Method and apparatus for rapidly heating printing plates
a printing plate and rapid heating technology, applied in the field of ovens, can solve the problems of large space requirements, large space requirements of conveyor ovens, and further exasperation of space limitations, and achieve the effects of reducing space limitations, reducing heat loss, and reducing heat loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
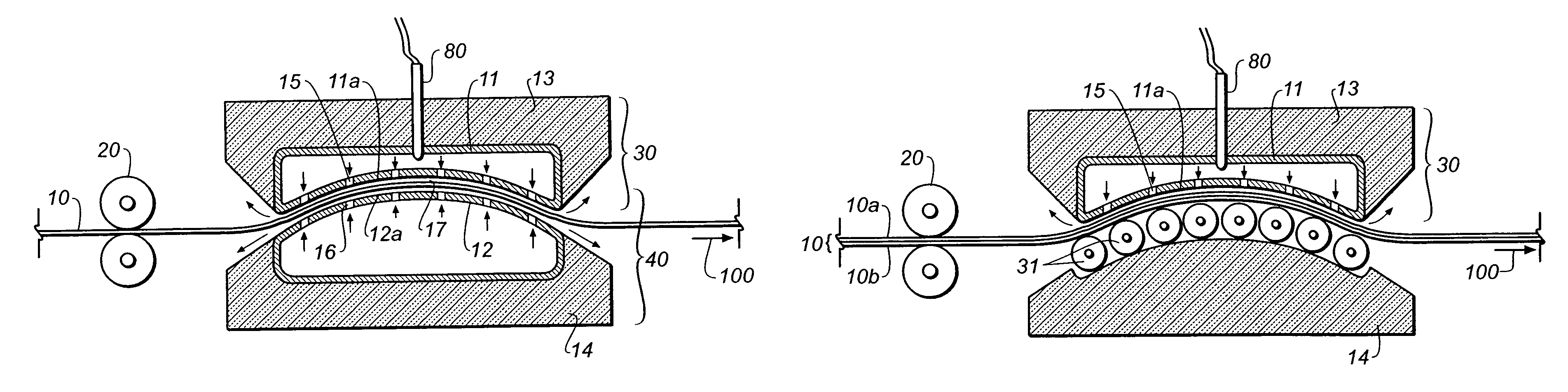
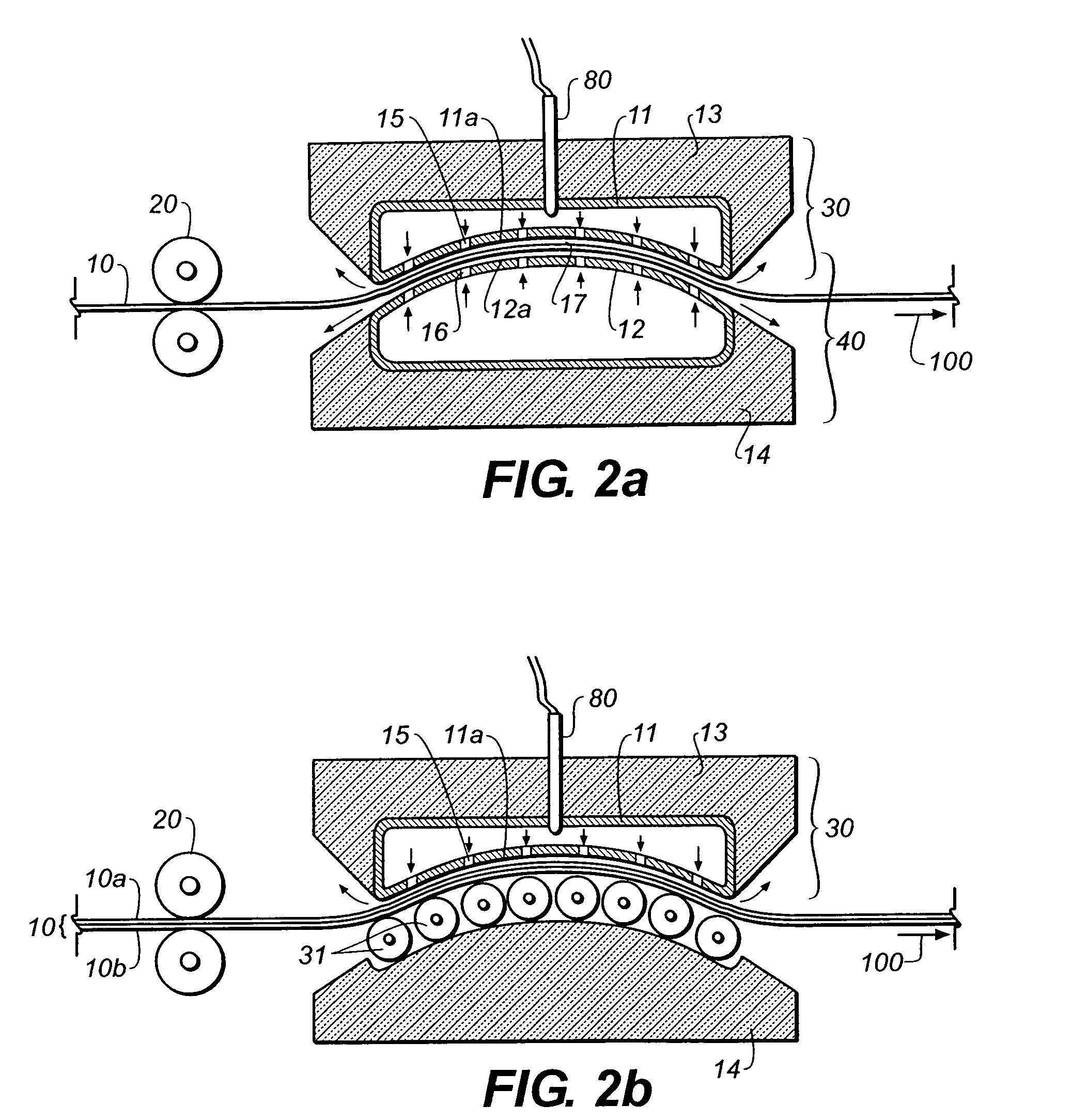
[0043]Regardless of whether a given printing plate is a “conventional” plate that is exposed through a film mask or a “digital” plate that is imaged by a CTP imager, the printing plate typically comprises a polyester or metal substrate. Further, aluminum and aluminum alloys are the preferred choice of most metal-based printing plates. Both polyester and metal printing plates are susceptible to thermal changes. Additionally, polyester is also susceptible to humidity changes. Both aluminum and polyester have coefficients of thermal expansion of approximately 20-23 μm / m / ° C. (or 20-23 parts per million (ppm) / ° C.). The coefficient of thermal of expansion is a material specific constant used to estimate the change in length or size that an object undergoes when heated or cooled from a known temperature. Required oven pre-heating temperatures are typically in range of from about 100 to about 250° C. above ambient conditions. As previously stated, the prior art has disclosed air bearing h...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com