USE OF INHALED NITRIC OXIDE (iNO) FOR IMPROVING ACTIVITY LEVELS IN PATIENTS WITH LUNG-RELATED CONDITIONS
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
tion of Precise Breath Sensitivity for Appropriate Trigger / Arming Thresholds
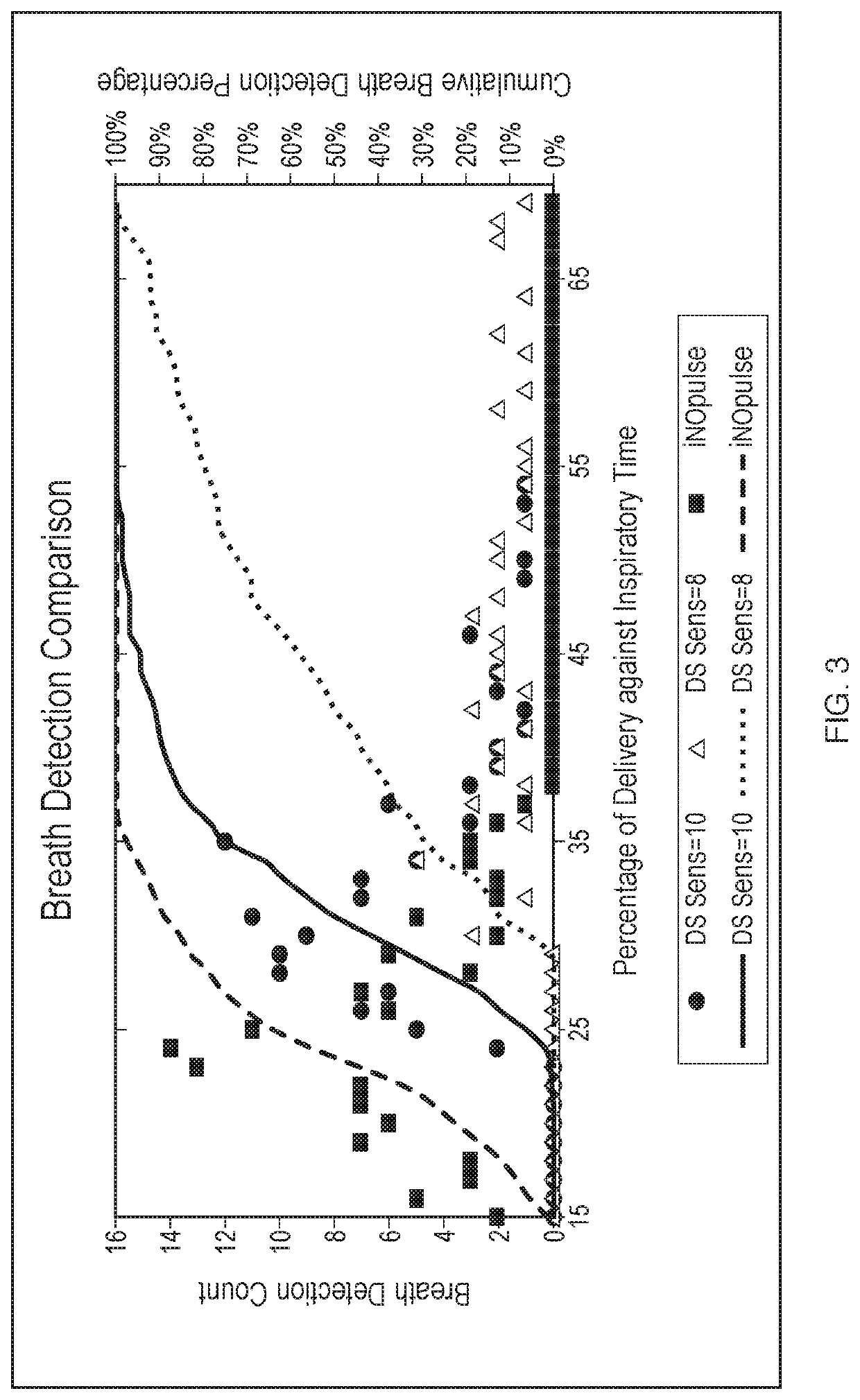
[0113]A device using a threshold algorithm to detect breaths was used in this Example (Embodiment 1). A threshold algorithm detects breaths using pressure; that is a pressure drop below a certain threshold must be met upon inspiration to detect and count a breath. That pressure threshold can be modified as a result of varying the detection sensitivity of the Embodiment 1 device. Several breath sensitivity settings were tested in the present Example. Settings from 1 to 10 were tested, with 1 being the least sensitive and 10 being the most sensitive. The trigger threshold, shown in cm H2O, is the threshold level at which nitric oxide is delivered. The arming threshold, also shown in cm H2O, is the threshold level at which the device is armed for the next delivery of nitric oxide. The data are shown below in Table 1.
[0114]Table 1, below, illustrates a data set collected in this Example. Variation in the breath ...
example 2
Device Against Various Breath Patterns
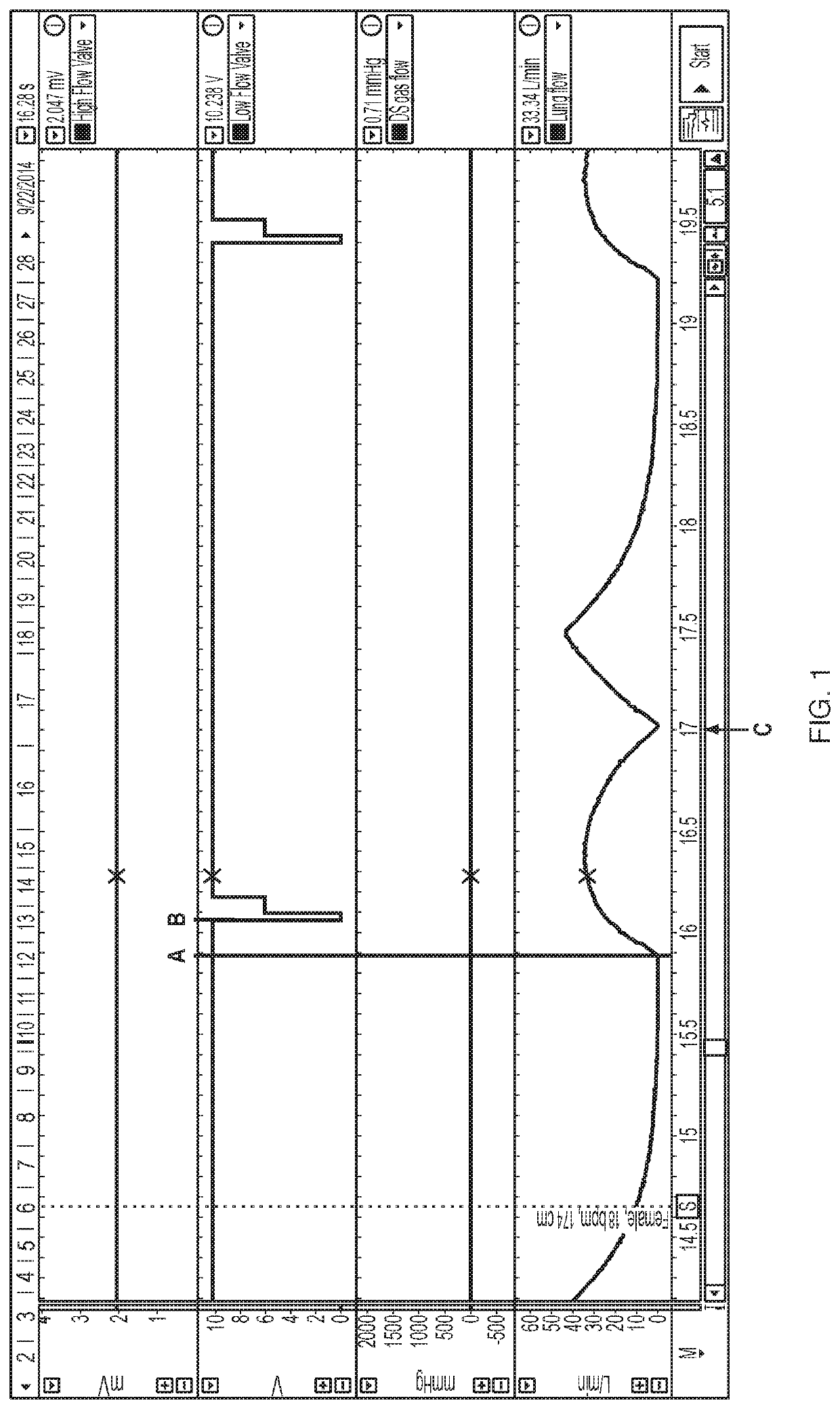
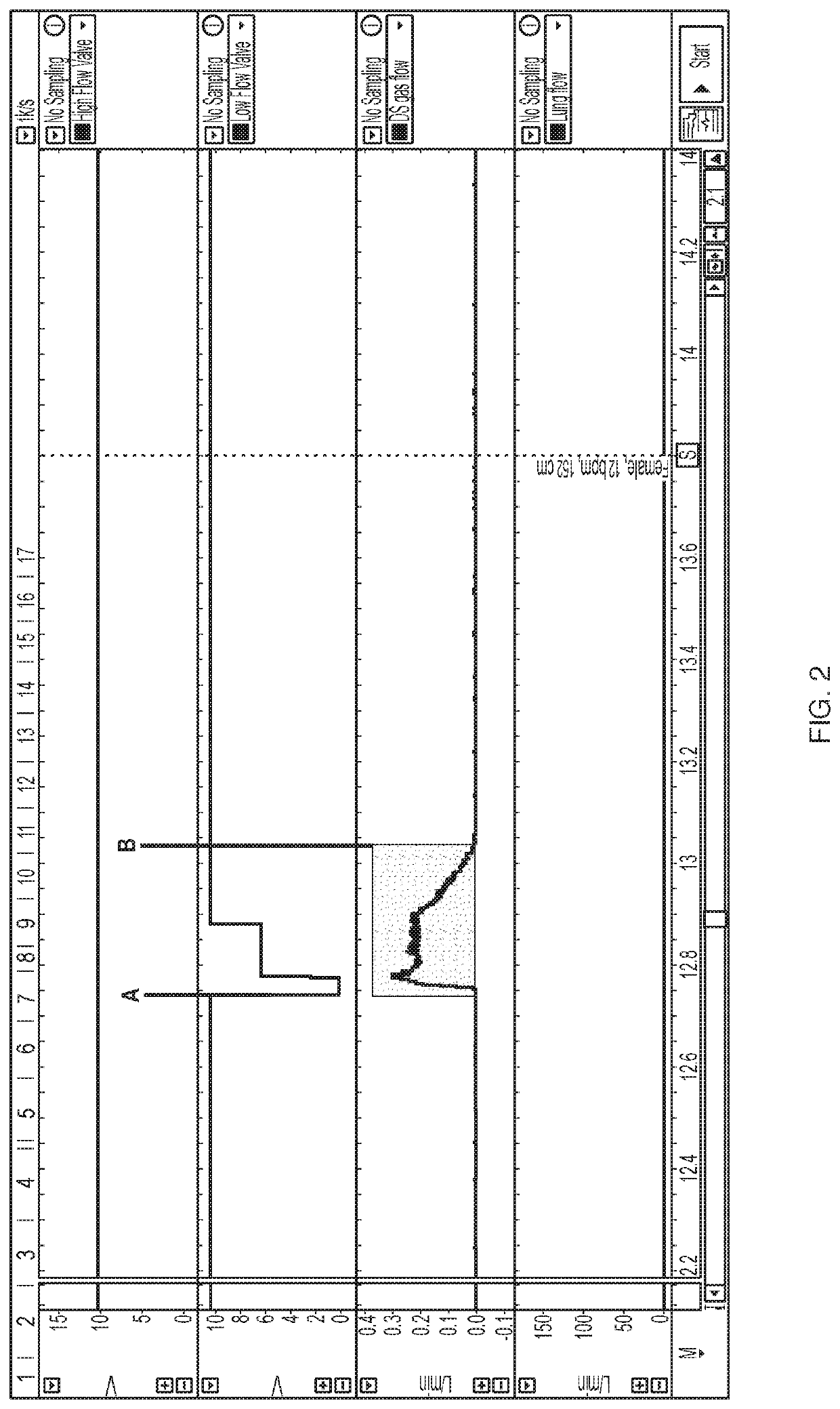
[0116]As discussed above, accurate and timely delivery of nitric oxide is critical to the present invention. In order to ensure that a device will deliver a precise dose of gas within a precise window of time, ten different breath patterns were tested using a mechanical lung and nose model. Ten different simulated breath patterns were analyzed, and the breath patterns had varying respiratory rate (8 to 36 bpm), tidal volume (316 to 912 ml), and Inspiration:Expiration (I / E) ratios (1:1 to 1:4). These variable breath patterns are patterns expected for subjects age 16 and up and are summarized in Table 2. Real world conditions were emulated to the extent possible.
TABLE 2Summary of Breath Patterns TestedTidalRespiratoryMale / HeightIdeal BodyVolumeInspirationI:ERate (bpm)Female(cm)Weight (kg)(mL)Time (sec)Ratio 8F17468.14561.51:4 8M18686.45641.51:412F15251.9316 1.251:312M18686.4564 1.251:318F17468.14561.11:218M18686.45641.11:224F15251.93161.0 1:1.524...
example 3
t of Activity Parameters in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Interstitial Lung Disease (Cohort 1)—Pulmonary Fibrosis
[0123]Patients were divided into 2 cohorts and randomized 1:1 (Cohort 1) or 2:1 (Cohort 2) for treatment:placebo. Patients were administered either 30 mcg / kg TBW / hr (iNO30, Cohort 1) or 45 mcg / kg TBW / hr (iNO45, Cohort 2) for up to 24 hours per day for a period of either 8 weeks (Cohort 1) or 16 weeks (Cohort 2). Cohort 1 comprised 41 patients and was extended to an open label phase, which is ongoing. The open label phase includes iNO patients dosed with iNO30 or iNO45. The data below represent top-line results for Cohort 1. Cohort 3 will be a pivotal Phase 3 arm using the iNO45 dose.
[0124]All patients were administered some level of background oxygen as prescribed by the treating physician for the duration of the study. Vital signs and a baseline 6MWD test were measured on Day 0, and an activity monitor was provided. Patient activity was measured th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com