System, method and apparatus for tolerance ring control of slip interface sliding forces
a technology of tolerance rings and sliding forces, applied in the field of tolerance rings, can solve problems such as increasing frictional forces, and achieve the effect of reducing radial stiffness and resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
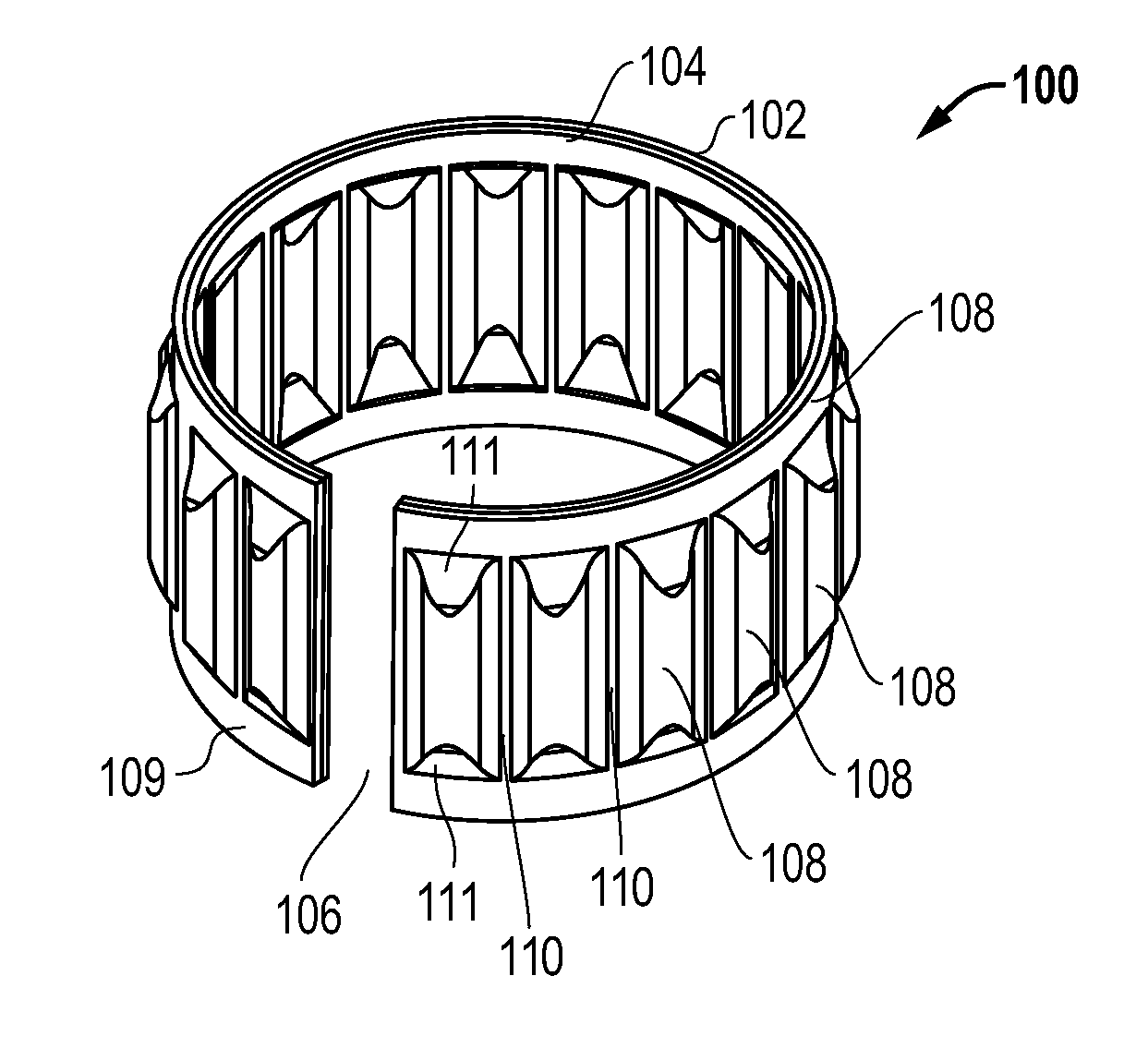
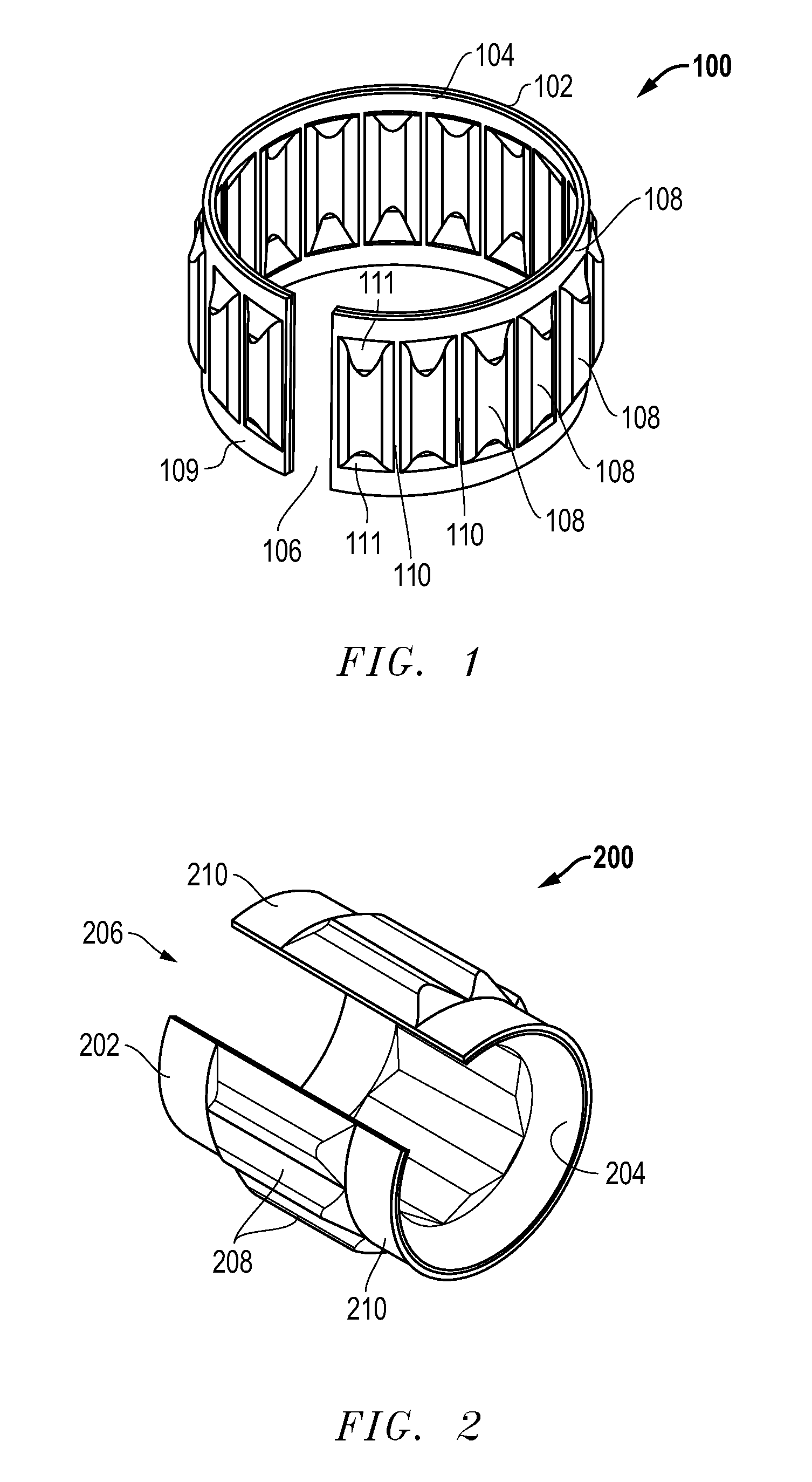
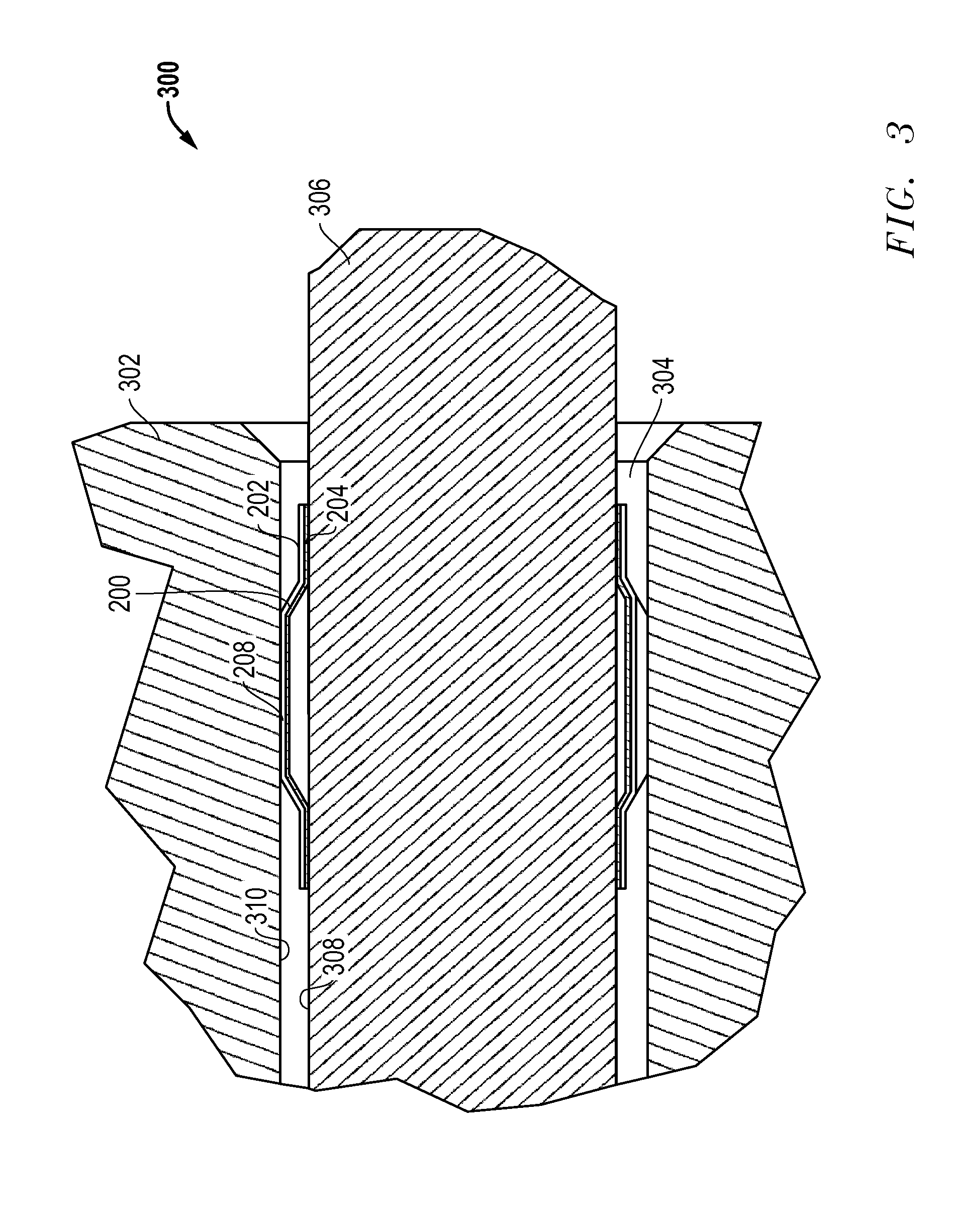
[0018]FIG. 1 depicts a tolerance ring 100 comprising one embodiment. The tolerance ring 100 comprises a band 102 of resilient material (e.g. spring steel) that is curved into a ring-like (substantially annular) shape. The ends of the band 102 do not meet (e.g., it may be formed as a split ring), thereby leaving an axially-extending gap 106 adjacent the circumference of the band. In other embodiments, the band may be curved so that the ends overlap with one another. In yet further embodiments, the band may be a continuous, unbroken ring. The inner surface of the tolerance ring 100 has a low friction layer 104 that conforms to the shape of the band.
[0019]The tolerance ring 100 has a plurality of spaced projections 108 that extend radially outward from the outer surface of the tolerance ring 100. There is a flat, circumferentially-extending rim 109 of material at each axial end of the projections 108. Each projection 108 also is separated from its neighboring projections by a flat sect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com