Methods for improving gut health
a gut health and gut technology, applied in the field of gut health promotion or improvement, can solve problems such as intestinal problems, and achieve the effect of reducing protein flow and reducing protein flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0077]The following examples are included to demonstrate various embodiments of the invention. It should be appreciated by those of skill in the art that the techniques disclosed in the examples represent techniques discovered by the inventors to function well in the practice of the invention. Those of skill in the art should, however, in light of the present disclosure, appreciate that many changes can be made in the specific embodiments that are disclosed and still obtain a like or similar result without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention, therefore all matter set forth is to be interpreted as illustrative and not in a limiting sense.
examples 1-4
[0078]Experimental models for producing NE generally have drawn from field experience linking its occurrence to coccidiosis challenge, diets containing a high content of poorly digestible non-starch polysaccharides (NSP) found in cereal grains, and diets containing fishmeal and animal protein. Models for inducing NE in chickens generally include a multiday challenge with actively replicating C. perfringens (Cp). The following examples were designed to exclude Cp challenge so that factors that trigger the growth of Cp, which are already present in the hindgut of day old chicks, could be analyzed. Thus, by studying subclinical enteritis, it may be possible to elucidate factors that can tip the balance of the relationship between microbiota and host to either positively or negatively impact overall gut health.
example 1
Effect of NSP Enzymes on Gut Health in Broilers Fed a Rye-Wheat Diet
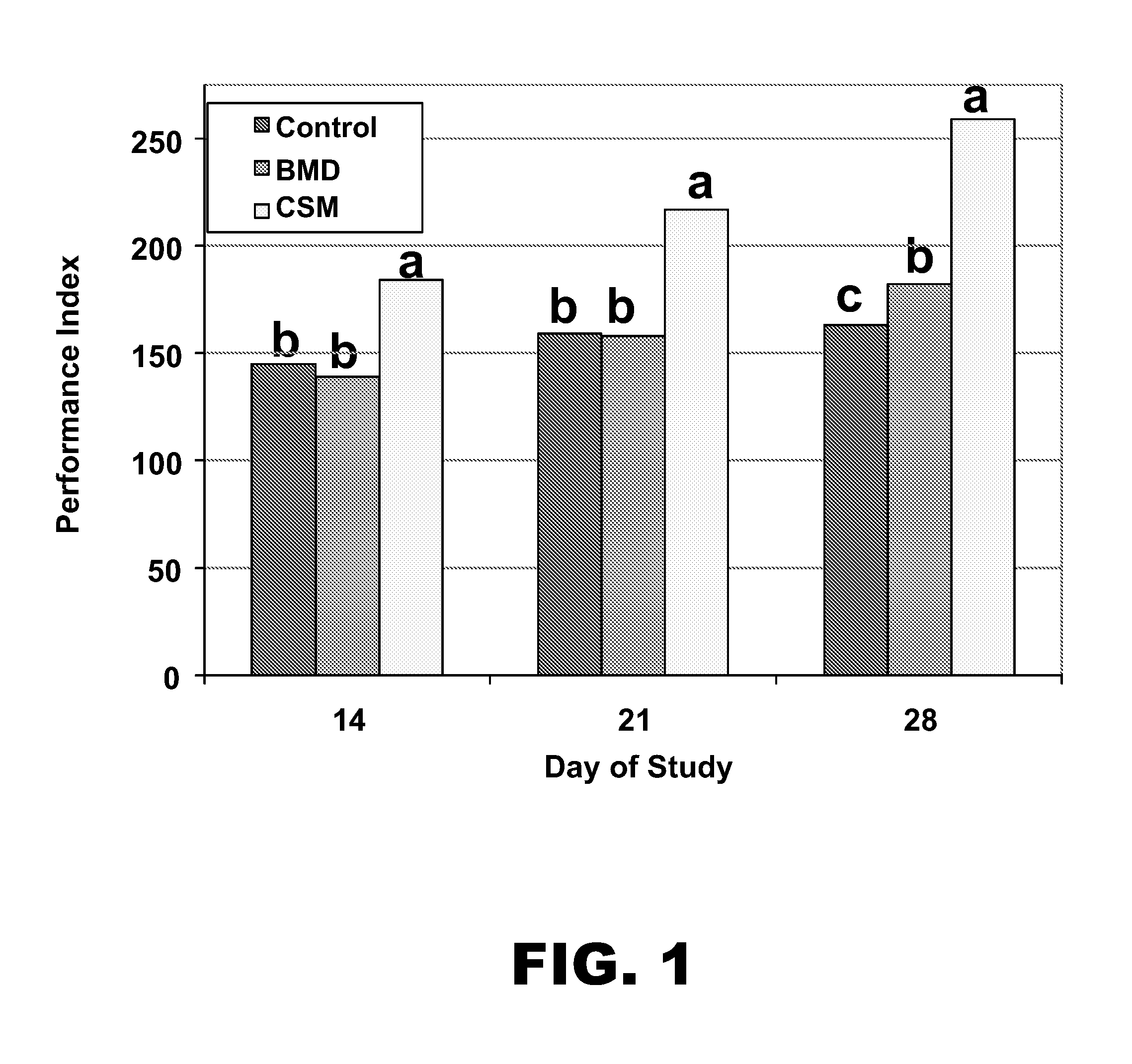
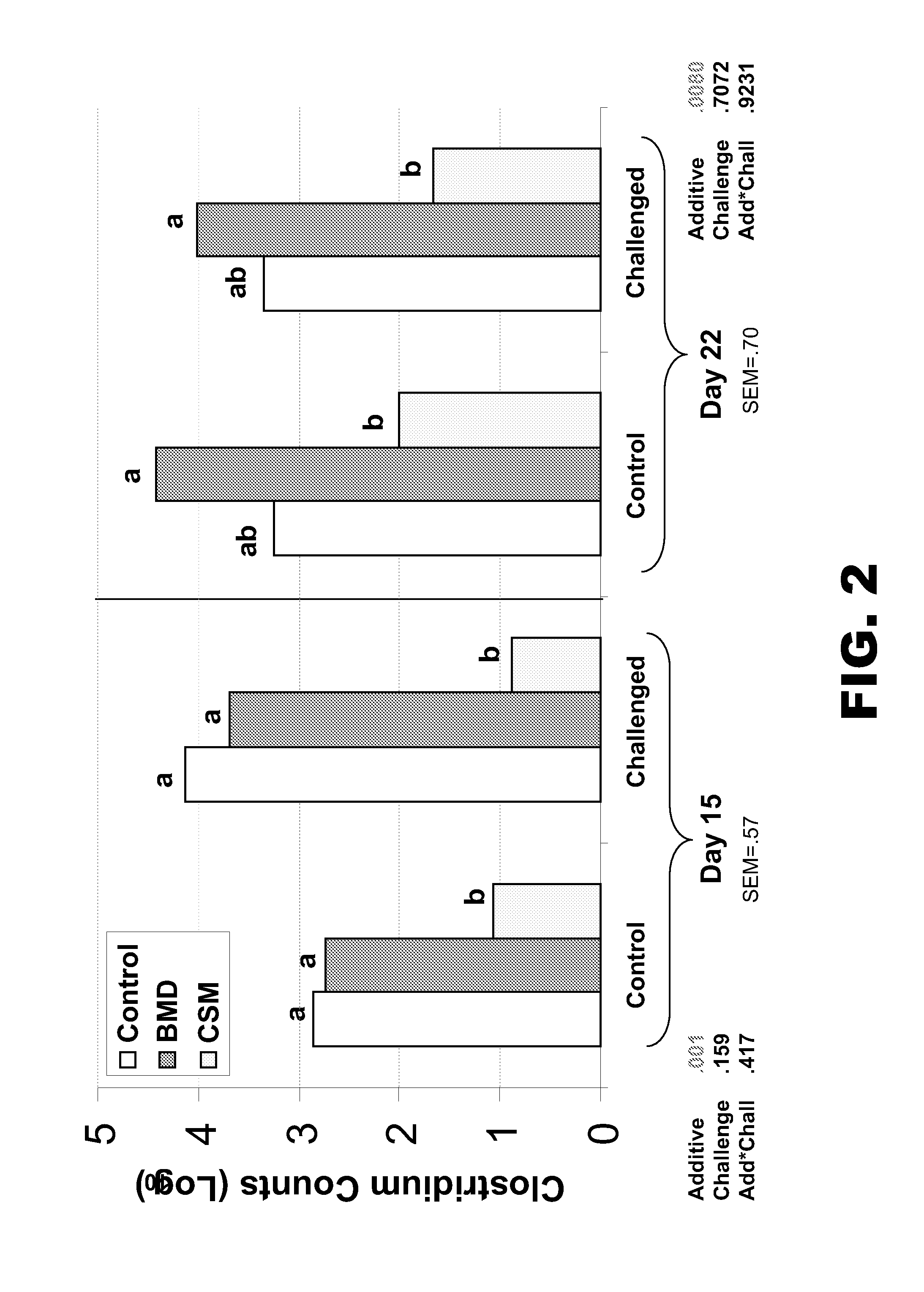
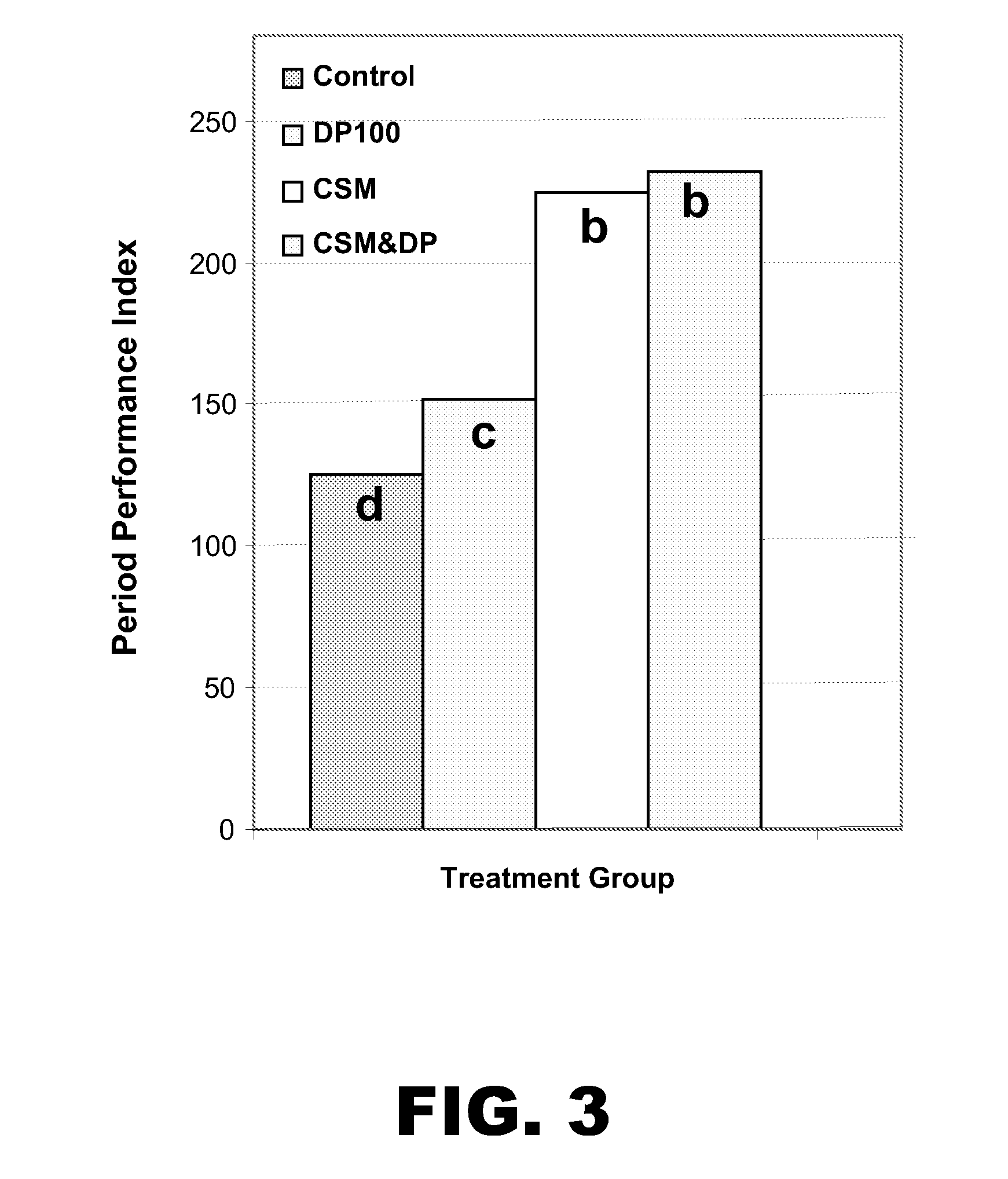
[0079]The objective of the following example was to study the effects of several feed additive treatments to improve gut health in chickens fed a diet containing rye and wheat as a cereal source and exposed to a coccidiosis challenge.
[0080]The diet was a 22% crude protein (CP), 1.21% / 1.07% total / digestible lysine mash diet containing 33% rye, 25% wheat, and 31% soybean meal. The feed additives were none (control), an antibiotic (bacitracin methylene disalicylate (BMD); 60 ppm) and an NSP enzyme mixture containing xylanase, glucanase, and glycosidase (sold under the tradename CIBENZA™ CSM by Novus International, Inc.; 500 mg / kg). Half of each group was challenged (on day 0) with cycling Eimeria as a 3× overdose of a 3-species live oocyst vaccine (available under ADVENT® from Viridus Animal Health, LLC). Body weights were taken on days 14, 21, and 28; Cp counts were taken on days 14 and 21; digesta viscosity was measu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| digestibility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| digestible | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com