Film forming material and preparation of surface relief and optically anisotropic structures by irradiating a film of the said material
A technology of photoisomerization and film formation, which is applied in the use of optical devices to transmit the directions of sensing components, optics, and photosensitive materials, and can solve the problems of optical orientation and photodiffusion that have not been studied.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1a
[0085] Example 1a "Recording"
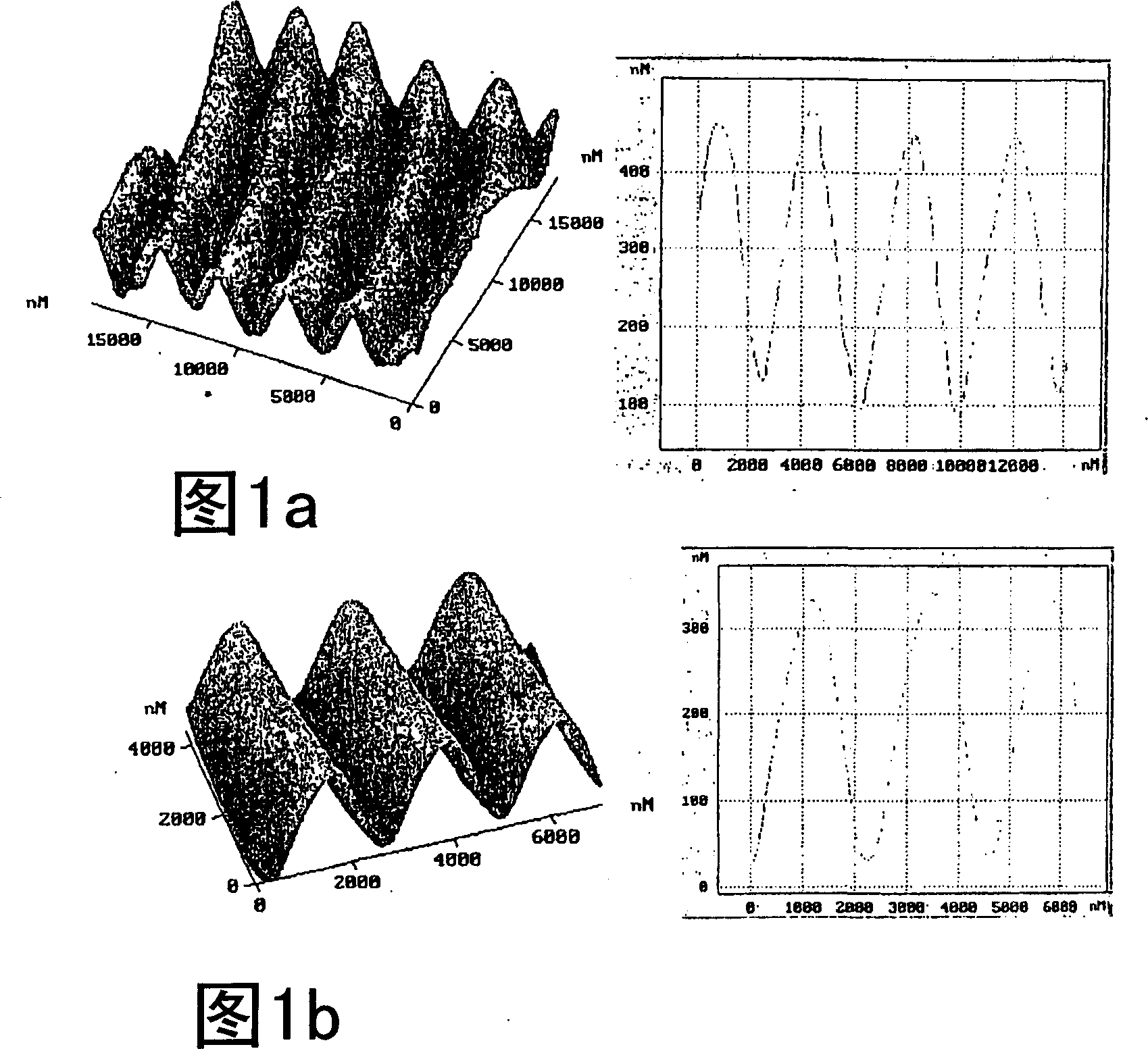
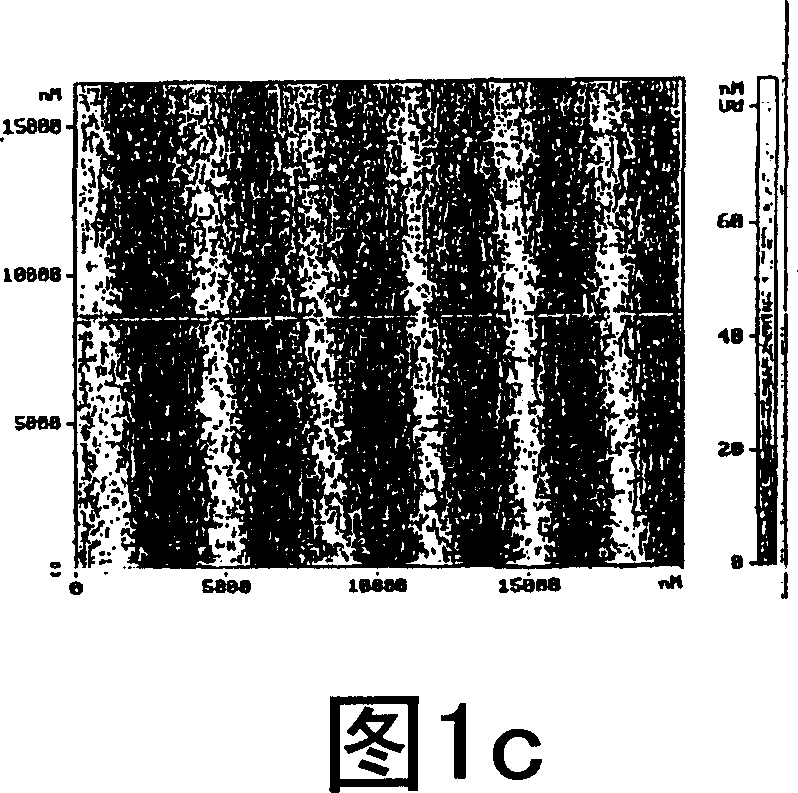
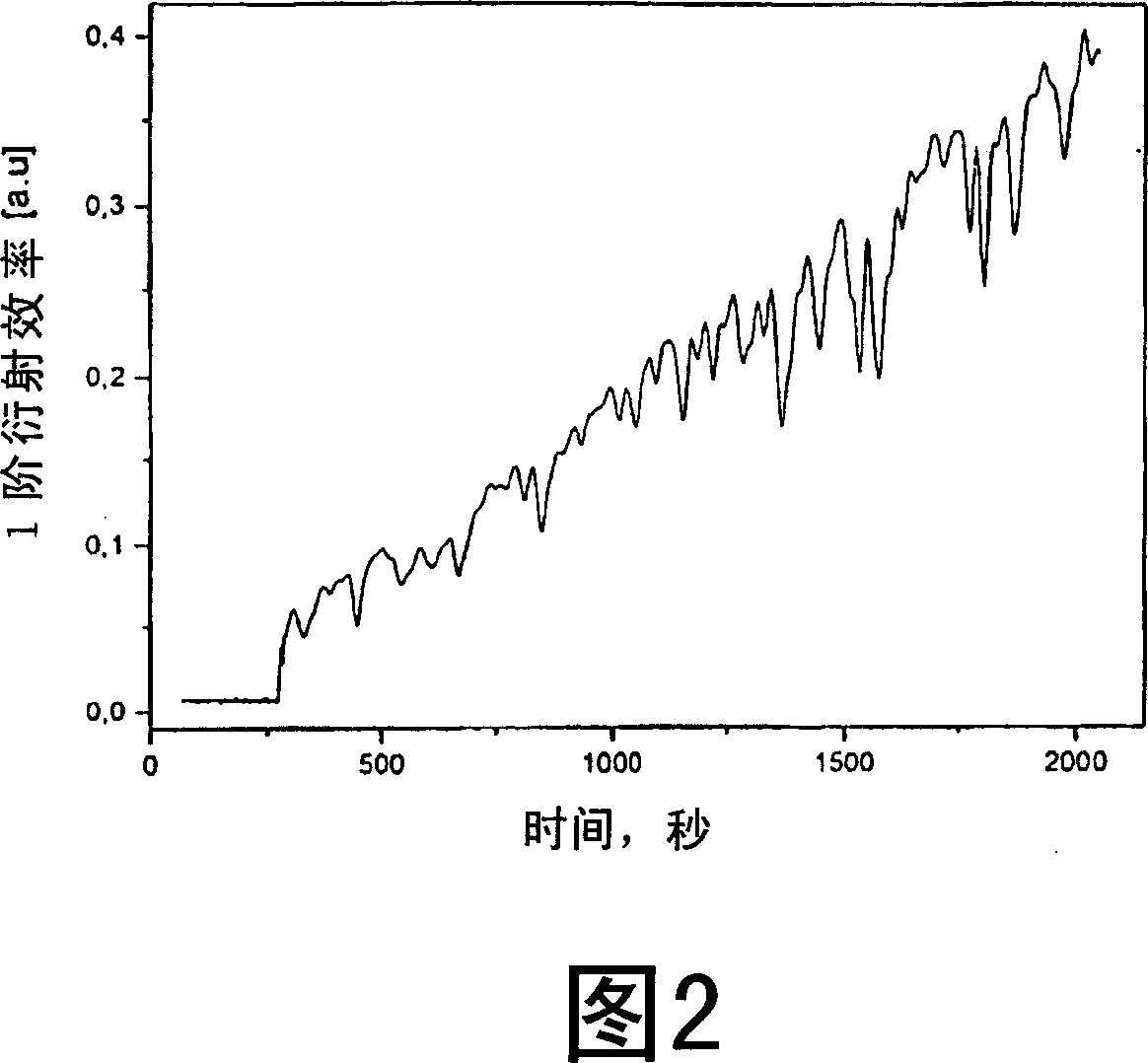
[0086] 54 mg of Alizarin Yellow GG (5-(3-nitrophenylazo)salicylic acid sodium salt produced by Aldrich) was dissolved in 20 ml of distilled water, and 40 µl of a 30% polyethyleneimine aqueous solution was added. The precipitate was isolated by filtration (30 mg after drying) and dissolved in 1 ml THF while discarding the mother liquor. Films approximately 2 [mu]m thick were prepared by casting THF solutions on glass substrates at room temperature in a closed vessel. After drying in air at room temperature for 5 h, the films were irradiated under an interference pattern formed by two linearly cross-polarized beams with planes of polarization at ±45° from the plane of incidence. The irradiation wavelength is 488 nm, and the angle between the beams is about 12°, resulting in a period of 2.3 μm. The intensity of the interference beam is equal to 250mW / cm 2 , the irradiation time is 40min. The 1st order diffraction efficiency measured during the ...
Embodiment 1b
[0087] Example 1b "Recording"
[0088]63 mg of Brilliant Yellow (4,4'-bis(4-hydroxyphenylazo)stylbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid disodium salt produced by Aldrich) was dissolved in 5 ml of methanol and then filtered. 130 mg of 30% polyethyleneimine (Aldrich) in water were added. As some precipitate formed, the solution was left standing and decanted. The red mother liquor was used for membrane preparation. Films approximately 3 [mu]m thick were prepared by casting this solution on glass substrates at room temperature in a closed vessel. After drying in air at room temperature for 5 h, the film was irradiated for 40 min under the conditions described in Example 1a. The 1st order diffraction efficiency of the recorded SRG was measured to be 14.5%.
Embodiment 1c
[0089] Example 1c "Recording"
[0090] To a solution of 80 mg Brilliant Yellow (Aldrich) dissolved in 2 ml methanol was added 130 mg triethoxy-3-aminopropylsilane (Witco Europa SA). After addition of 10 μM concentrated HCl, the solution was allowed to stand. The clear red mother liquor was decanted. Films approximately 3 [mu]m thick were prepared by casting this solution on glass substrates at room temperature in a closed vessel. After drying in air at room temperature for 10 h, the film was irradiated for 30 min under the conditions described in Example 1a. The 1st order diffraction efficiency of the recorded SRG was measured to be 8%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com