Methods and Compositions for Localized Secretion of Anti-CTLA-4 Antibodies
an antictla4 antibody and localized secretion technology, applied in the field of methods and compositions for localized secretion of antictla4 antibodies, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory toxicities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0120]The 9D9 mouse anti-mouse CTLA4 antibody was typed using the IsoStrip kit from Roche diagnostics. The 9D9 antibody was determined to be IgG2b-κ (data not shown).
example 2
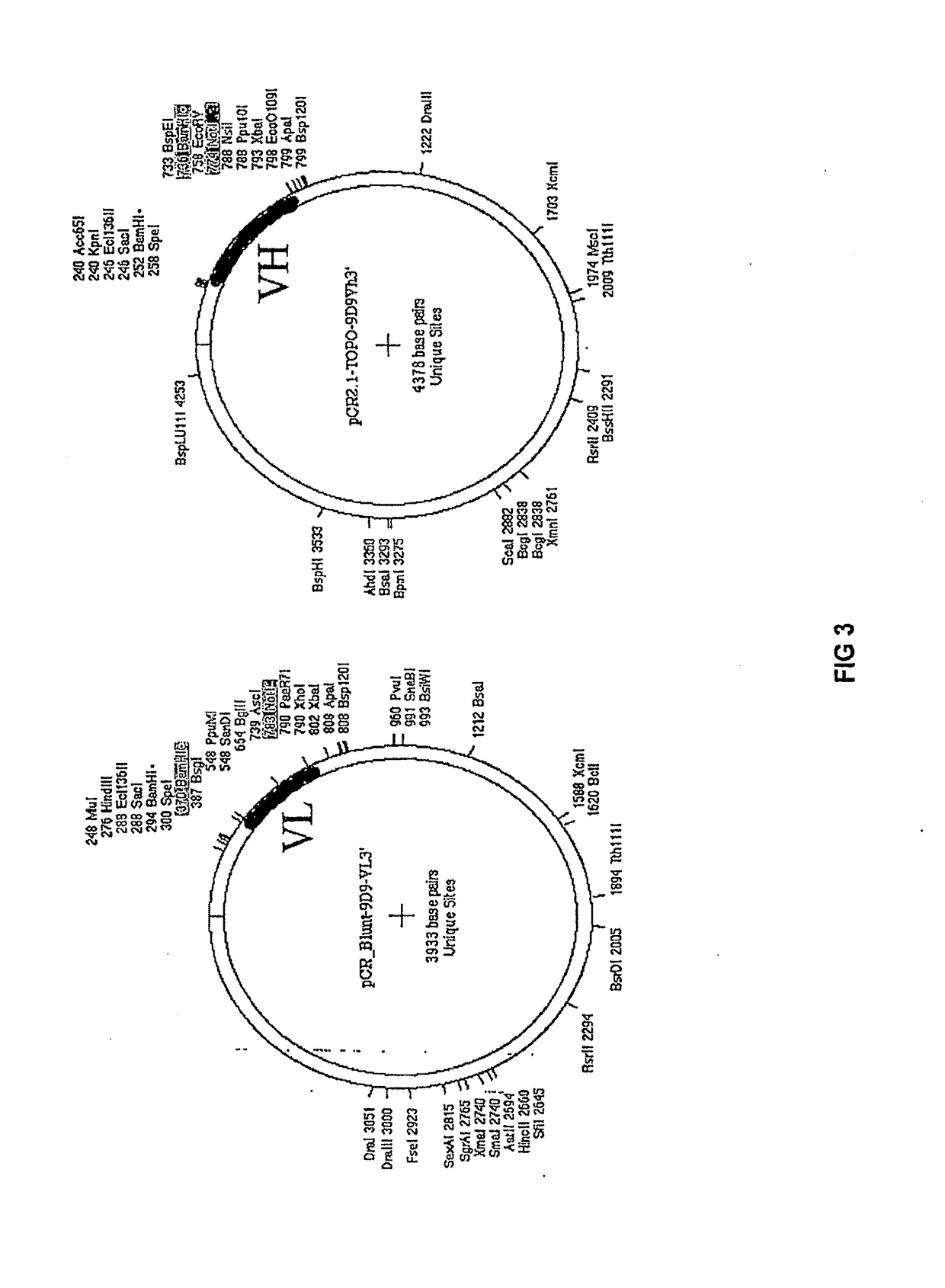
[0121]The 9D9 antibody was cloned into Ig: FIG. 1 shows the cloning strategy.
[0122]Redundant primers for the 9D9 light chain and heavy chain were designed based on Wang, Z and Ratner, D (J Immunol Methods, 2000 Jan. 13; 233(1-2):167-77) to amplify the light chain (VL) and heavy chain (VH) variable regions. PCR was performed using the Advantage 2 PCR kit from Clontech to generate products with T-A ends, and using a 3:1 mix of Vent (NEB) and Pfu (Stratagene) polymerases to generate blunt-ended fragments. FIG. 2 shows the sequences of the light and heavy chain primers.
[0123]A low, 45 degree annealing temperature was used to promote hybridization of partially mis-matched primer / template sequences. Primers were designed to contain restriction sites to facilitate subsequent cloning of the VH and VL PCR producers as well as to append a (Gly4Ser)3 linker at the tail of the VL and head of the VH for later joining.
[0124]Blunt ended PCR products were cloned using the Zero Blunt PCR Cloning Kit...
example 3
[0129]MLV-based retroviral vectors expressing the Myc-HIS tailed and the IgG1 tailed versions of the 9D9 scFv were used to make 293T cells stably expressing each of the scFv molecules. FIG. 5 shows the expression vector used for production of the myc-HIS tailed 9D9 scFv molecule, and FIG. 6 shows the expression vector used for production of the IgG1 tailed version of the 9D9 scFv molecule.
[0130]Supernatants from these cells were collected and used to stain DT230 cells (a mouse L-cell line which expresses high levels of surface CTLA4). scFv bound to the surface of these cells was quantitated using an anti-mouse-PE secondary antibody and analyzed by flow cytometry on a Cyan-LX (Dako-Cytomation).
[0131]FIGS. 12 and 13 show CD specta of scFv antibodies against DT230 cells expressing surface CTLA-4 protein.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| nucleic acid | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| affinities | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com