Sense circuit for reading data stored in nonvolatile memory cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
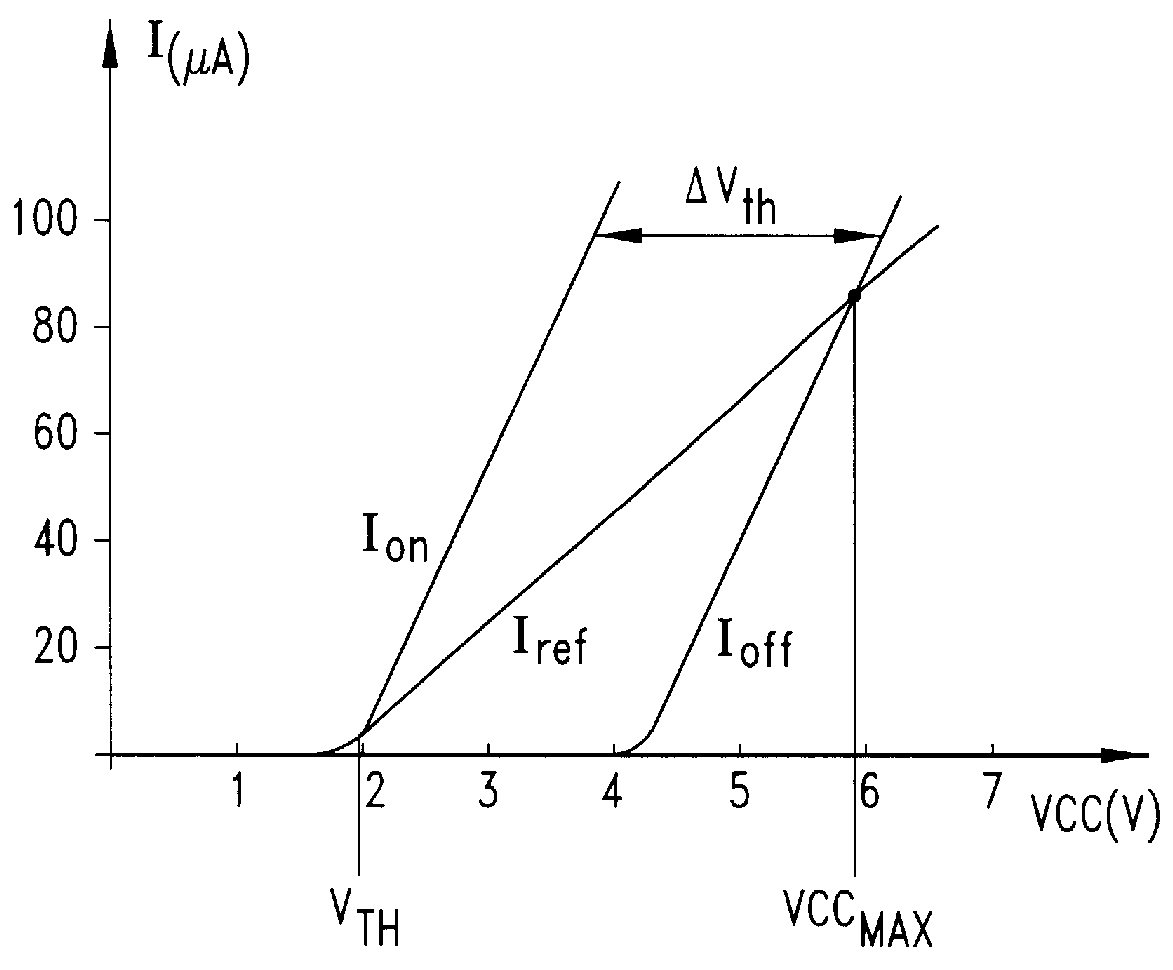
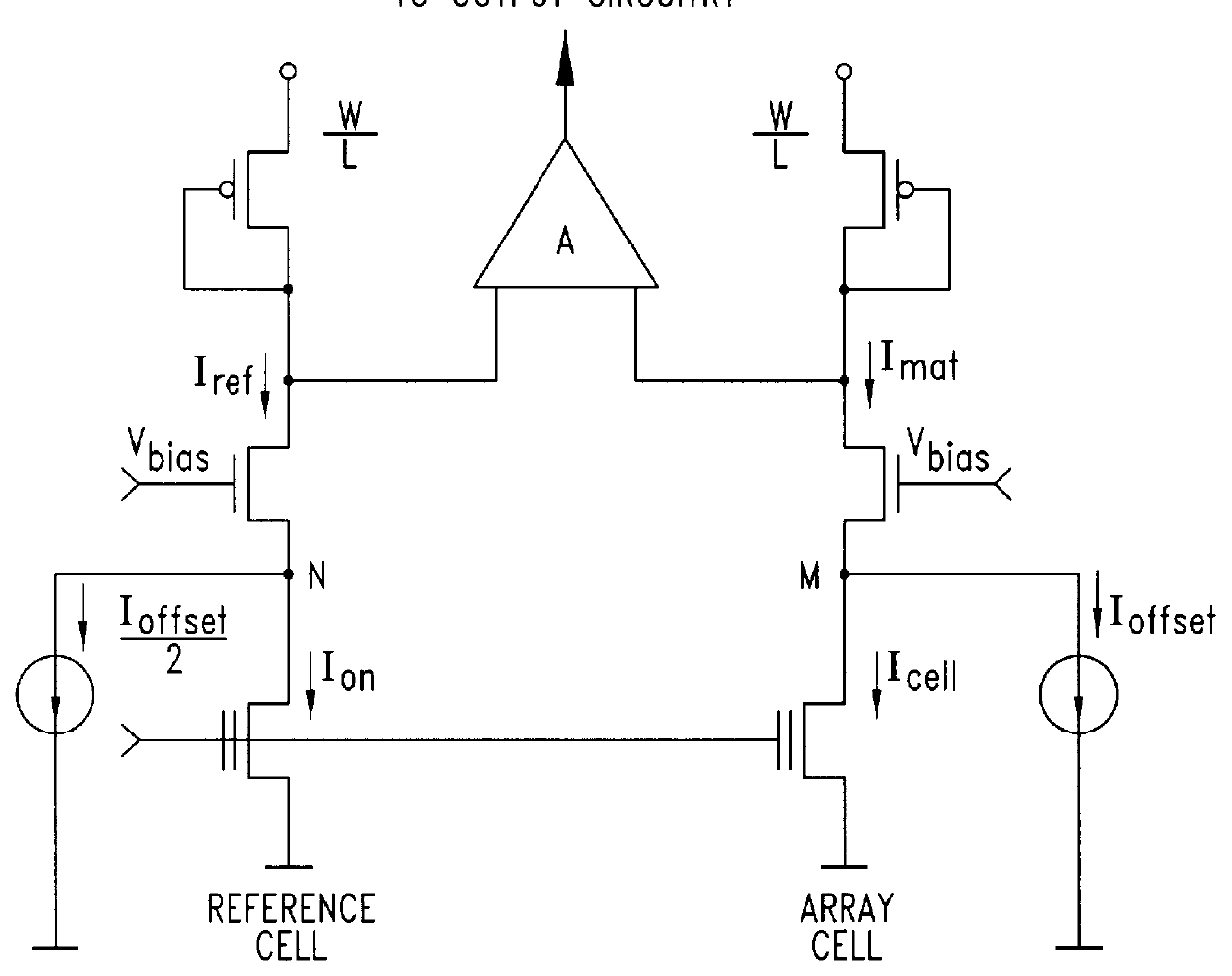
For simplicity's sake, in the circuit diagram of FIGS. 5 and 8, only the offsetting current generating circuit of the offset-current-type sense circuit as shown in FIG. 3 is depicted; the circuit nodes M and N of the circuit of FIG. 3 being indicated in the so-partialized circuit diagrams of FIGS. 5 and 8.
Moreover the label DUMMY ROW used in FIGS. 5 and 8, indicates a drive voltage line derived from a supplementary row of cells of the array of cells which is decoded at every reading and which therefore replicates perfectly the behaviour of .[.anyone.]. .Iadd.current unbalance .Iaddend.row of memory cells of the array which is selected for reading, during a transient.
Normally, the reference column line, REFERENCE BITLINE, serves a certain number of column lines, MATRIX BITLINE, of the array and to these is adjacently formed on the silicon chip so as to make as similar as possible the voltages present on the gate of the reference cell and on the gate of a selected cell of the array al...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com