Force Mitigating Athletic Shoe
a technology of athletic shoes and force, applied in the field of athletic shoes, can solve the problems of reducing the traction of the shoe/playing surface, reducing preventing non-compliance, so as to prevent the generation of injurious force, and reduce the risk of injury
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
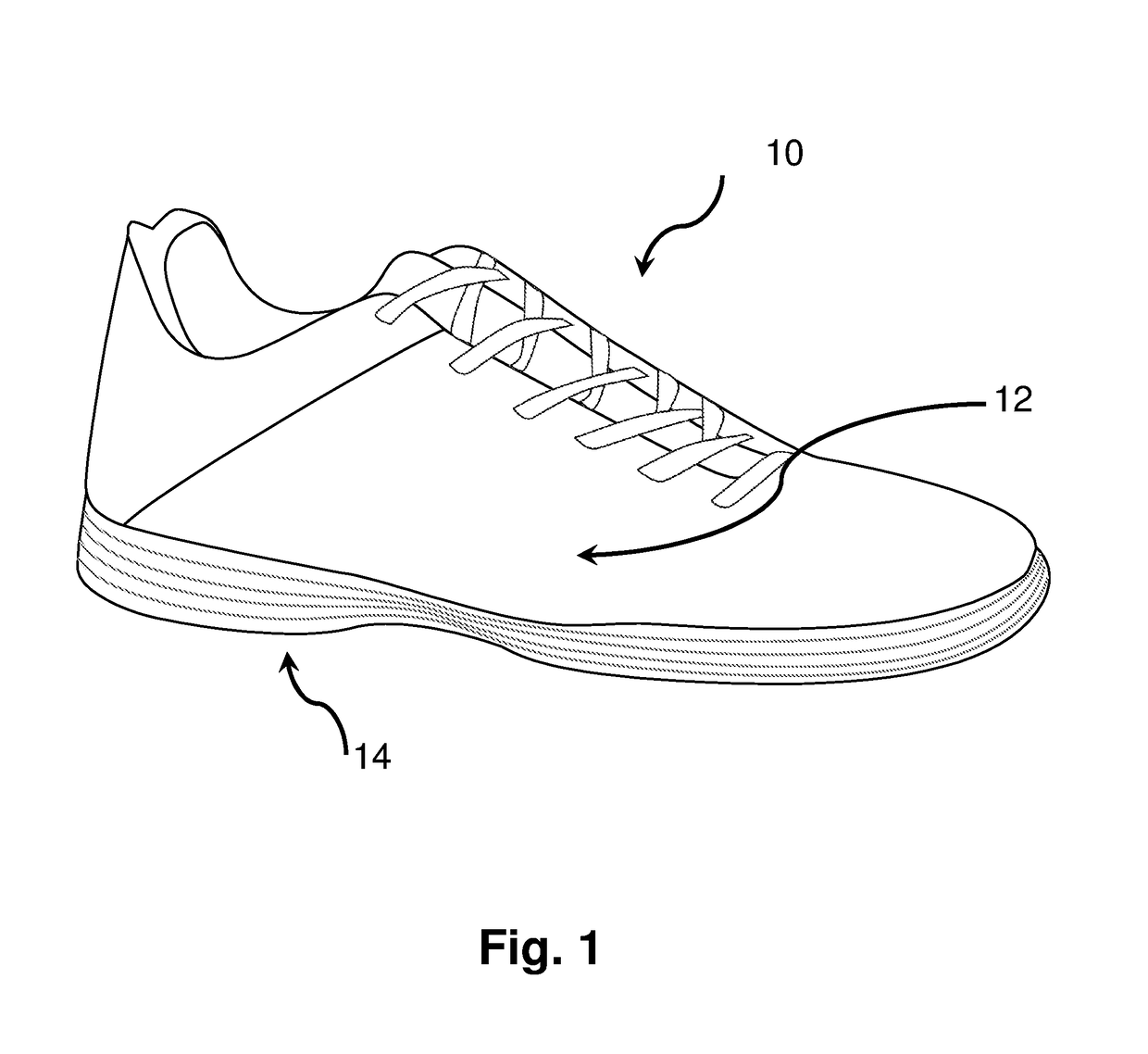
[0046]The athletic shoe 10 according to the invention is shown in FIGS. 1-8. The athletic shoe soles shown in FIGS. 1-8 are designed to protect an athlete's lower extremities against both injurious torsional [torque] forces and injurious longitudinal forces.
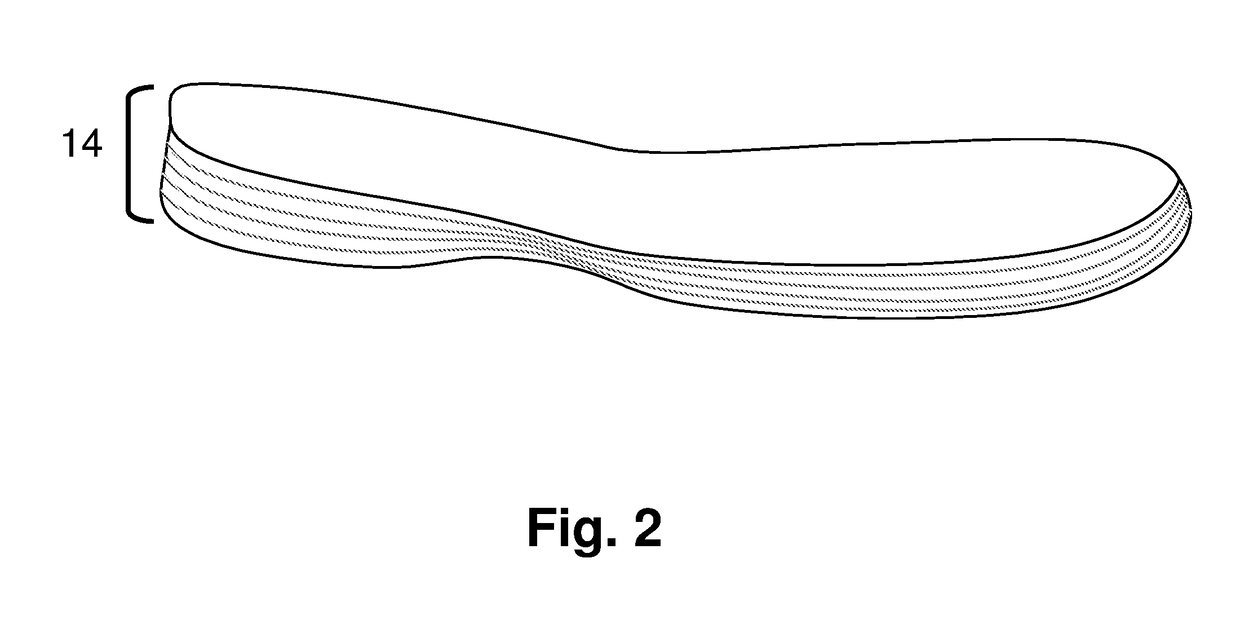
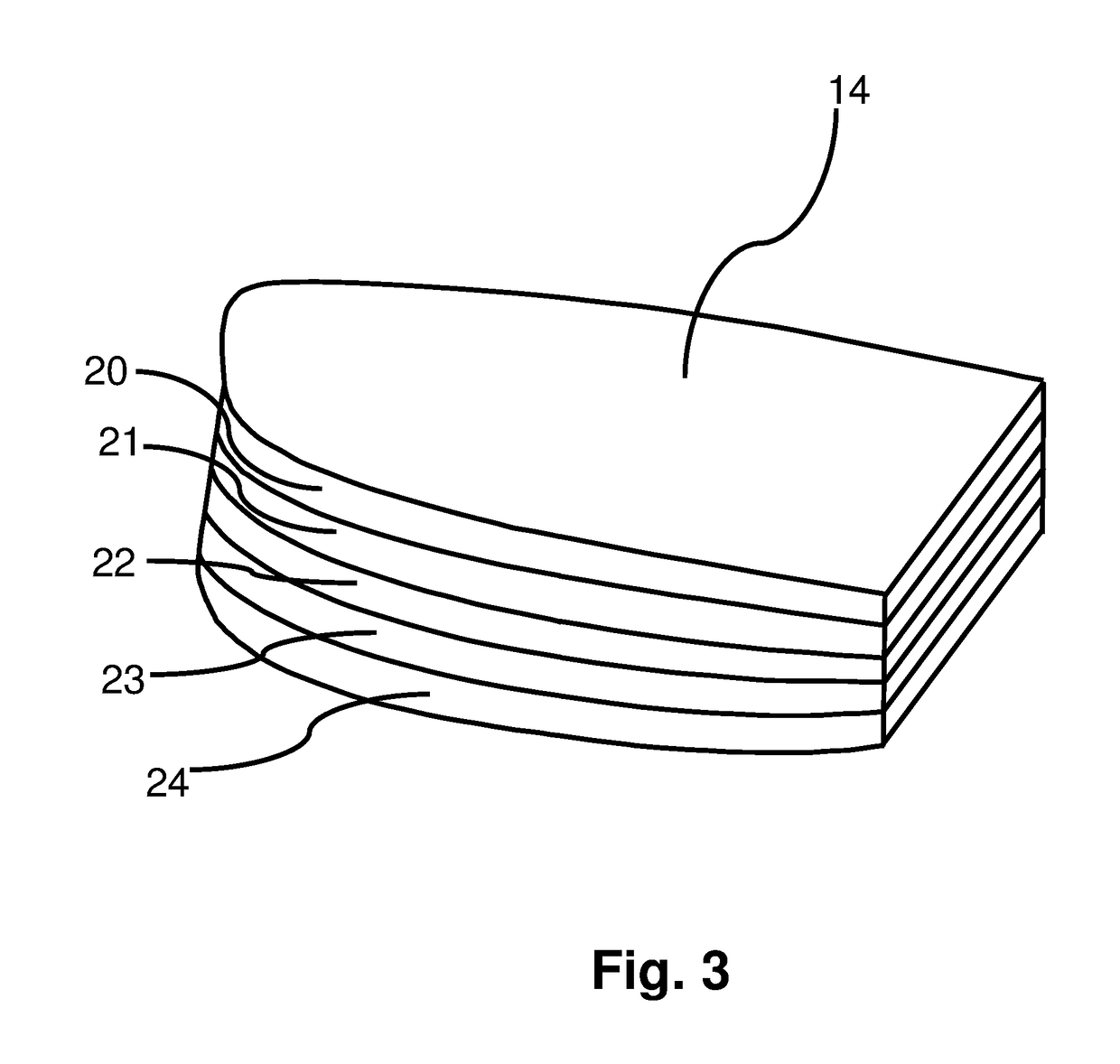
[0047]The shoe sole shown in FIGS. 1-8 comprises an upper body 12 and a multi-layer composite sole 14. Multi-layer composite sole 14 is shown in FIGS. 2-8 as comprising 5 thin layers of materials, although the exact number of layers could be more or less than 5 depending upon the specific situation the shoe is designed for. As shown in FIG. 3, sole 14 comprises layers 20, 21, 22, 23 and 24. Layers 20, and 24 are designed to provide rigid translational (straight ahead) stability during competition, like a traditional athletic shoe, only up to a pre-determined, athlete-specific, pre-injury target force threshold. These layers will also contribute limited rigidity during lateral as well as rotational (twisting) force generation. Lay...
second embodiment
[0056]FIGS. 12-14 show an athletic shoe sole constructed according to the invention. The three figures will be described together with it being understood that elements shown in one figure may or may not be shown in the other figures.
[0057]Sole 70 is a multi-layer composite sole similar in construction to the first embodiment soles shown and described above. Multi-layer composite sole 70 is shown as comprising composite layers 73, 74, and 75, although the exact number of layers could be more or less, as desired. Sole 70 comprises materials similar to those of the first embodiment. Multi-layer sole 70 has a cut-out or channel 72 incised into the outer surface of layer 73. Channel 72 is shown in the figures as being incised into the forward portion of sole 70. It should be understood that the exact placement of channel 72 can and will vary depending upon the desired force-resisting characteristics of sole 70 just as the width, depth and exact pathway of channel 72 can and will be vari...
third embodiment
[0061]FIGS. 16-23 show the invention. In this embodiment the sole is strategically weakened to provide the desired temporary deformation via inserts in the sole rather than by incising a channel in the sole. FIGS. 16 and 17 will be described together with it being understood that elements shown in one figure may or may not be shown in the other figure. It is noted that the inserts are all shown in the forward [toe] portion of the sole. Obviously, one or more inserts could be positioned in the mid portion of the sole, or even in the heel portion of the sole, if desired.
[0062]Sole 110 is a multi-layer composite sole similar in construction to the first and second embodiment soles shown and described above. The forward portion of sole 110 contains 4 inserts, 112, 112′, 114 and 114′. These inserts are made of a composite filler material similar to the sole materials described above; however, the filler material may or may not include bound fibers. The filler material of the inserts will...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pre-injury force threshold | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| force threshold | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| stability | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com