Methods and compositions for evaluating breast cancer prognosis
A technology for breast cancer and prognosis, which is applied in special data processing applications, instruments, measuring devices, etc., and can solve problems such as specificity and sensitivity method requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0107] Example 1: Detection of Biomarker Overexpression Using Immunohistochemistry
[0108] Slide preparation
[0109] 4 [mu]M sections of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded breast tumor tissue samples were cut using a microtome and mounted on SuperFrost+ slides (VWR). The slides were baked in a forced air oven for 20 minutes and then exposed to the Histo-Orienter until the paraffin melted. Slides were washed 3 times with xylene for 5 minutes each to remove paraffin and then rinsed 3 times with absolute ethanol for 2 minutes each.
[0110] Pretreatment and Antigen Retrieval
[0111] To prevent nonspecific background staining, slides were incubated in a hydrogen peroxide / methanol block for 5 min at room temperature. Then replace dH several times with 2 ORinse slides thoroughly.
[0112] To render the antigen ready for antibody binding, slides were incubated in antigen retrieval solution for 5 minutes in a pressure cooker. Allow the slides to cool on the benchtop to room tem...
Embodiment 2
[0119] Example 2: Detection of overexpression of various biomarkers in clinical samples
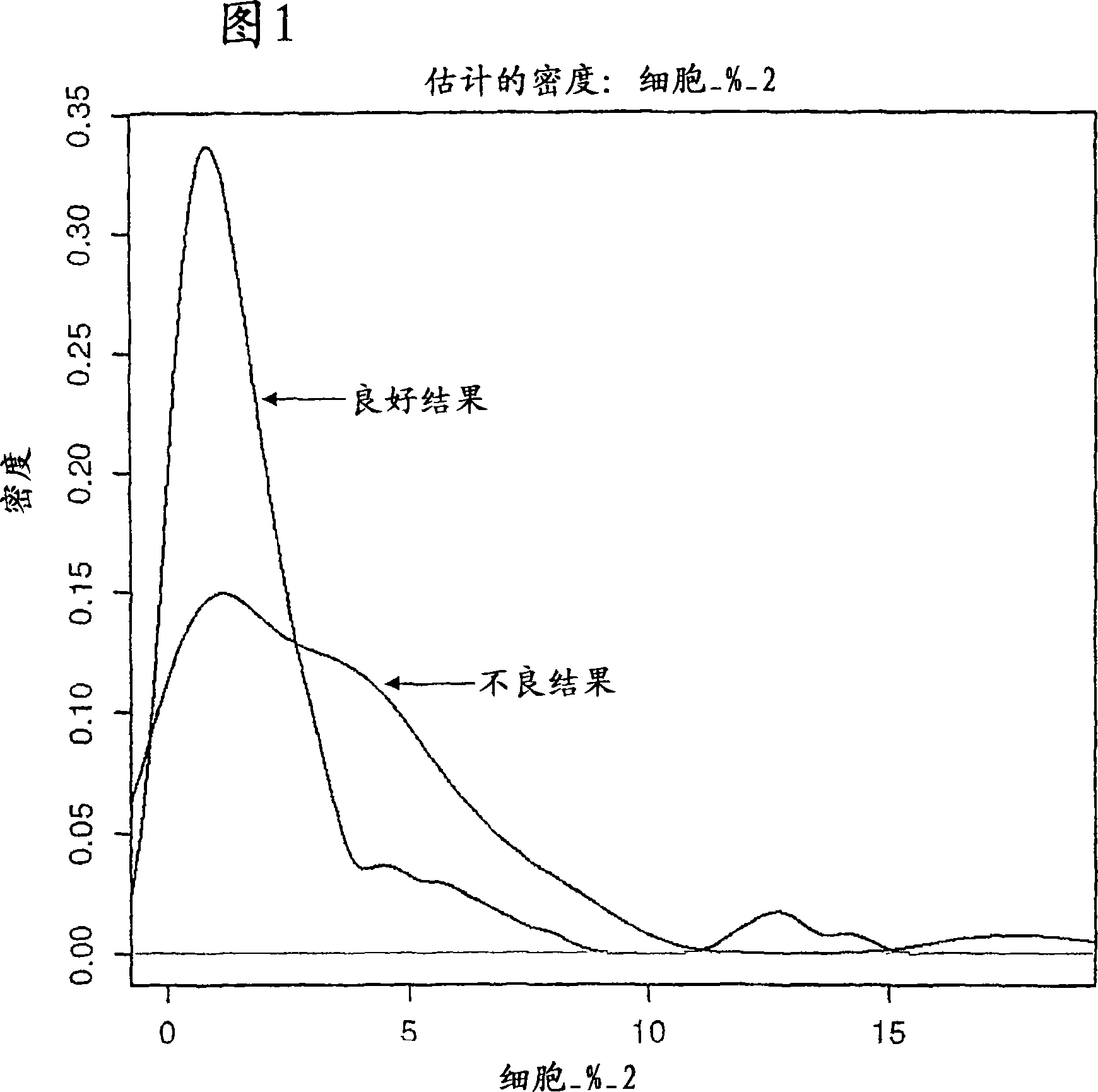
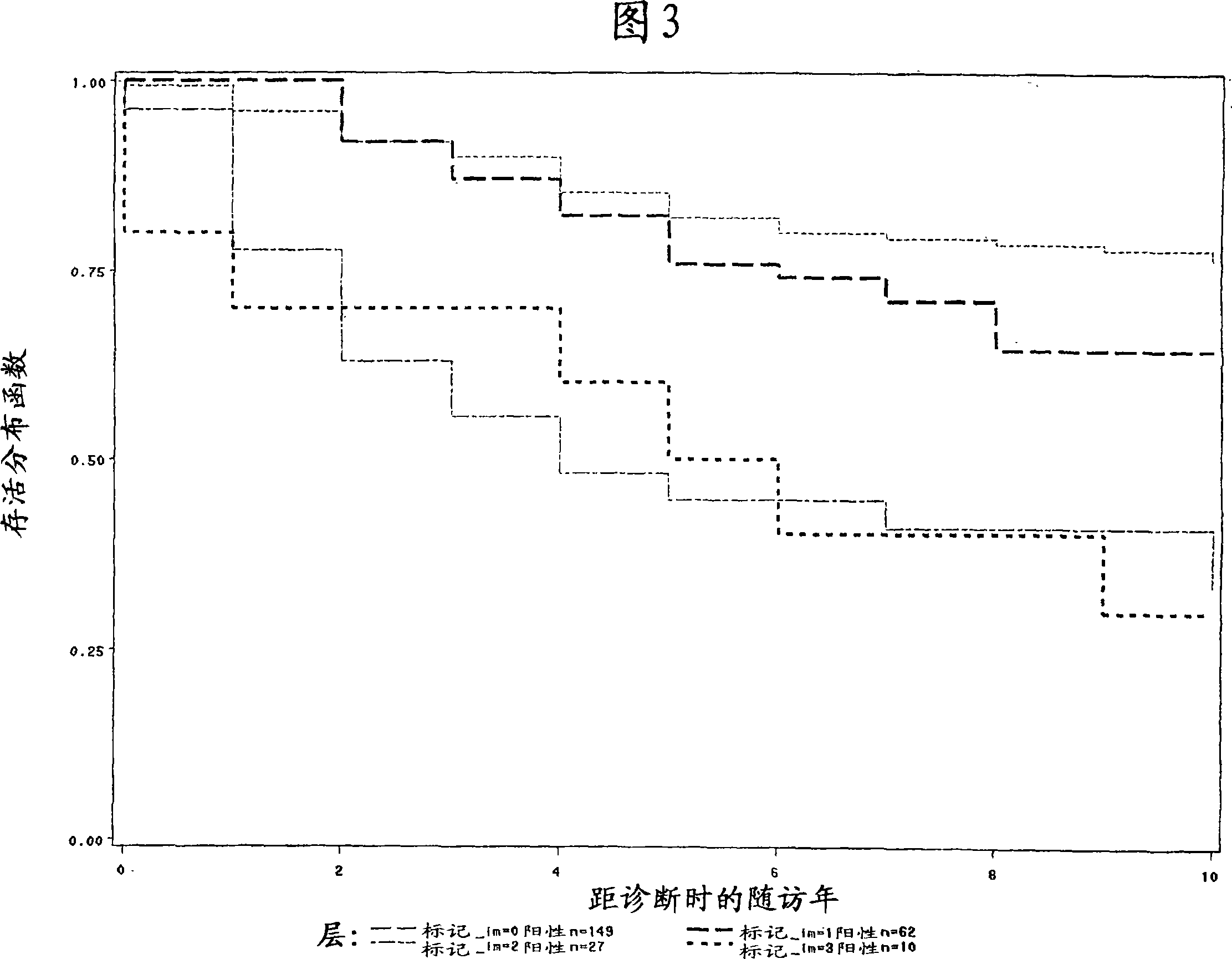
[0120] About 130 breast tumor tissue samples from different disease stages were collected. The mean age of the patients was 77 years. The actual clinical outcome data for each patient is known and each patient is classified as having a good or poor outcome. In this study, a good outcome was defined as remaining cancer-free for at least 5 years; a poor outcome was defined as experiencing disease recurrence, recurrence, or death within 5 years. The table below represents the number of samples within each diagnostic group analyzed and the actual clinical outcome data.
[0121] stage
good result
bad result
total
T1N0
50
13
63
T1N1
6
4
10
T2N0
26
19
45
T2N1
9
7
16
T3N0
0
3
3
T3N1
0
1
1
Lymph node status
g...
Embodiment 3
[0147] Example 3: Detection of Biomarker Overexpression in Clinical Samples - Pooled Biomarkers
[0148] The data from Example 2 were further analyzed to determine whether the sensitivity and specificity of the methods of the invention could be improved if multiple biomarkers were combined. Thus, combinations of various biomarkers were considered and samples that stained positive for any biomarker in the combination of interest were considered positive. These results are compared to known actual clinical outcome data obtained for each patient and then given as described above for each slide for True Positive (TP), True Negative (TN), False Positive (FP) , the final result of a false negative (FN). Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated for each biomarker combination.
[0149] result
[0150] The results for each combination of biomarkers are summarized below.
[0151] TP
[0152] TP ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com