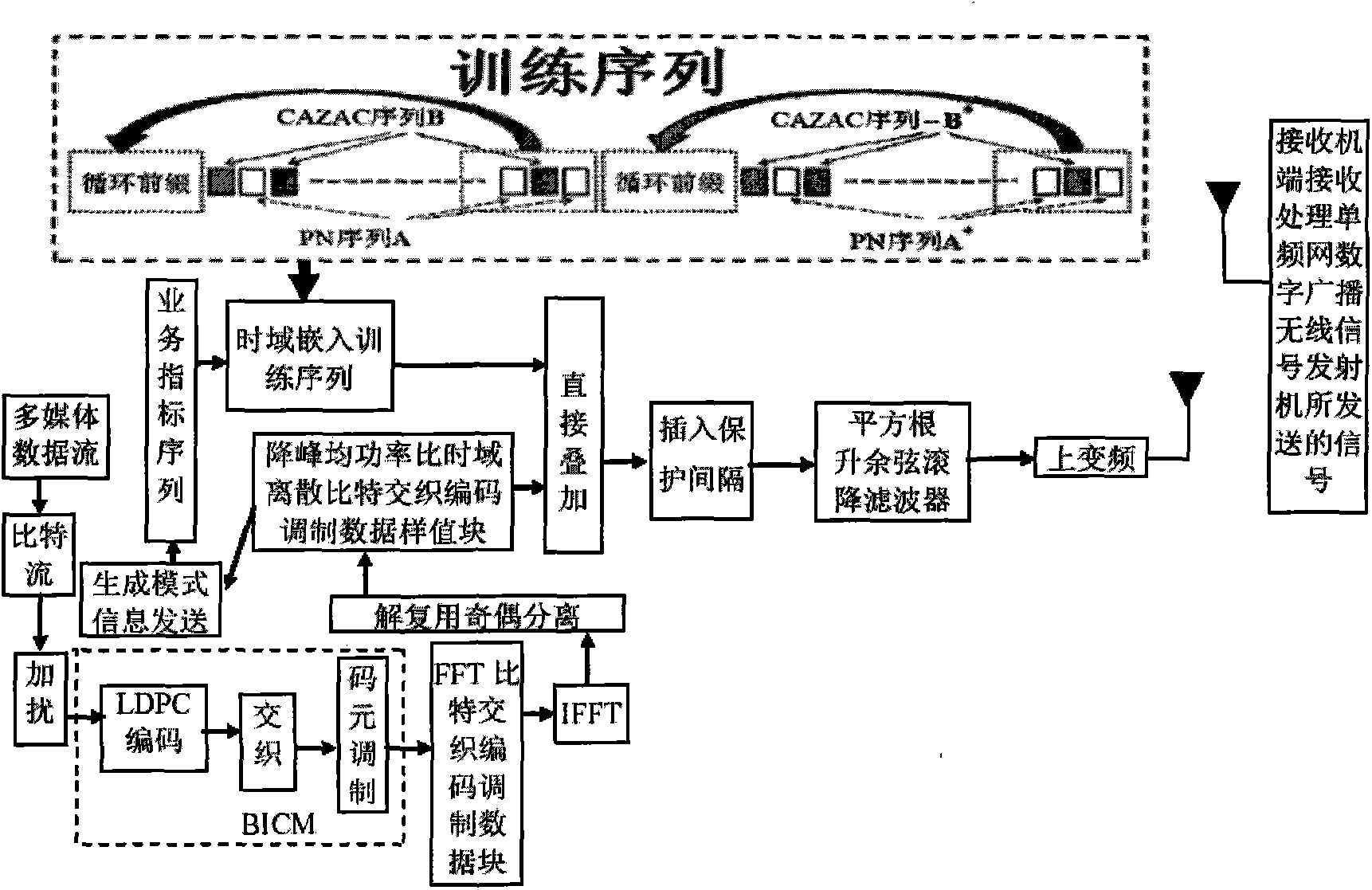
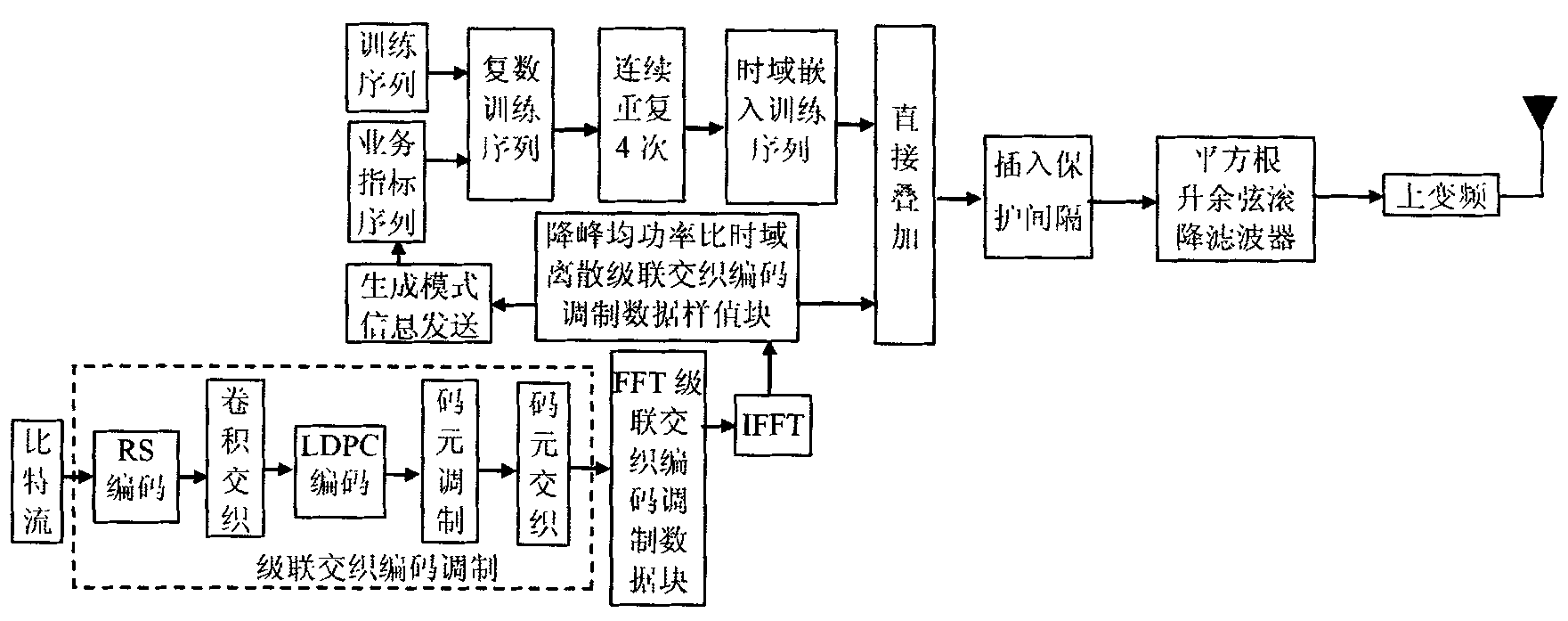
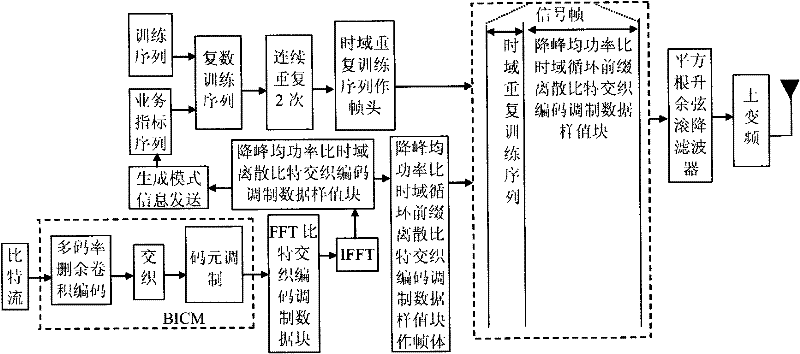
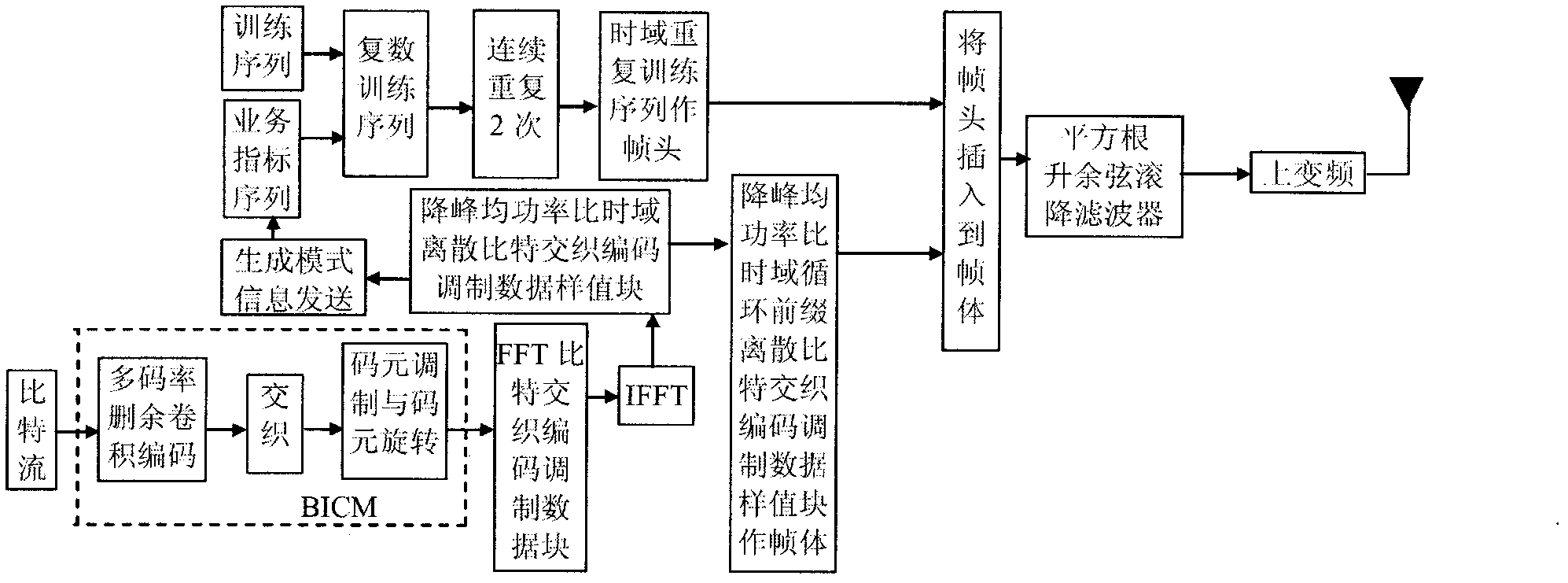
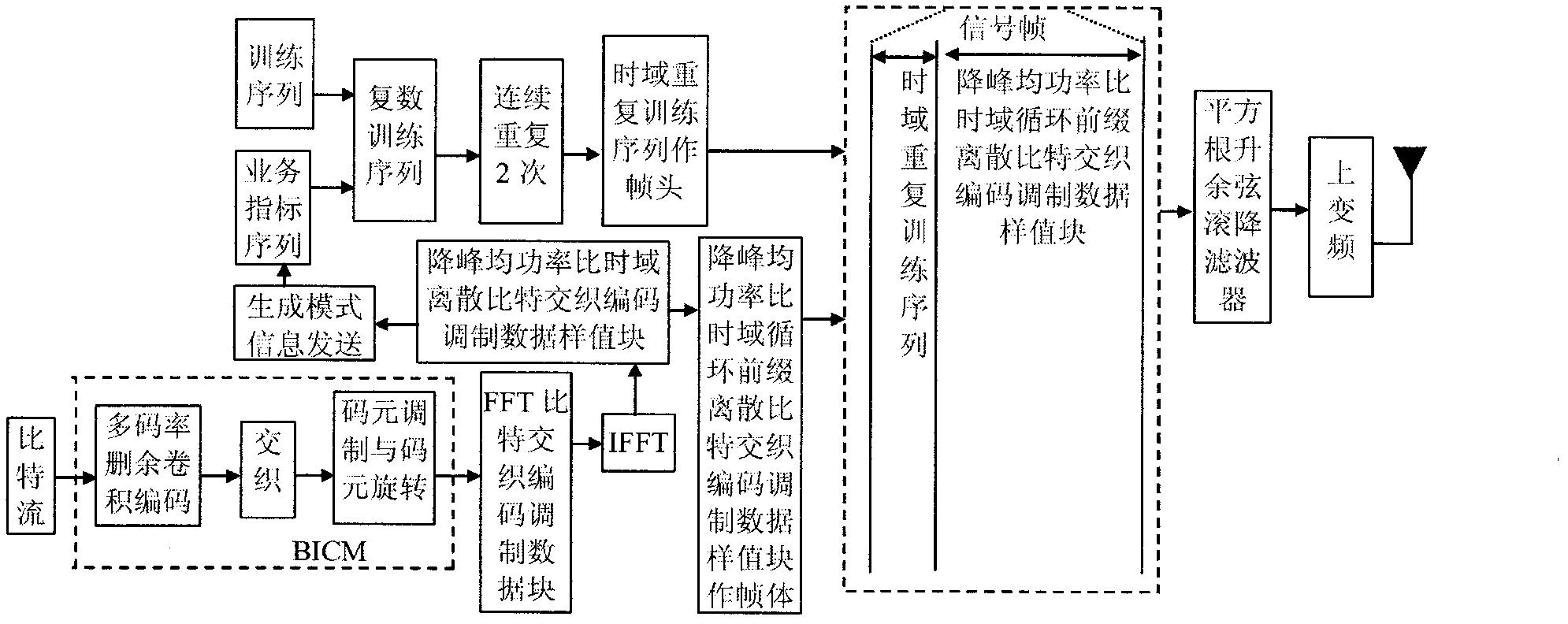
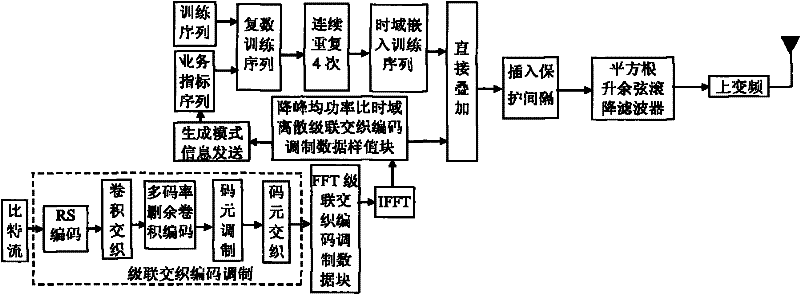
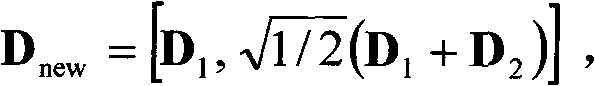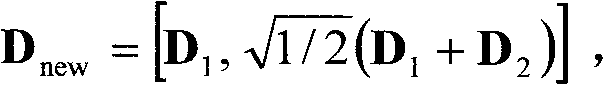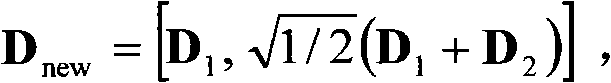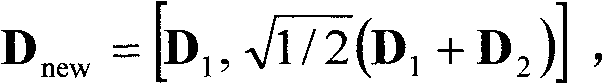Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
143results about How to "Increase the order of diversity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
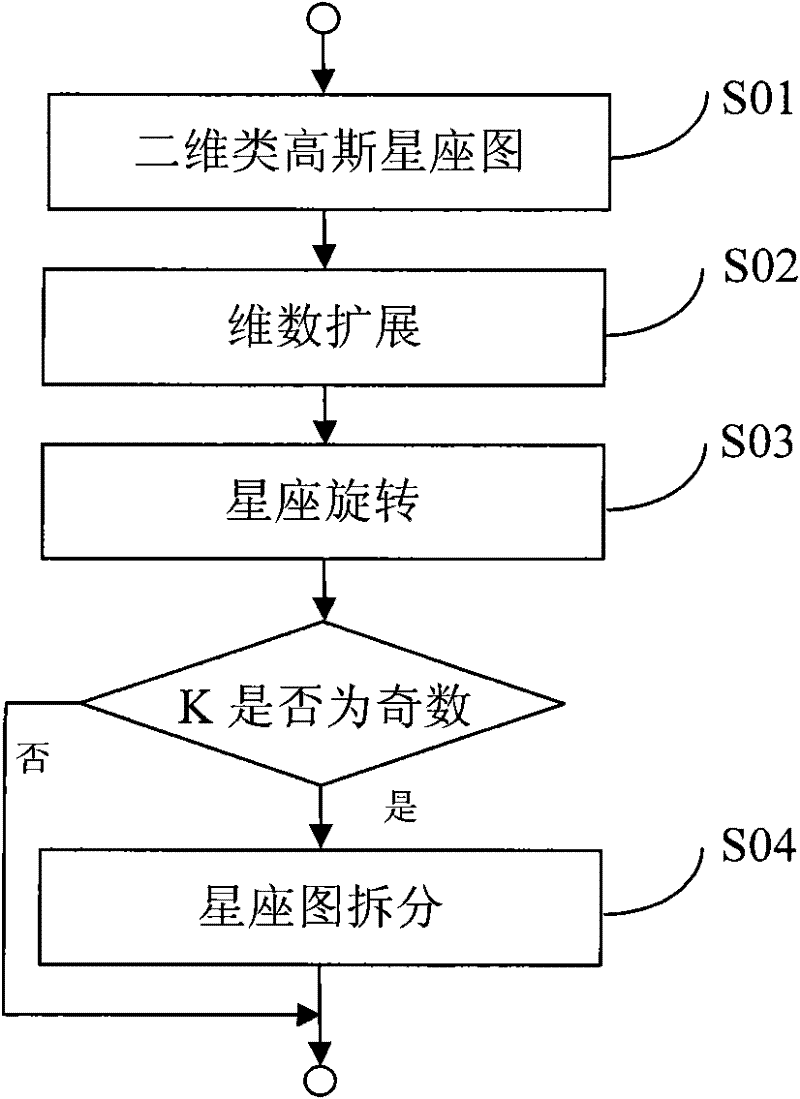
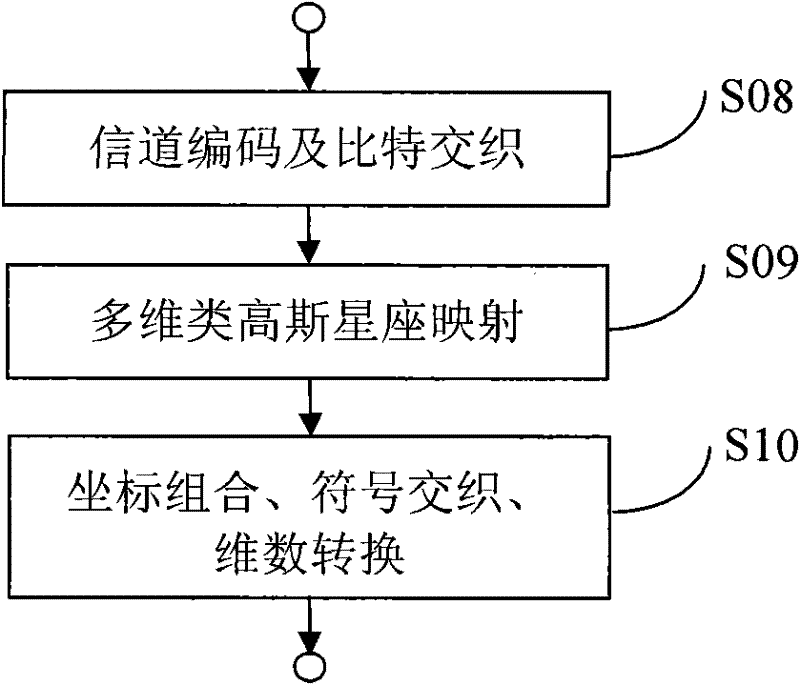
Construction method of multi-dimensional constellation graph, and method and system for code modulation and demodulation and decoding
ActiveCN102244556AReduce lossesIncrease the order of diversityError preventionMultiple carrier systemsChannel capacityConstellation
The invention discloses a construction method of a multi-dimensional constellation graph, and a code modulation system and a demodulation and decoding system based on the multi-dimensional constellation graph. The multi-dimensional constellation graph is a K-dimensional constellation graph, and the construction method comprises the following steps of: taking M points of a K0-dimensional constellation graph, wherein K0 is less than K; expanding dimensions of the K0-dimensional constellation graph to get a K0L-dimensional constellation graph; performing constellation rotation on the K0L-dimensional constellation graph to get a K0L-dimensional rotated constellation graph; and obtaining the K-dimensional constellation graph from the K0L-dimensional constellation graph. The construction method provided by the invention is simple; the system using the multi-dimensional constellation graph can significantly reduce Shaping loss and improve diversity order of the system so as to obtain diversity gain in a fading channel; and overall performance of a receiving end using the construction method can approach the channel capacity in both low and middle spectrum efficiency and various channel conditions.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
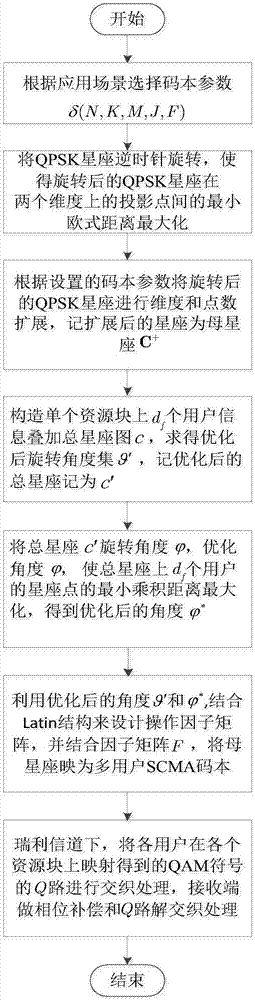
SCMA optimization codebook design method
ActiveCN107276960AImprove noiseImprove interferenceForward error control useMultiple carrier systemsResource blockSymbol of a differential operator
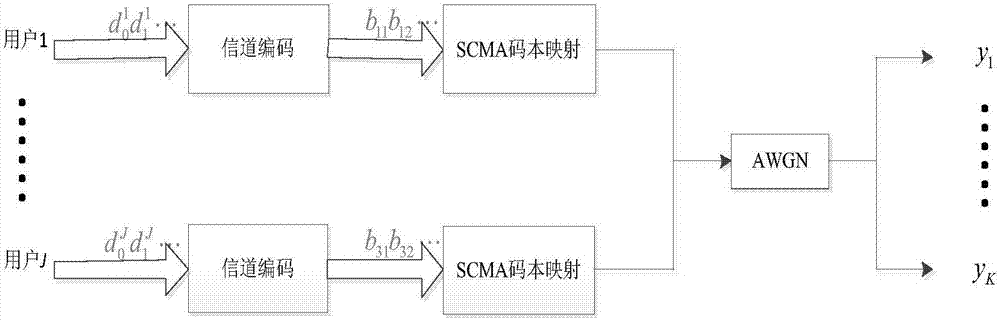
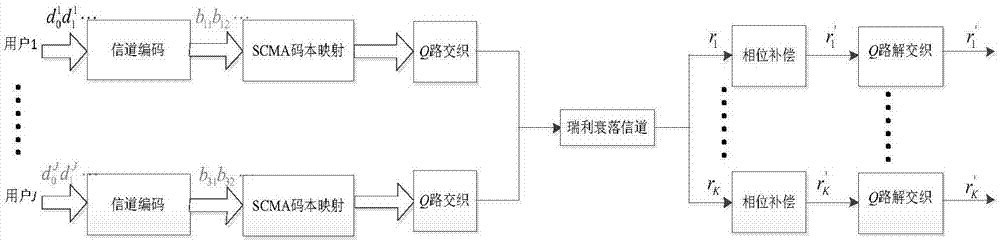
Disclosed is an SCMA (Sparse Code Multiple Access) optimization codebook design method, comprising the following steps: firstly, setting an SCMA codebook parameter; secondly, rotating a QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) constellation an angle anticlockwise to maximize the minimum Euclidean distance between projection constellation points of QPSK on two dimensions; thirdly, performing dimensional and point extension on C to obtain a mother constellation C+, and then rotating the C+ to construct a total constellation map c of df users on a single resource block to maximize the minimum Euclidean distance between the users; fourthly, rotating the total constellation anticlockwise to maximize the minimum product distance of each user on the resource block, and then mapping the mother constellation C+ to an SCMA codebook of multiple users with the use of the optimized rotating angle and in combination with a factor matrix F; and finally, in a Rayleigh fading channel, interweaving Q channels of QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) symbols, obtained by mapping on each resource block, of the users. The SCMA codebook designed by the method has good capability of resisting noise, interference and fading.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A robust framing modulation method for multimedia broadcasting mobile signals
ActiveCN102281230ANo nonlinear distortionFrequency synchronizationError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainComputer science
The invention discloses a multimedia broadcast mobile signal robust framing modulation method, and belongs to a time domain and frequency domain mixed framing modulation scheme. The multimedia broadcast mobile signal robust framing modulation method has the advantages of low peak-to-average power ratio, short synchronous time, robustness, controllable multi-service and the like.
Owner:ANHUI SAFE ELECTRONICS
Anti-fading digital mobile broadcast signal transmission method
InactiveCN102255859ADoes not destroy the orthogonalityReduce the amount of informationError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainComputer science
The invention discloses an anti-fading digital mobile broadcast signal transmission method which is a time domain frequency domain mixed transmission scheme. The anti-fading digital mobile broadcast signal transmission method of the present invention has the advantages of low peak-to-average power ratio, short synchronization time, fading resistance, control of multiple services and the like.
Owner:刘志军
Transmission method of anti-noise digital wireless broadcasting signals
InactiveCN103780554AReduce the amount of informationPromote recoveryError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainWireless broadcasting
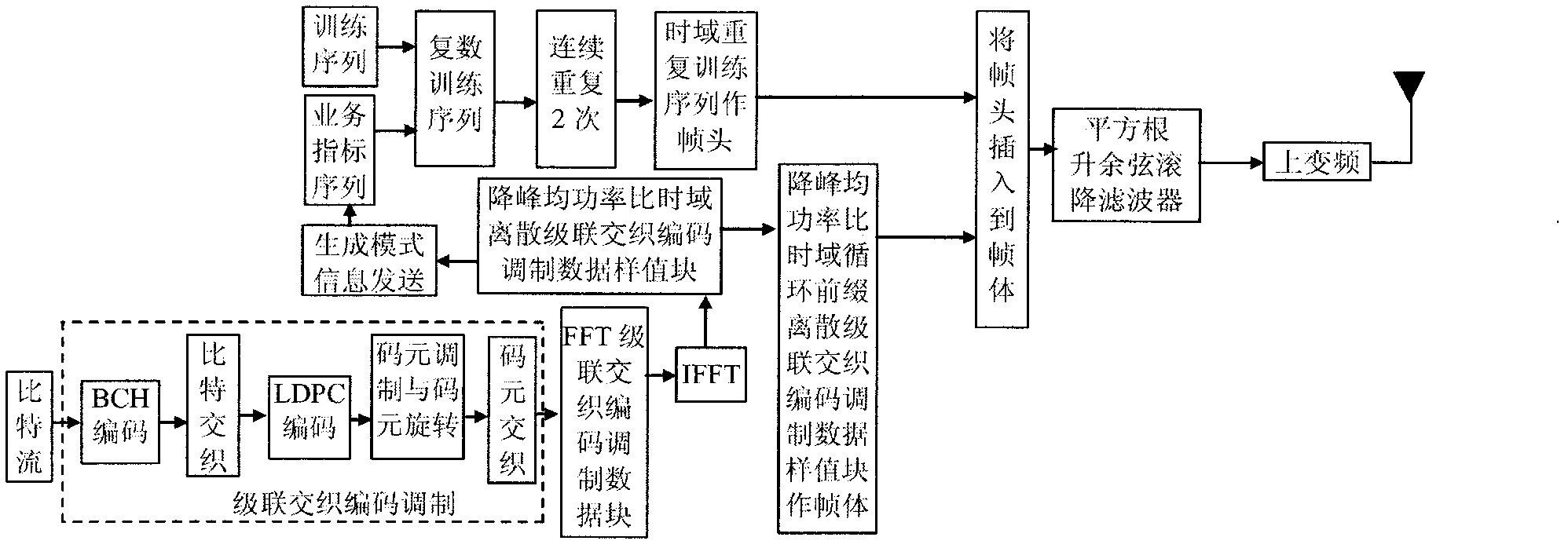
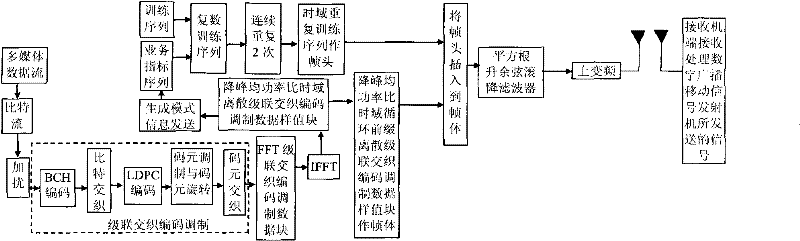
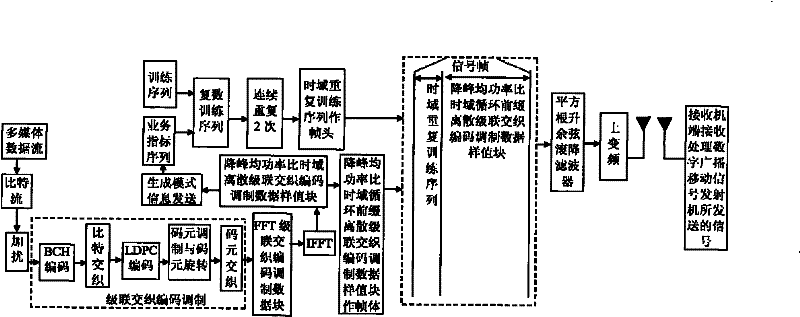
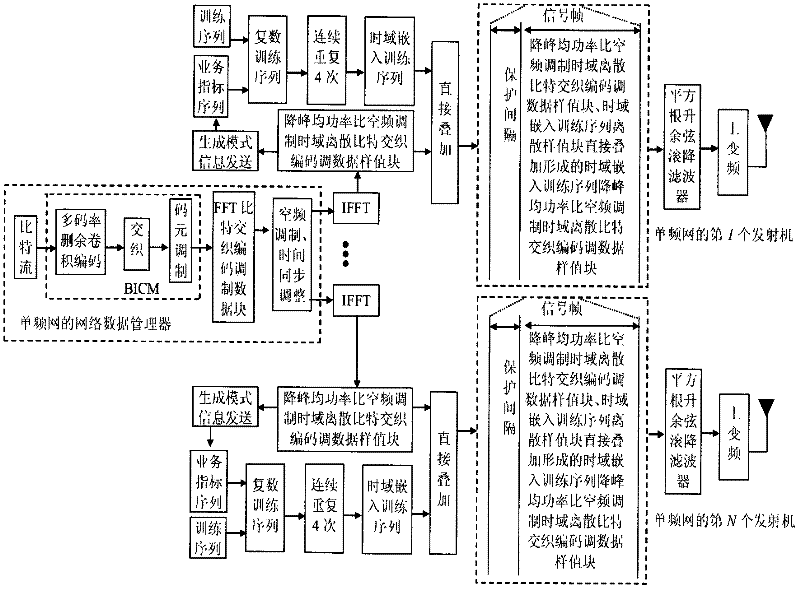
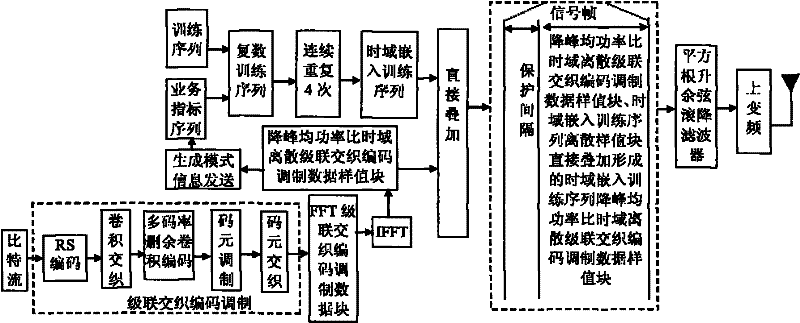
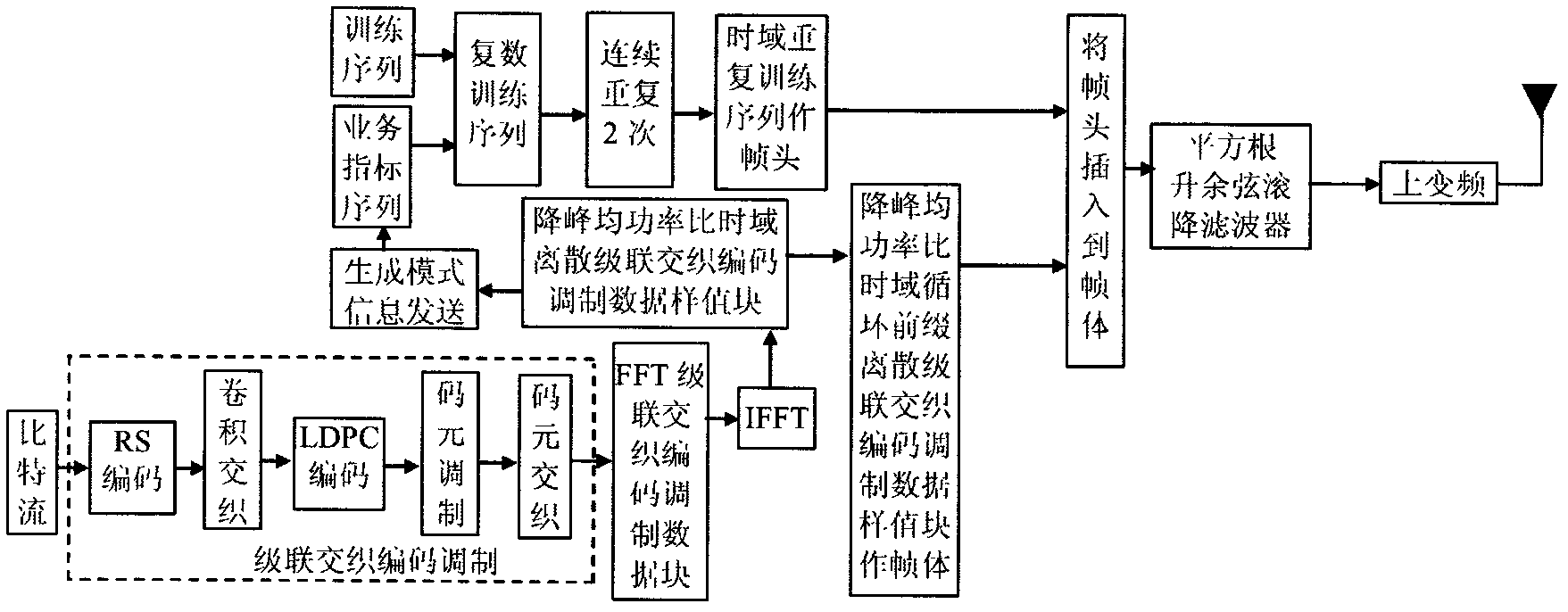
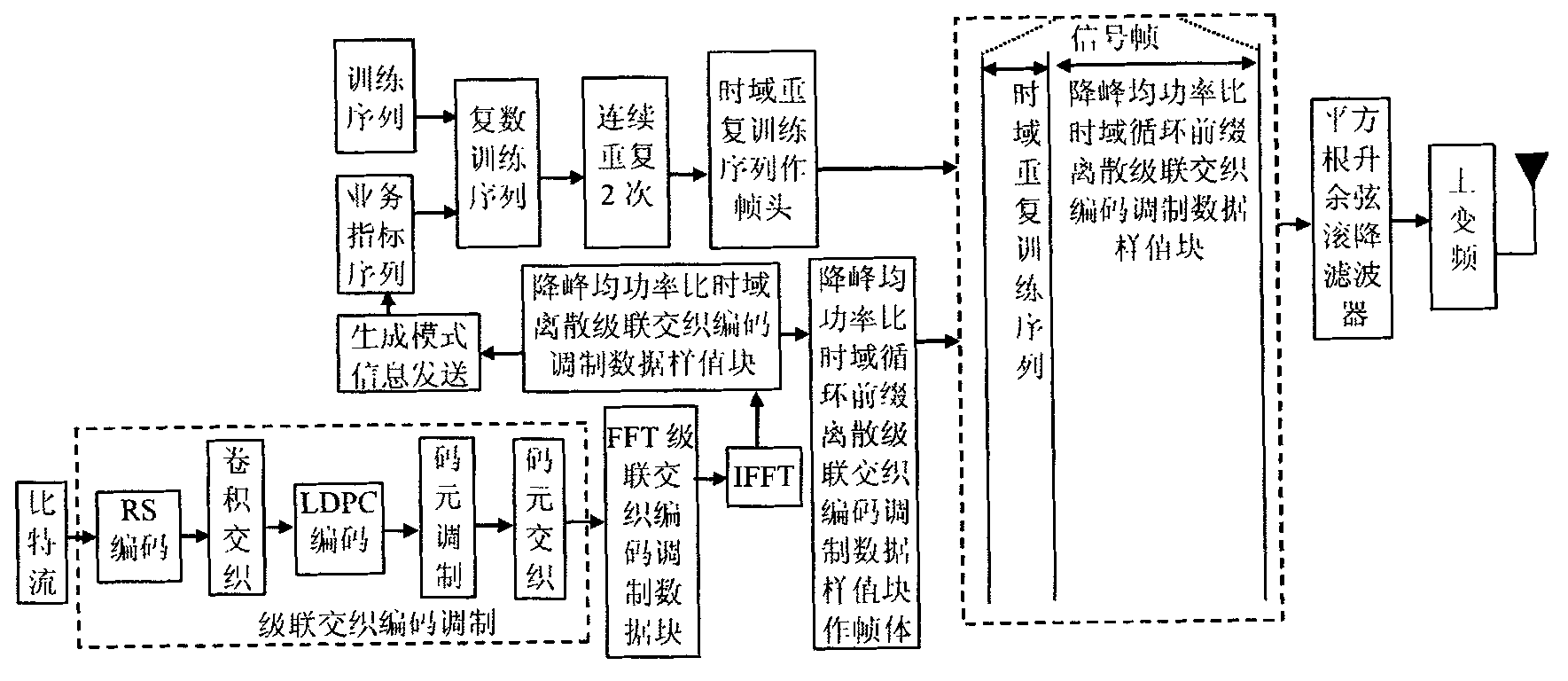
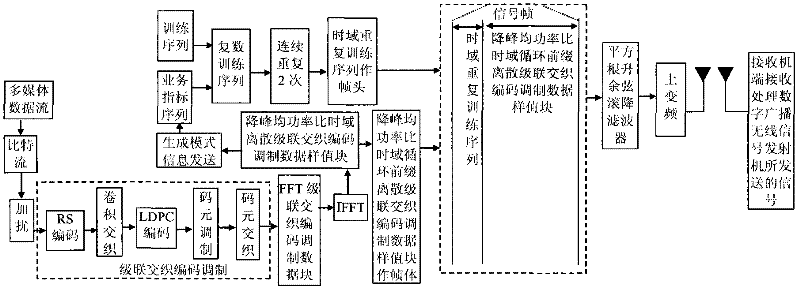
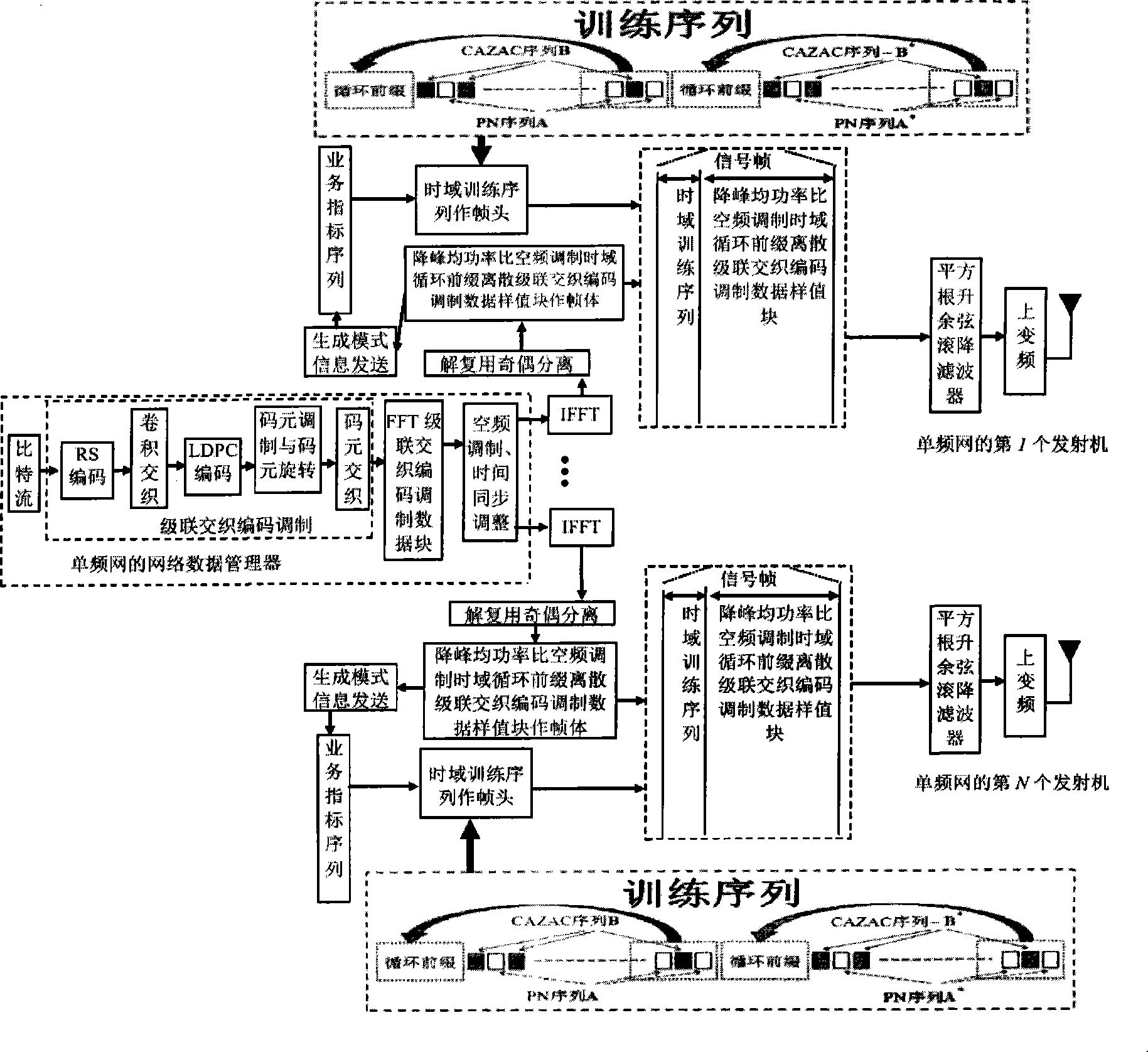
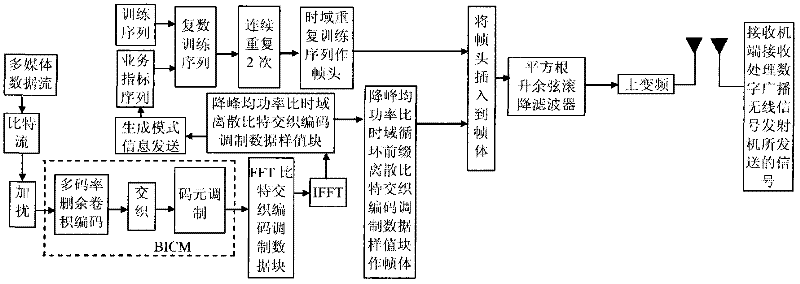
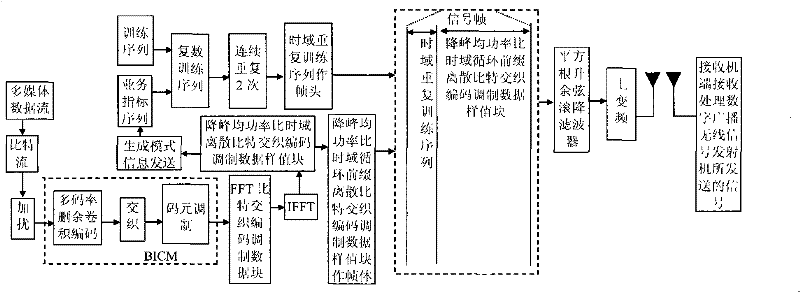
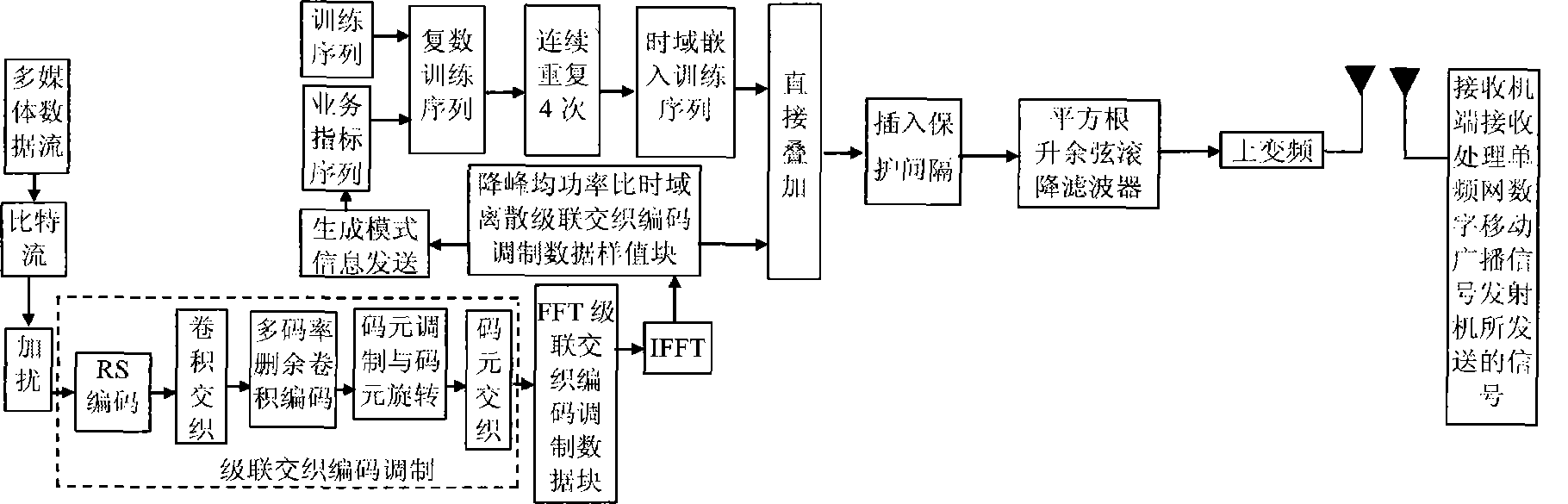
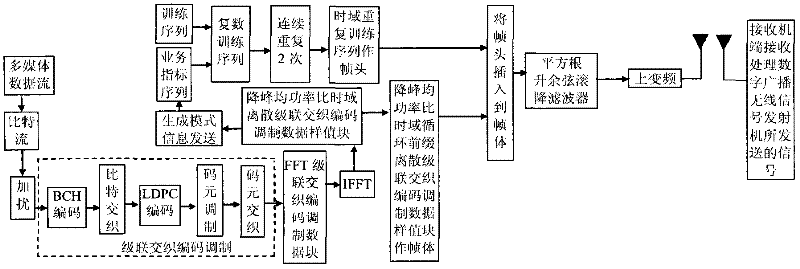
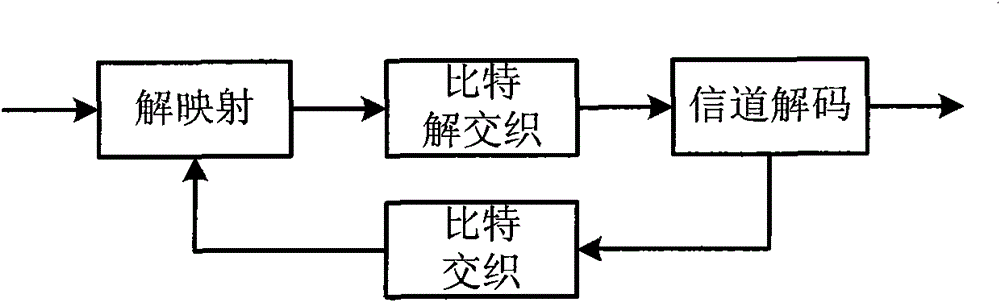
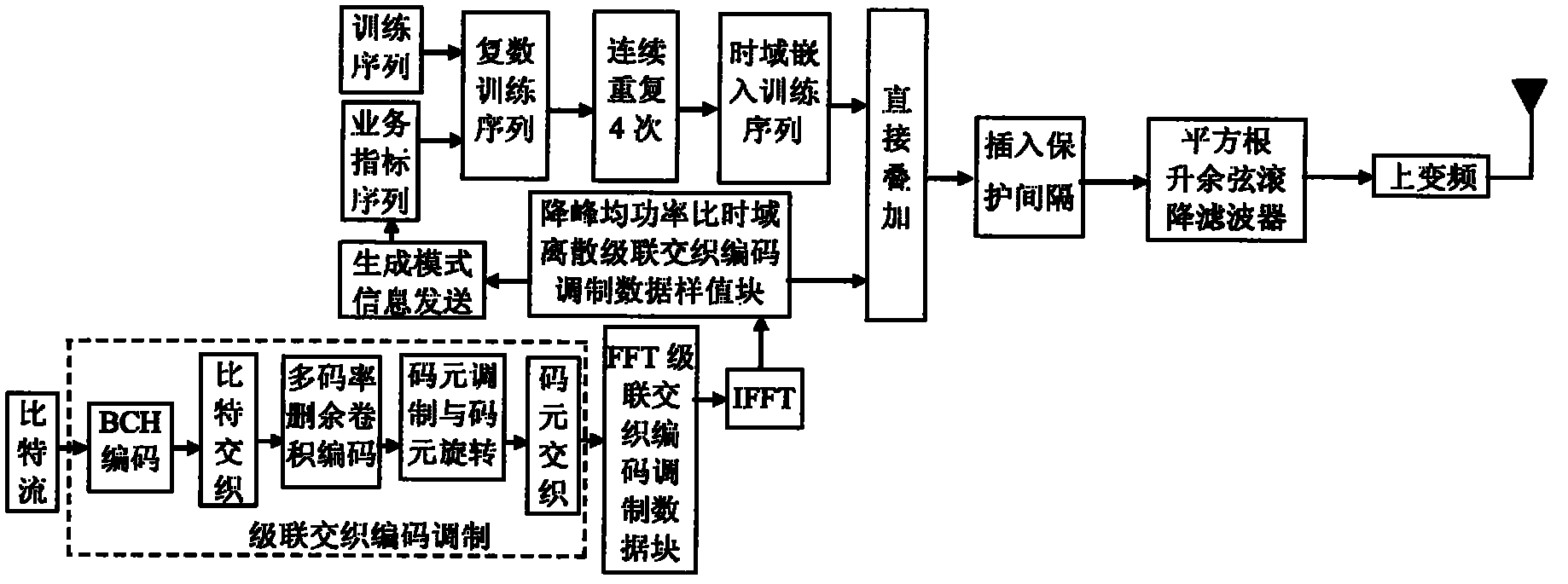
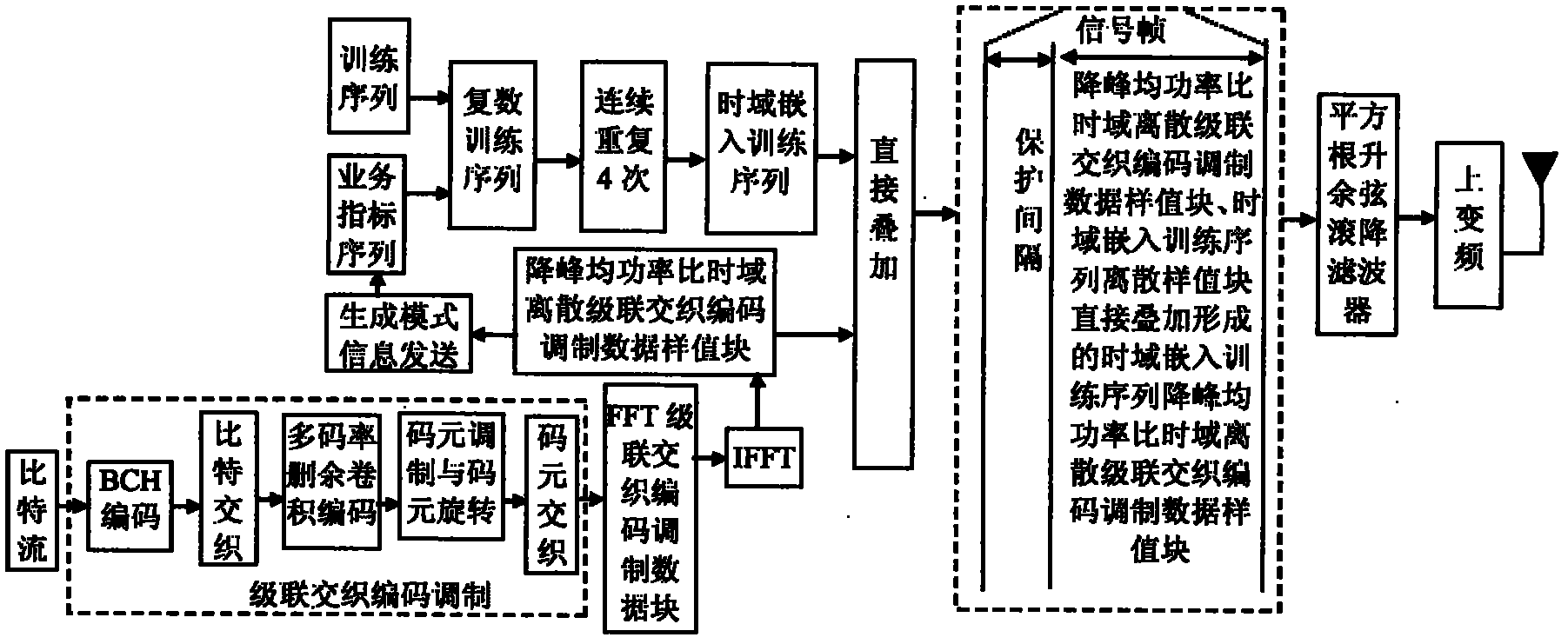
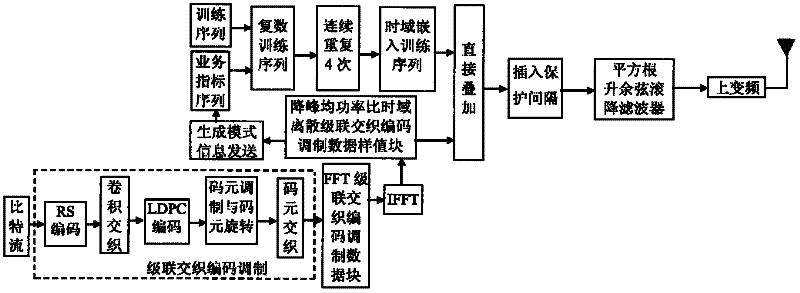
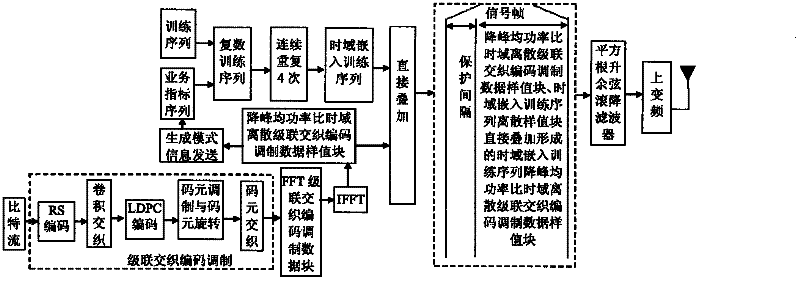
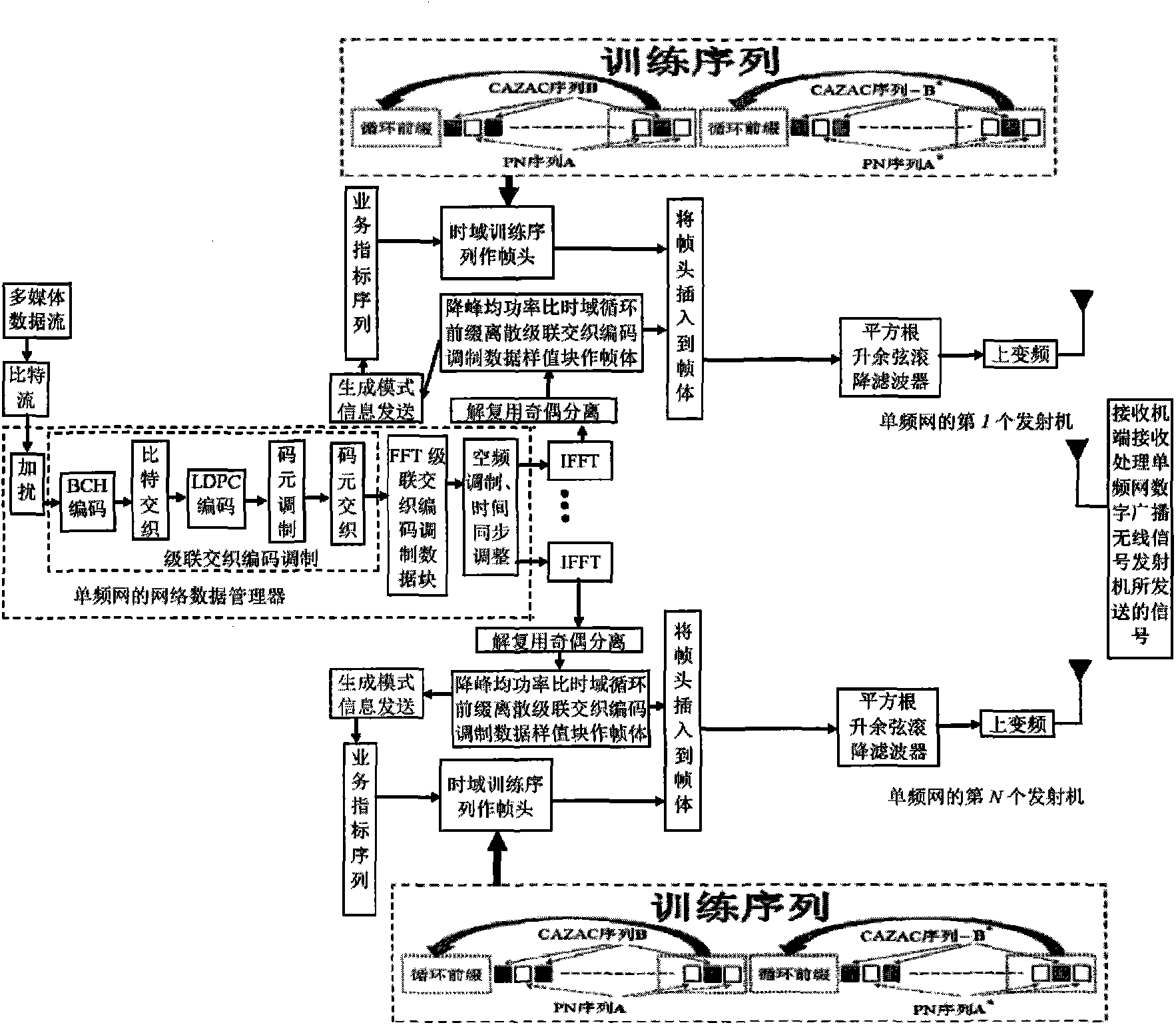
The invention discloses a transmission method of anti-noise digital wireless broadcasting signals. The transmission method is a framing modulation scheme with time domains and frequency domains being mixed. By means of the cascading interleaving coded modulation, the training sequence optimization design, the signal generating models and a signal selection method of the transmission method of the anti-noise digital wireless broadcasting signals, original signals of OFDM signals can be easily processed at a receiver end through processing and restoring, and the transmission method has the advantages of being low in PAPR, short in synchronous time, channel fading resistant, capable of controlling multiple services, and the like.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for framing and modulating anti-fading wireless multimedia broadcast signals
InactiveCN102255699ADoes not destroy the orthogonalityNo nonlinear distortionError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainVIT signals
The invention discloses a method for framing and modulating anti-fading wireless multimedia broadcast signals, which is a framing and modulating scheme that time domains and frequency domains are mixed. The method for framing and modulating the anti-fading wireless multimedia broadcast signals disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low peak-to-average power ratio, short synchronization time, anti-fading property, controllable multi-service and the like.
Owner:刘晶
A method for anti-jamming framing modulation of multimedia broadcasting wireless signals
InactiveCN102299890AAccurate synchronizationDoes not destroy the orthogonalityError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainInterference resistance
The invention discloses a multimedia broadcasting wireless signal anti-interference framing modulation method which is a time domain and frequency domain mixed framing modulation scheme. The multimedia broadcasting wireless signal anti-interference framing modulation method provided by the invention has the advantages of low peak average power ratio, short synchronizing time, anti-interference, capability of controlling multiple services, and the like.
Owner:广德睿纳鲜果酒业有限公司
Anti-interference wireless signal transmission method for digital broadcast
InactiveCN103763249AReduce the amount of informationEasy to handle recoveryError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsVIT signalsPower ratio
The invention discloses an anti-interference wireless signal transmission method for a digital broadcast, and relates to a mixed framing modulation scheme of the time domain and the frequency domain. According to the training sequence optimization design, the signal generating scheme and the signal selecting method of the anti-interference wireless signal transmission method for the digital broadcast, OFDM signals can be processed and recovered at a receiver end easily to obtain original signals of the OFDM signals. The anti-interference wireless signal transmission method for the digital broadcast has the advantages of being low in peak-to-average power ratio, short in synchronization time, resistant to channel fading, multiple in controllable service and the like.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Anti-interference radio signal framing modulation method for multimedia broadcast single-frequency network
InactiveCN102238131ADoes not destroy the orthogonalityEasy to handleMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainInterference resistance
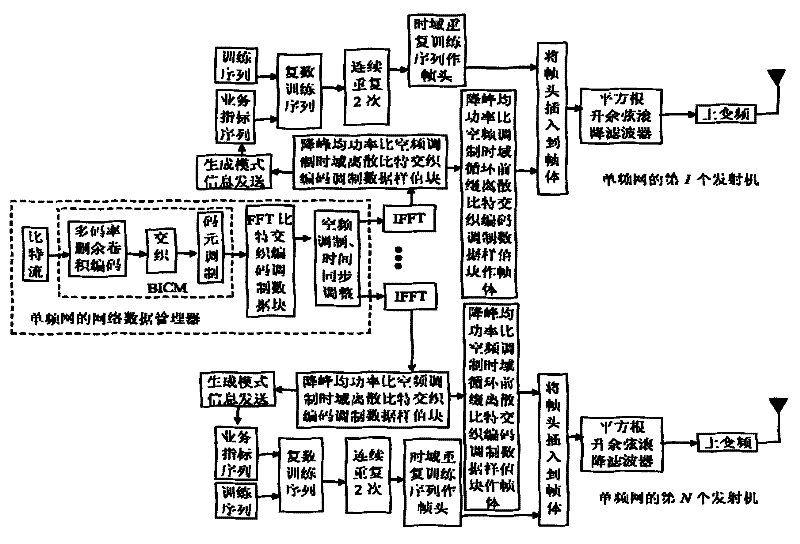
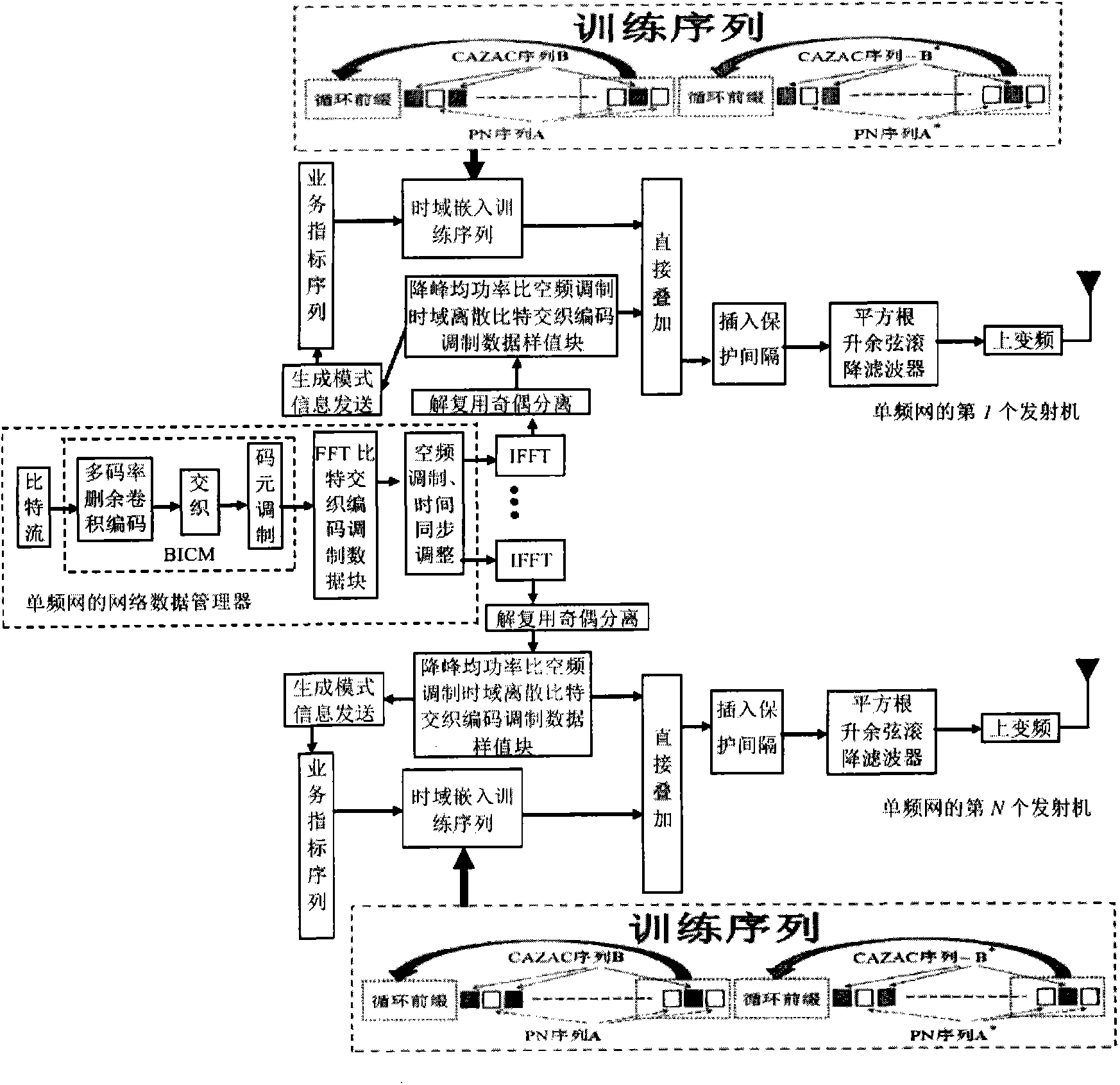
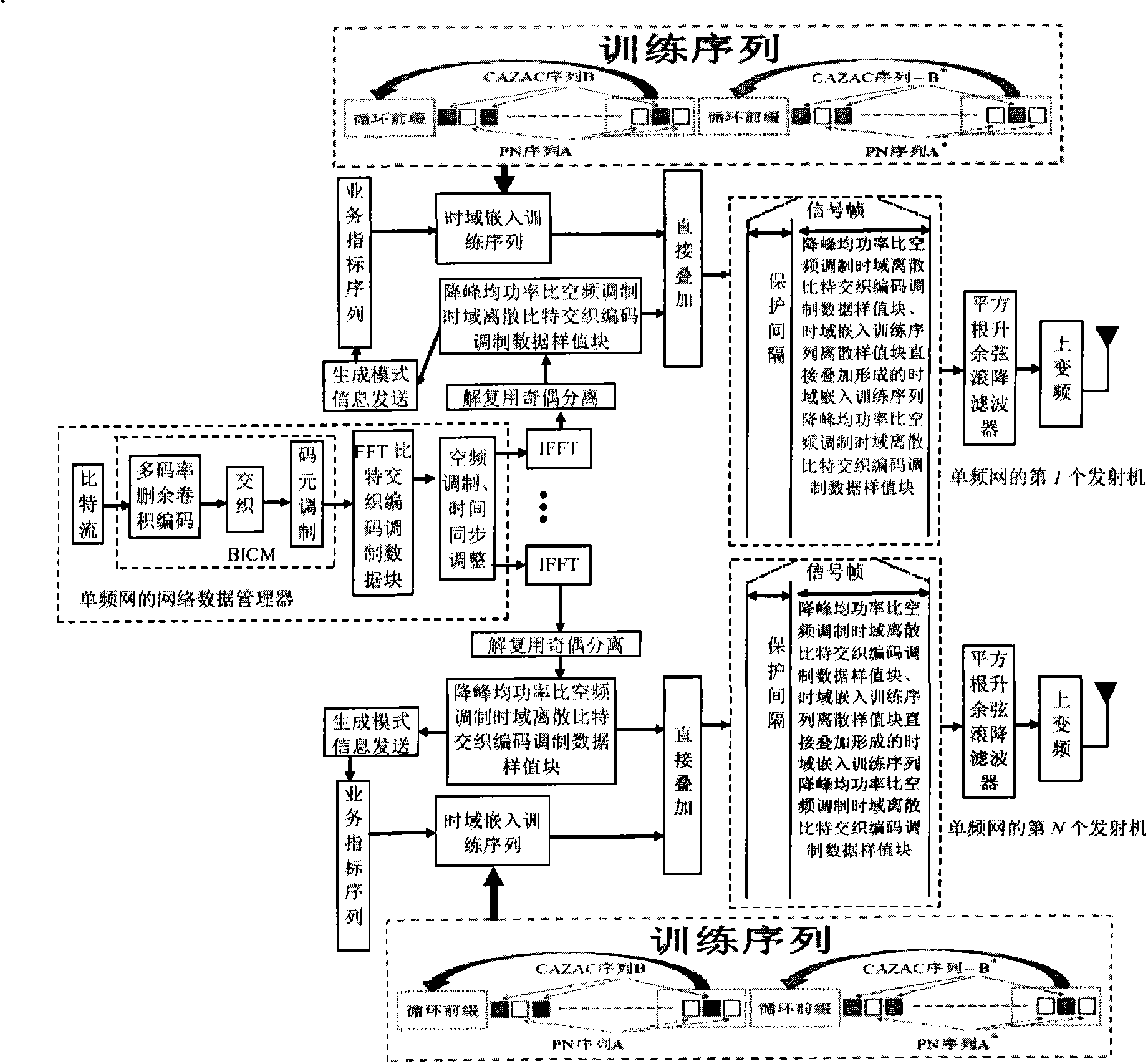
The invention discloses an anti-interference radio signal framing modulation method for a multimedia broadcast single-frequency network. The method is a time domain / frequency domain / space domain hybrid framing modulation scheme. The anti-interference radio signal framing modulation method for the multimedia broadcast single-frequency network has the advantages of low peak to average power ratio, short synchronization time, anti-interference performance, multi-service controllability and the like.
Owner:广西良将自动化工程有限公司
Anti-interference wireless multimedia broadcast signal framing modulation method
InactiveCN102307171ADoes not destroy the orthogonalityNo nonlinear distortionError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainControllability
The invention discloses an anti-interference wireless multimedia broadcast signal framing modulation method, which is a time domain / frequency domain combined framing modulation scheme. The anti-interference wireless multimedia broadcast signal framing modulation method has the advantages of low peak-to-average power ratio, short synchronization time, anti-interference performance, multi-service controllability and the like.
Owner:广德睿纳鲜果酒业有限公司
Robust mobile signal framing modulation method for multimedia broadcast single frequency network
InactiveCN103763082AReduce the amount of informationDoes not destroy the orthogonalityPhase-modulated carrier systemsMulti-frequency code systemsSingle-frequency networkVIT signals
The invention discloses a robust mobile signal framing modulation method for a multimedia broadcast single frequency network, and relates to a mixed framing modulation scheme of the space domain, the time domain and the frequency domain. According to the training sequence optimization design, the signal generating scheme and the signal selecting method of the robust mobile signal framing modulation method for the multimedia broadcast single frequency network, OFDM signals can be processed and recovered at a receiver end easily to obtain original signals of the OFDM signals. The robust mobile signal framing modulation method for the multimedia broadcast single frequency network has the advantages of being low in peak-to-average power ratio, short in synchronization time, resistant to channel fading, multiple in controllable service and the like.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for framing and modulating anti-interference wireless multimedia broadcast signals in single frequency network
InactiveCN103763290AReduce the amount of informationDoes not destroy the orthogonalityMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainComputer science
The invention discloses a method for framing and modulating anti-interference wireless multimedia broadcast signals in a single frequency network. The method provides a framing and modulating scheme mixing a space domain, a time domain and a frequency domain. According to a training sequence optimal design, a signal generation pattern and a signal selection method of the method for framing and modulating the anti-interference wireless multimedia broadcast signals in the single frequency network, an original signal of an OFDM signal can be easily obtained through processing and recovery on a receiver terminal. The method for framing and modulating the anti-interference wireless multimedia broadcast signals in the single frequency network has the advantages that the peak-to-average power ratio is low, synchronization time is short, channel fading is prevented, and multiple services can be controlled.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
A Robust Transmission Method for Digital Broadcasting Mobile Signals
InactiveCN102263765ANo nonlinear distortionAccurate synchronizationError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsPower ratioFrequency domain
The invention discloses a robust transmission method of digital broadcast mobile signals, which is a mixed transmission scheme of time domain and frequency domain. The method has the advantages of low PAPR (peak-to-average power ratio), short synchronous time, robustness, multiple controllable services and the like.
Owner:周洪晨
Anti-noise digital mobile broadcast signal transmitting method
InactiveCN102255863AReduce the amount of informationNo nonlinear distortionError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainControllability
The invention discloses an anti-noise digital mobile broadcast signal transmitting method, which relates to a time domain-frequency domain hybrid transmitting scheme. The anti-noise digital mobile broadcast signal transmitting method has the advantages of low peak-to-average power ratio, short synchronization time, noise resistance, multi-service controllability, and the like.
Owner:薛岗
A framing modulation method for anti-jamming multimedia wireless broadcasting signal
InactiveCN102271117ADoes not destroy the orthogonalityNo nonlinear distortionError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainInterference resistance
The invention discloses an anti-interference multimedia wireless broadcast signal framing modulation method, which is a time domain / frequency domain hybrid framing modulation scheme. The anti-interference multimedia wireless broadcast signal framing modulation method has the advantages of low peak-to-average power ratio, short synchronization time, anti-interference performance, multi-service controllability and the like.
Owner:孙波
A framing modulation method of anti-noise multimedia wireless broadcasting signal
InactiveCN102263760ANo nonlinear distortionReduce the impact of interferenceError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainComputer network
The invention discloses an anti-noise multimedia wireless broadcast signal framing modulation method, which is a time domain / frequency domain combined framing modulation scheme. The anti-noise multimedia wireless broadcast signal framing modulation method has the advantages of low peak-to-average power ratio, short synchronization time, anti-noise performance, multi-service controllability and the like.
Owner:广德睿纳鲜果酒业有限公司
Anti-interference wireless multimedia broadcast signal framing modulation method for single frequency network
InactiveCN102244638ADoes not destroy the orthogonalityEasy to handleMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainControllability
The invention discloses an anti-interference wireless multimedia broadcast signal framing modulation method for a single frequency network, which is a time domain / frequency domain / space domain hybrid framing modulation scheme. The anti-interference wireless multimedia broadcast signal framing modulation method for the single frequency network has the advantages of low peak-to-average power ratio, short synchronization time, anti-channel interference performance, multi-service controllability and the like.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
A method for anti-jamming framing modulation of multimedia broadcasting mobile signals
InactiveCN102281231AAccurate synchronizationTime synchronizationError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainInterference resistance
The invention discloses a multimedia broadcast mobile signal anti-interference framing modulation method and in particular relates to a framing modulation scheme with mixing of time domains and frequency domains. The multimedia broadcast mobile signal anti-interference framing modulation method has the advantages that the peak-average power ratio is low, the synchronization time is short, the interference resistance is achieved, and the multiple services can be controlled and the like.
Owner:天津中新众信智能科技有限公司
An anti-fading multimedia wireless broadcast signal framing modulation method
InactiveCN102271116ADoes not destroy the orthogonalityNo nonlinear distortionError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainComputer science
The invention discloses an anti-fading multimedia wireless broadcast signal framing modulation method, which is a framing modulation scheme of mixing time domain and frequency domain. The anti-fading multimedia wireless broadcast signal framing modulation method of the invention has the advantages of low peak-to-average power ratio, short synchronization time, anti-fading, controllable multi-service and the like.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Anti-fading framing modulating method for multimedia broadcast radio signal
ActiveCN102255698AAccurate synchronizationDoes not destroy the orthogonalityError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsVIT signalsPower ratio
The invention discloses an anti-fading framing modulating method for a multimedia broadcast radio signal, and is a time-domain and frequency-domain hybrid framing modulating scheme and has the advantages of low PAPR (Peak to Average Power Ratio), short synchronous time, anti-fading property, capability of controlling multi-service, and the like.
Owner:ANHUI SAFE ELECTRONICS
A digital broadcast wireless signal anti-fading transmission method
InactiveCN102263736ANo nonlinear distortionAccurate synchronizationError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsVIT signalsFrequency domain
The invention discloses an anti-fading digital broadcast wireless signal transmitting method, and relates to a time domain / frequency domain mixed scheme. The anti-fading digital broadcast wireless signal transmitting method has the advantages of low peak-to-average power ratio, short synchronization time, resistance to fading, controllable multiple services and the like.
Owner:谌晓晴
Anti-fading mobile signal framing modulation method for multimedia broadcast single frequency network
InactiveCN103763061AReduce the amount of informationDoes not destroy the orthogonalityError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainMultimedia broadcast single frequency network
The invention discloses an anti-fading mobile signal framing modulation method for a multimedia broadcast single frequency network, and relates to a mixed framing modulation scheme of the space domain, the time domain and the frequency domain. According to the training sequence optimization design, the signal generating scheme and the signal selecting method of the anti-fading mobile signal framing modulation method for the multimedia broadcast single frequency network, OFDM signals can be processed and recovered at a receiver end easily to obtain original signals of the OFDM signals. The anti-fading mobile signal framing modulation method for the multimedia broadcast single frequency network has the advantages of being low in peak-to-average power ratio, short in synchronization time, resistant to channel fading, multiple in controllable service and the like.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
A digital broadcast wireless signal anti-interference transmission method
InactiveCN102263738ANo nonlinear distortionAccurate synchronizationError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainInterference resistance
The invention discloses an anti-interference transmission method for a digital broadcast wireless signal. The method is a time domain / frequency domain combined transmission scheme. The anti-interference transmission method has the advantages of low peak-to-average power ratio, short synchronization time, anti-interference performance, multi-service controllability and the like.
Owner:弭希瑞
Anti-fading wireless digital broadcast signal transmitting method
InactiveCN102255852AHas pseudorandom propertiesDoes not destroy the orthogonalityError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainDigital radio
The invention discloses an anti-fading wireless digital broadcast signal transmitting method, which relates to a time domain-frequency domain hybrid transmitting scheme. The anti-fading wireless digital broadcast signal transmitting method has the advantages of low peak-to-average power ratio, short synchronization time, fading resistance, multi-service controllability, and the like.
Owner:广德睿纳鲜果酒业有限公司
Anti-fading digital mobile broadcast signal transmission method
InactiveCN102255859BDoes not destroy the orthogonalityReduce the amount of informationError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainComputer science
Owner:刘志军
A method for robust transmission of digital broadcast wireless signals
InactiveCN102263737ANo nonlinear distortionAccurate synchronizationError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainDigital radio
The invention discloses a robust transmission method for digital broadcasting wireless signals, which is a time domain and frequency domain hybrid transmission scheme. The method has the advantages of low peak-to-average power ratio, short synchronous time, robustness, controllability in multiple services and the like.
Owner:王运国
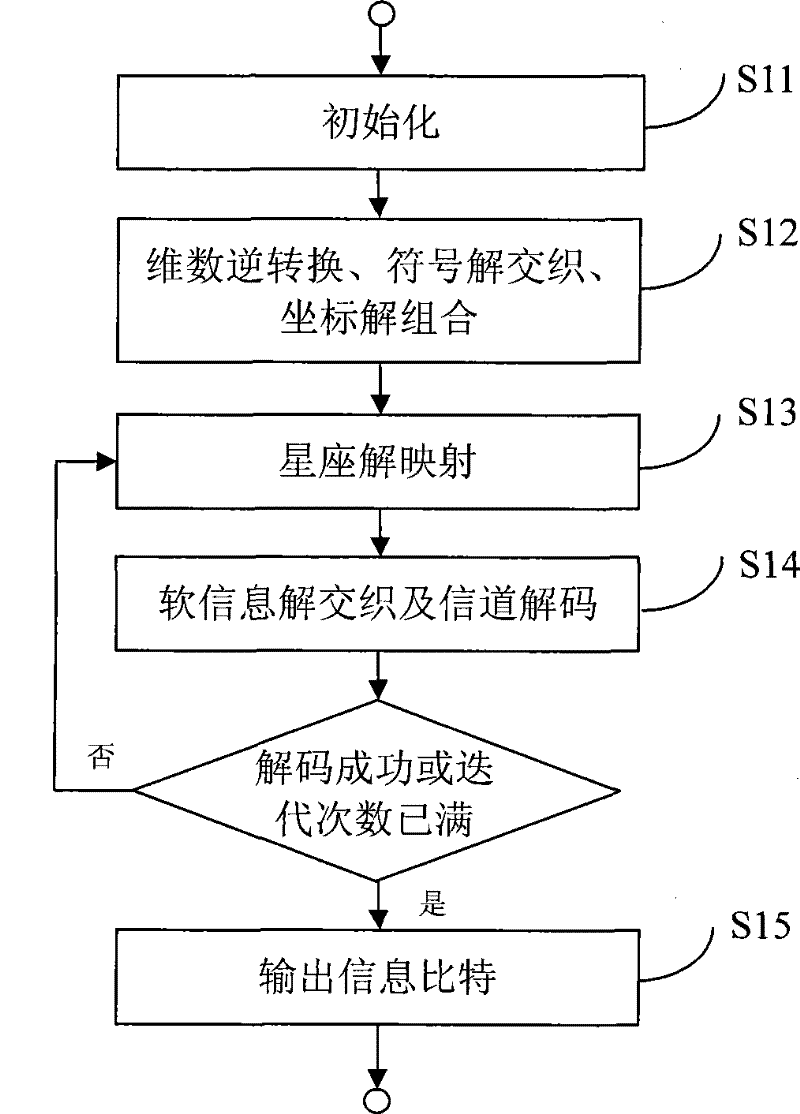
Code modulation method, demodulation and decoding method and system
ActiveCN101989887BReduce Shaping LossIncrease the order of diversityError preventionMultiple carrier systemsUltrasound attenuationFrequency spectrum
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A robust multimedia mobile broadcast signal framing modulation method
InactiveCN102291358AReduce the amount of informationNo nonlinear distortionError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsBroadbandFrequency domain
The invention discloses a robust multi-media mobile broadcast signal framing modulation method which is a framing modulation scheme of mixing a time domain and a frequency domain. According to the robust multi-media mobile broadcast signal framing modulation method disclosed by the invention, a low-complexity peak-to-average power ratio reduction technology and a combined code modulation technology are designed aiming at the technical problems of high signal peak-to-average power ratio, channel time variant, Doppler frequency shift and noise of a broadband multi-carrier multi-media mobile broadcast system, which need to be solved, and therefore the broadband multi-carrier multi-media mobile broadcast system has the advantages of low peak-to-average power ratio, short synchronization time,robustness, controllable multi-service, and the like.
Owner:任桂文
An anti-fading mobile multimedia broadcasting signal framing modulation method
InactiveCN102271111ANo nonlinear distortionReduce the impact of interferenceError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainComputer science
The invention discloses an anti-fading mobile multimedia broadcasting signal framing modulation method which is a time domain and frequency domain mixed framing modulation scheme. The anti-fading mobile multimedia broadcasting signal framing modulation method provided by the invention has the advantages of low peak average power rate, short synchronous time, fading resistance, capability of controlling multiple services, and the like.
Owner:司长海
Robust wireless signal transmission method for digital broadcast single frequency network
InactiveCN103763262AReduce the amount of informationDoes not destroy the orthogonalityError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsSingle-frequency networkFrequency domain
The invention discloses a robust wireless signal transmission method for a digital broadcast single frequency network, and relates to a mixed framing modulation scheme of the space domain, the time domain and the frequency domain. According to the training sequence optimization design, the signal generating scheme and the signal selecting method of the robust wireless signal transmission method for the digital broadcast single frequency network, OFDM signals can be processed and recovered at a receiver end easily to obtain original signals of the OFDM signals. The robust wireless signal transmission method for the digital broadcast single frequency network has the advantages of being low in peak-to-average power ratio, short in synchronization time, resistant to channel fading, multiple in controllable service and the like.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com