Rare earth multiphase alloy material and its preparation
A technology of alloy material and preparation process, which is applied in the field of preparation of rare earth multi-phase alloy materials, to achieve the effects of ensuring quality, eliminating high-temperature crystallization treatment, and reducing the amount of rare earth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
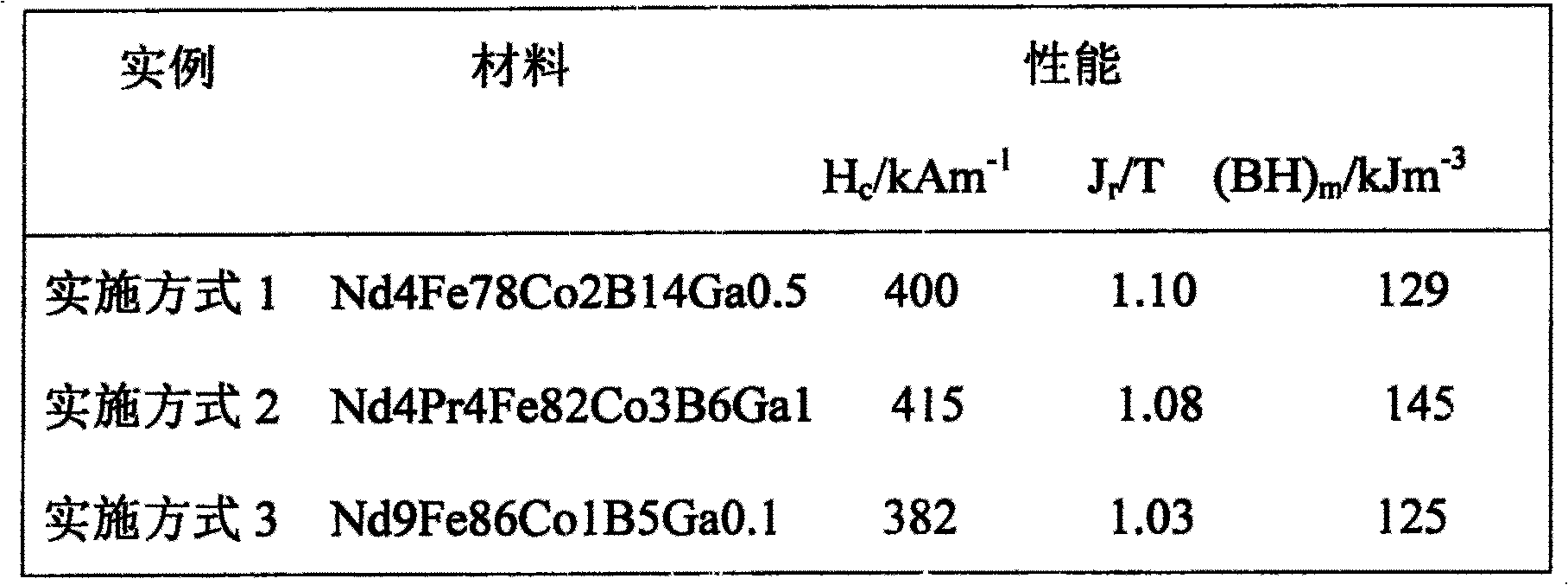
[0007] Embodiment 1: Melt in a vacuum induction melting furnace into an intermediate alloy ingot divided into Nd4at%, Fe78at%, Co2at%, B14at%, Ga0.5at%, namely Nd4Fe78Co2B14Ga0.5, the alloy ingredient is: Nd4.3at %, Fe79at%, Co2.1at%, B14.1at%, Ga0.5at%, melted into iron-based coarse-grained alloy in a vacuum induction furnace, the average diameter of the crystal grains is 10μm-100μm; then the crushed ingot The block is placed in a copper crucible in a vacuum. Under the action of an electric arc, the ingot is melted again, and the molten alloy is poured on the edge of the high-speed rotating wheel when the crucible is tilted. The linear velocity is 15ms -1 The molybdenum alloy wheel quickly solidifies to form a sheet with a thickness of 300μm-600μm, and then the alloy sheet is placed in a heat treatment furnace at 350°C to obtain the raw material for powdering. The main phase of the alloy material is R 2 F 14 B, the auxiliary phase contains α-Fe, and the average diameter of the cr...
Embodiment approach 2
[0008] Embodiment 2: Use a vacuum induction furnace to melt into an intermediate alloy ingot divided into Nd4at%, Pr4at%, Fe82at%, Co3at%, B6at%, and Ga1at%, namely Nd4Pr4Fe82Co3B6Ga1. The alloy ingredients are: Nd4.at%, Pr4 .3at%, Fe83at%, Co3.1at%, B6.2at%, Ga1.1at%, and then process the master alloy into powder raw materials. The method used is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that the linear velocity at the edge of the molybdenum wheel is 25ms -1 , The thickness of the alloy flakes is 50μm-100μm. The alloy flakes are placed in a heat treatment furnace for heat preservation at 390°C to obtain raw materials for powdering. The main phase of the alloy is R 2 F 14 B, the auxiliary phase contains α-Fe, and the average diameter of the crystal grains is 50nm-100nm. The properties of the raw materials are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment approach 3
[0009] Embodiment 3: Use a vacuum induction furnace to melt into an intermediate alloy ingot divided into Nd9at%, Fe86at%, Co1at%, B5at%, Ga0.1at%, that is, Nd9Fe86Co1B5Ga0.1, the alloy ingredients are: Nd9.3at%, Fe87at%, Co1.2at%, B5.2at%, Ga0.15at%, and then the master alloy is processed into the raw material for powdering. The method used is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that the linear velocity of the molybdenum wheel edge is 20ms -1 , The thickness of the alloy flakes is 100μm-300μm. The alloy flakes are kept in a heat treatment furnace at 370℃ to obtain the raw material for powder making. The main phase of the alloy material is R 2 F 14 B, the auxiliary phase contains α-Fe, and the average diameter of the crystal grains is 100nm-500nm. The properties of the raw materials are shown in Table 1.
[0010] Table 1 Properties of raw materials
[0011]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com