Methods for Nuclear Reprogramming Using Synthetic Transcription Factors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
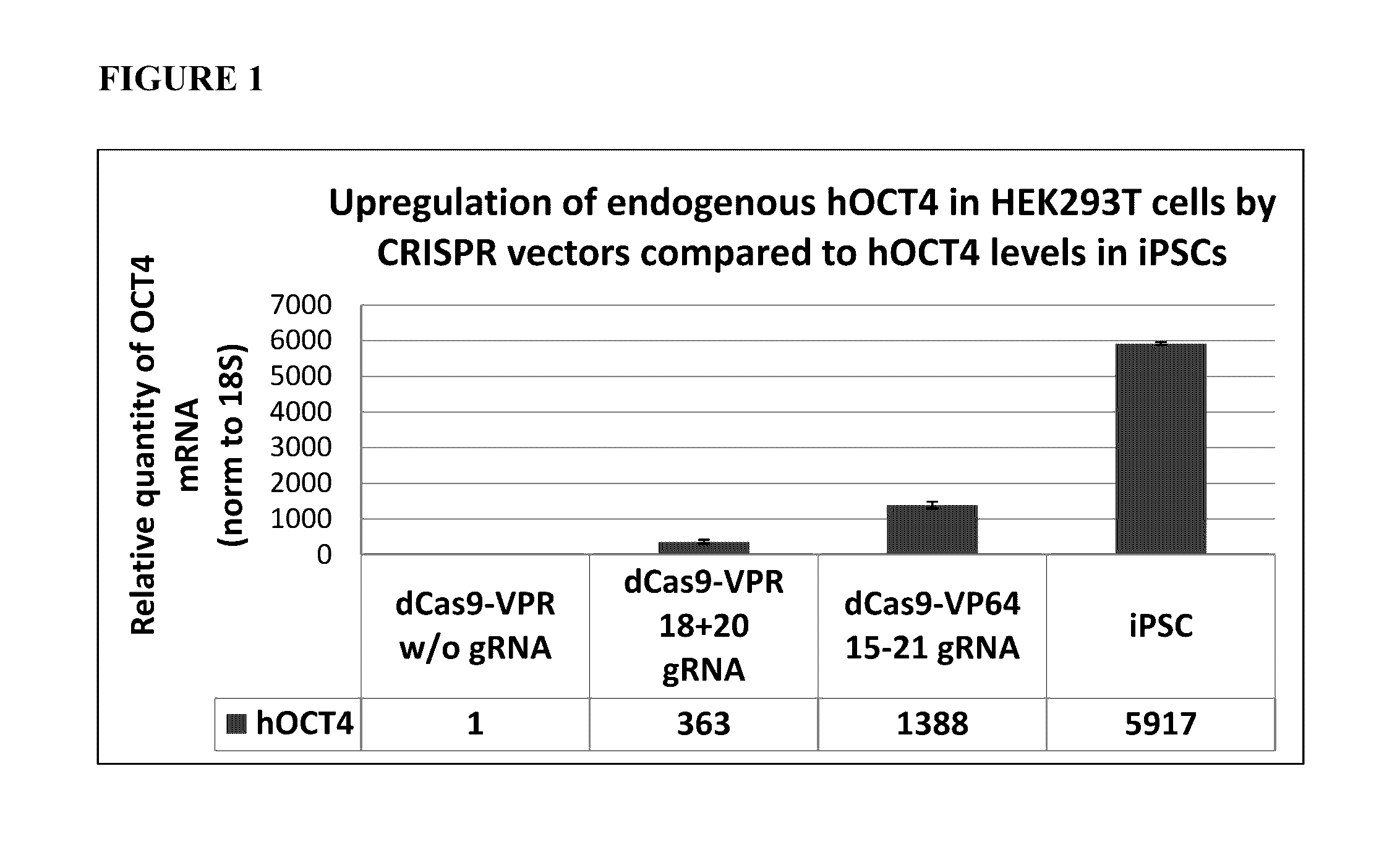
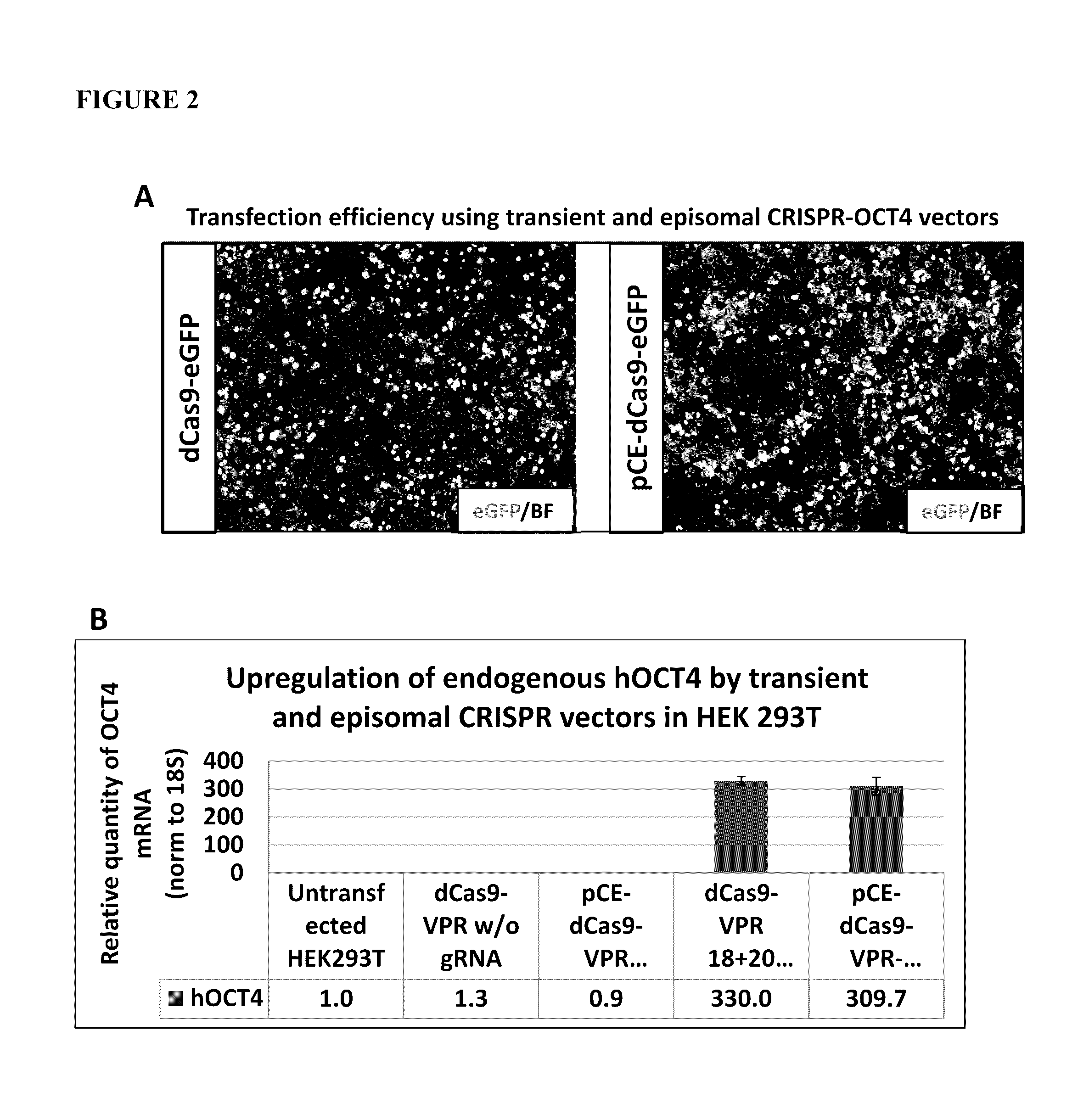
Reprogramming Rescue by Endogenous Activation of the Human POU5F1 / OCT4 Gene Transcription (CRISPR-Based Reprogramming)
Vector Sequences
[0174]DNA sequences for dCas9, dCas9-VP64 and guide RNA constructs were prepared as described in Mali, P. et al. “CAS9 transcriptional activators for target specificity screening and paired nickases for cooperative genome engineering.”Nat Biolechnol 2013, 31(9): 833-8, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein in its entirety. Additional sequences for gRNAs containing MS2 binding loops and the MS2-transcriptional regulator fusion proteins (e.g. MS2-VP64) were prepared as described in Konermann et al., Nature 2015, 517: 583-588 (and supporting material), the disclosure of which is incorporated herein in its entirety. Sequences were synthesized by GeneART and cloned into episomal cloning vectors. These vectors were used directly in the following experiments.
[0175]Selection of gRNA for Human POU5F1 / OCT4 Transcription Activation
[0176]Human peripheral...
example 2
Reprogramming Rescue by Endogenous Activation of the Human OCT4 Gene Transcription (CRISPR-Based Reprogramming)
Vector Sequences
[0187]DNA sequences for dCas9-VPR consisting of VP64-p65-Rta activation domains fused to the C-terminus of dCas9 protein and guide RNA constructs were prepared as described in Mali, P. et al. (Mali, P. et al. “CAS9 transcriptional activators for target specificity screening and paired nickases for cooperative genome engineering.”Nat Biotechnol 2013, 31(9): 833-8) and Chavez, A. et al. (Chavez, A. et al. “Highly efficient Cas9-mediated transcriptional programming.”Nat Methods. 2015 April; 12(4):326-8). Sequences were synthesized by GeneART and cloned into standard cloning vectors. These vectors were used directly in the following experiments.
Determining gRNA Combination for Human OCT4 Transcription Activation
[0188]HEK293T cells were transfected with various combinations of transient Cas9-VPR and gRNA encoding vectors (see Table 1). The plasmids were co-transf...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com