume ratio of 3:1, Use a syringe to inject the mixture...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com