Marine Engine Lubrication
a technology for marine engines and lubricating fluids, applied in the direction of non-fuel substance addition to fuel, liquid carbonaceous fuels, base materials, etc., can solve the problems of crack formation and propagation through the piston, and crankcase explosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0085]The present invention is illustrated by but in no way limited to the following examples.
Components
[0086]The following components were used:
Ester Basestocks (A1)
[0087]a polyol ester (PRIOLUBE® 3970), a trimethylolpropane ester with C8-10 fatty acids, having a viscosity of 4.4 mm2s−1 at 100° C., ex Croda Lubricants;[0088]a polymer ester (KETJENLUBE® 115), in the form of a copolymer of alpha-olefins and a dicarboxylic acid dibutylester with an average molecular weight of approximately 1400.
Basestocks (A2)
[0089]a Group I oil (XOMAPE 600) (for comparison)
[0090]a Group II oil (RLOP 600)
[0091]a Group III oil (YUBASE 8)
[0092]Commercial identifications are in parentheses.
Detergents (B)
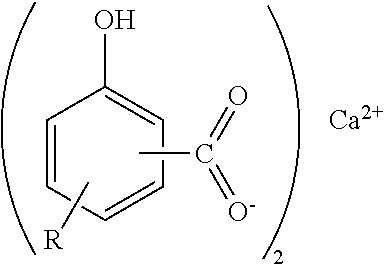
[0093]calcium alkyl salicylate (BI 8.0)
[0094]calcium alkyl salicylate (BI 3.0)
Basicity indices are in parentheses.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| mass % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| kinematic viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| kinematic viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com