Kit for preparing sample for detecting monoclonal antibody
a monoclonal antibody and sample technology, applied in the field of kits for preparing samples for monoclonal antibody detection through mass spectrometry, can solve the problems of no technology to prove such characteristics, time-consuming and costly, and virtually impossible to provide personalized medical techniques and medications ,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
eparation Kit
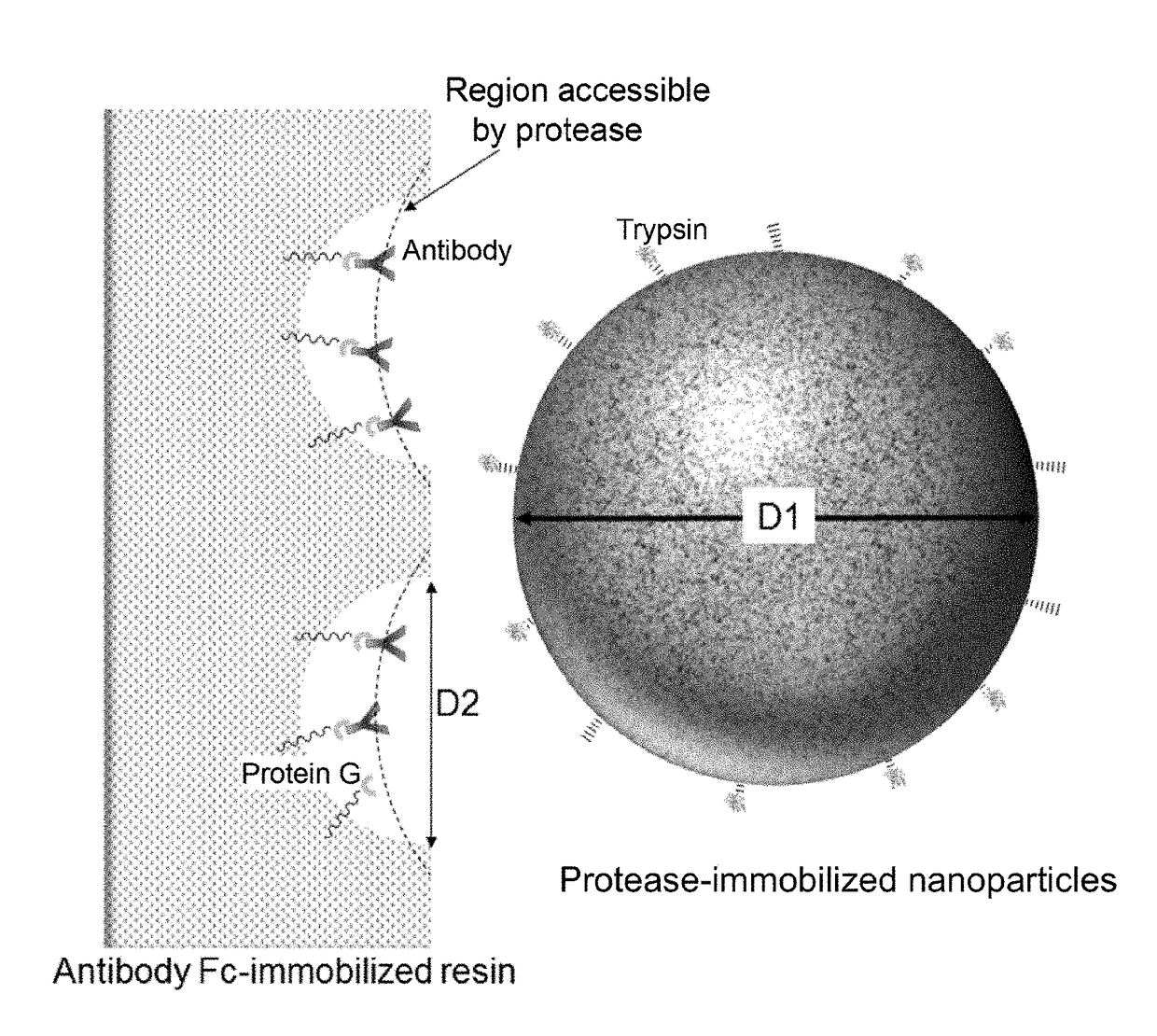
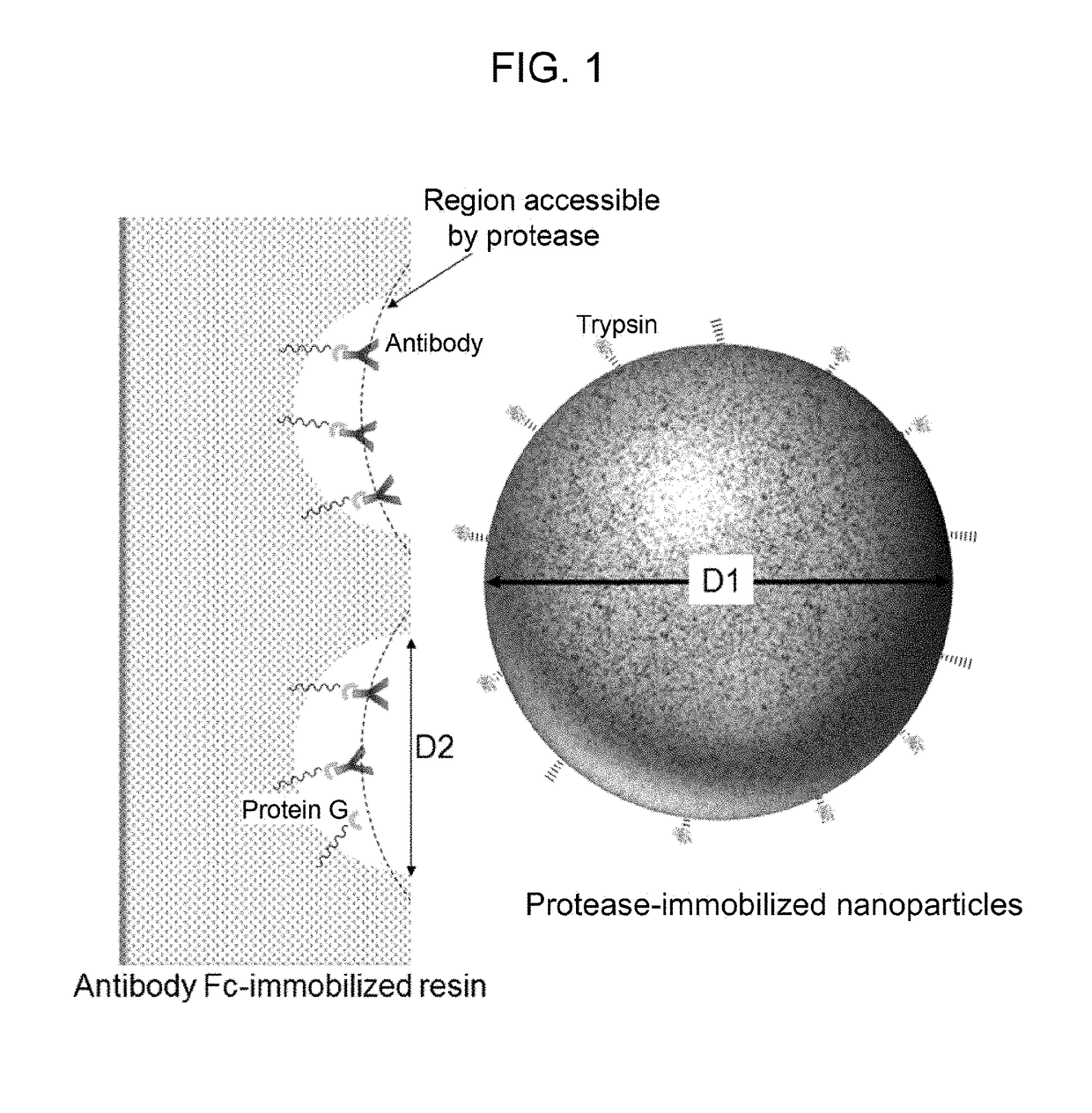
[0190]A kit structured as follows is prepared for analyzing a single sample.[0191](1) PBS buffer (PBS+0.1% n-octyl-β-D-thioglucoside, Dojindo)[0192](2) enzyme reaction buffer (25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0)[0193](3) enzyme reaction termination solution (10% formic acid)[0194](4) filter tube (low-binding hydrophilic PVDF, pore size 0.2 μm, Millipore)[0195](5) low adsorption tube (Richell Microresico® tube 92017)[0196](6) LC-MS vial, insert (Shimadzu GLC, GLC4010-VP, Target vial VP, Target Polyspring insert C4010-630P)[0197](7) porous body (Pierce Protein G UltraLink Resin 53126, 40 μL dispense)[0198](8) nanoparticles (trypsin immobilized FG beads (trypsin 40 μg))[0199](9) instructions
[0200]1. Take 20 μL of blood sample in low adsorption tube (5), and dilute it with 180 μL of buffer (1).[0201]2. Centrifuge porous body (7) using a tabletop-type centrifugal device and discard the supernatant; add 100 μL of buffer (1), gently stir and centrifuge the mixture; discard the supernatant...
example 2
n Filtration Membrane
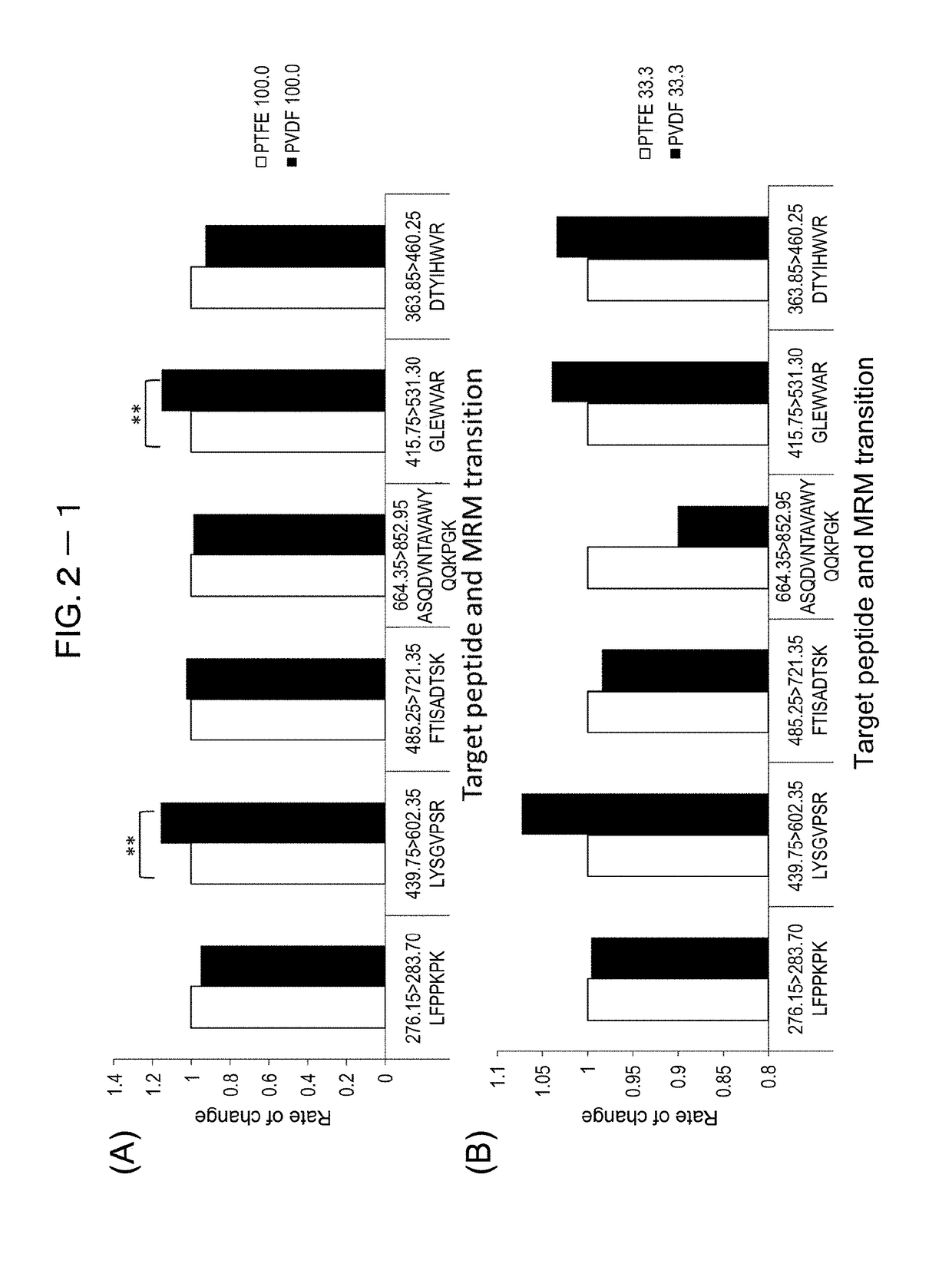
[0215]To study peptide recovery rates when different membrane materials are used for filtration, two membrane materials—polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF)—were compared.
[0216]The study on peptide recovery rates started with 100 μg / mL trastuzumab, which was then diluted by 3-fold serial dilution (N=4). Protease reaction was performed using nanoparticles with immobilized trypsin (Trypsin TPCK treated). Then, relative to peptides with known sequences (LFPPKPK (SEQ ID NO: 46), LYSGVPSR (SEQ ID NO: 21), FTISADTSK (SEQ ID NO: 3), ASQDVNTAVAWYQQKPGK (SEQ ID NO: 47), GLEWVAR (SEQ ID NO: 6), DTYIHWVR (SEQ ID NO: 5)), recovered peptides were quantified through mass spectrometry (LCMS-8040, Shimadzu Corporation). FIG. 2-1 through FIG. 2-3 show the recovery results of PVDF relative to those of PRFE (rate of variation). In significant difference testing, T-test was employed; (*) was marked for p<0.05 and (**) for p<0.01.
[0217]As a result, no ...
example 3
n Filtration Membrane
[0218]The same test as in Example 2 was conducted using bevacizumab. The results are shown in FIG. 3-1 through FIG. 3-3.
[0219]As a result, the same as in Example 2, no difference in the results was observed in recovery rates among high-concentration peptides, whereas a significant difference was evident in the recovery rates among low-concentration peptides. Accordingly, PVDF was found to be suitable as a filtration membrane.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com