Porous polyvinylidene blending porous membrane and process for producing same
A polyvinylidene fluoride, porous membrane technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, membrane technology, semi-permeable membrane separation, etc., can solve the problems of low efficiency, high manufacturing cost, complex process, etc., achieve low energy consumption, reduce cleaning cost, the effect of improving compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
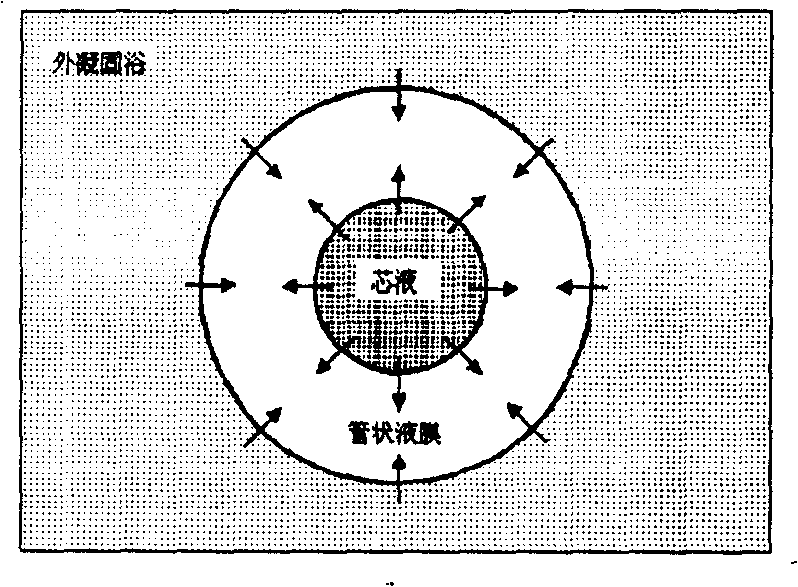
[0067] The PVDF blend flat plate and tubular porous membrane with outstanding hydrophilicity of the present invention, the main components are PVDF, fluorine-containing carbon chain two-block amphiphilic polyethylene oxide and inorganic particles, the objective essence of its preparation method The above is to realize the effective control of the content of the above three components, the distribution of components in the membrane body and the membrane pore structure (mainly pore size and porosity). The preparation method of the membrane is realized through three main steps of preparation of membrane-forming liquid, phase inversion to form a film, and cleaning and drying, among which the preparation of membrane liquid and phase inversion to form a film are key steps.
[0068] Membrane solution preparation refers to mixing PVDF, amphiphilic polyethylene oxide containing fluorocarbon chains, inorganic particles, pore size regulators and solvents, fully stirring at 50-90°C for 24-...
Embodiment 1
[0090] The implementation steps of preparing polyvinylidene fluoride blended flat porous membrane:
[0091] (1) Preparation of film-making solution: Stir polyvinylidene fluoride, amphiphilic polyethylene oxide, inorganic particles, pore size regulator, and solvent at 70°C for 24 hours, and degas to obtain a film-making solution. The mass percentage of component is:
[0092] Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF): FR904, 10%;
[0093] Amphiphilic polyethylene oxide (PTFE-b-PEG): the structure is CF 3 (CF 2 ) x -O-(CH 2 CH 2 O) y -H, fluorine-containing carbon chain two-block polyethylene oxide with a molecular weight of 725, 1%;
[0094] Inorganic particles: titanium dioxide (TiO2) with a particle size of 50 nm 2 ),1%;
[0095] Pore size regulator: molecular weight is polyethylene oxide (PEG) of 600, 3%;
[0096] Solvent: N, N-dimethylacetamide (DMAc), 85%;
[0097](2) Film formation by scraping: Scrape the film-making solution at 70°C on the flat carrier to form a nascent...
Embodiment 2
[0107] The implementation steps are as in Example 1, and the various implementation conditions and the structure and performance of the obtained PVDF blended flat porous membrane are shown in Table 2.
[0108] Table II:
[0109]
[0110]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com