Robotic Surface Treatment Device
a robotic surface and treatment device technology, applied in the field of robotic surface treatment devices, can solve the problems of ineffective development of a robotic surface cleaning system that can clean any hard surface (e.g. concrete, tiles, vinyl, hardwood, etc., and remains difficult to achieve, and the ability of commercially available, robotic or manual (local or controlled), surface cleaning systems that are commercially available for domestic or industrial surface cleaning applications is extremely limited in comparison to common, hand-held mops, commercially available,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029]For purposes of the description hereinafter, the terms “upper”, “lower”, “right”, “left”, “vertical”, “horizontal”, “top”, “bottom”, “lateral”, “longitudinal”, and derivatives thereof shall relate to the invention as it is oriented in the drawings. However, it is to be understood that the invention may assume alternative variations and step sequences, except where expressly specified to the contrary. It is also to be understood that the specific devices and processes illustrated in the attached drawings, and described in the following specification, are simply exemplary embodiments of the invention. Hence, specific dimensions and other physical characteristics related to the embodiments disclosed herein are not to be considered as limiting.
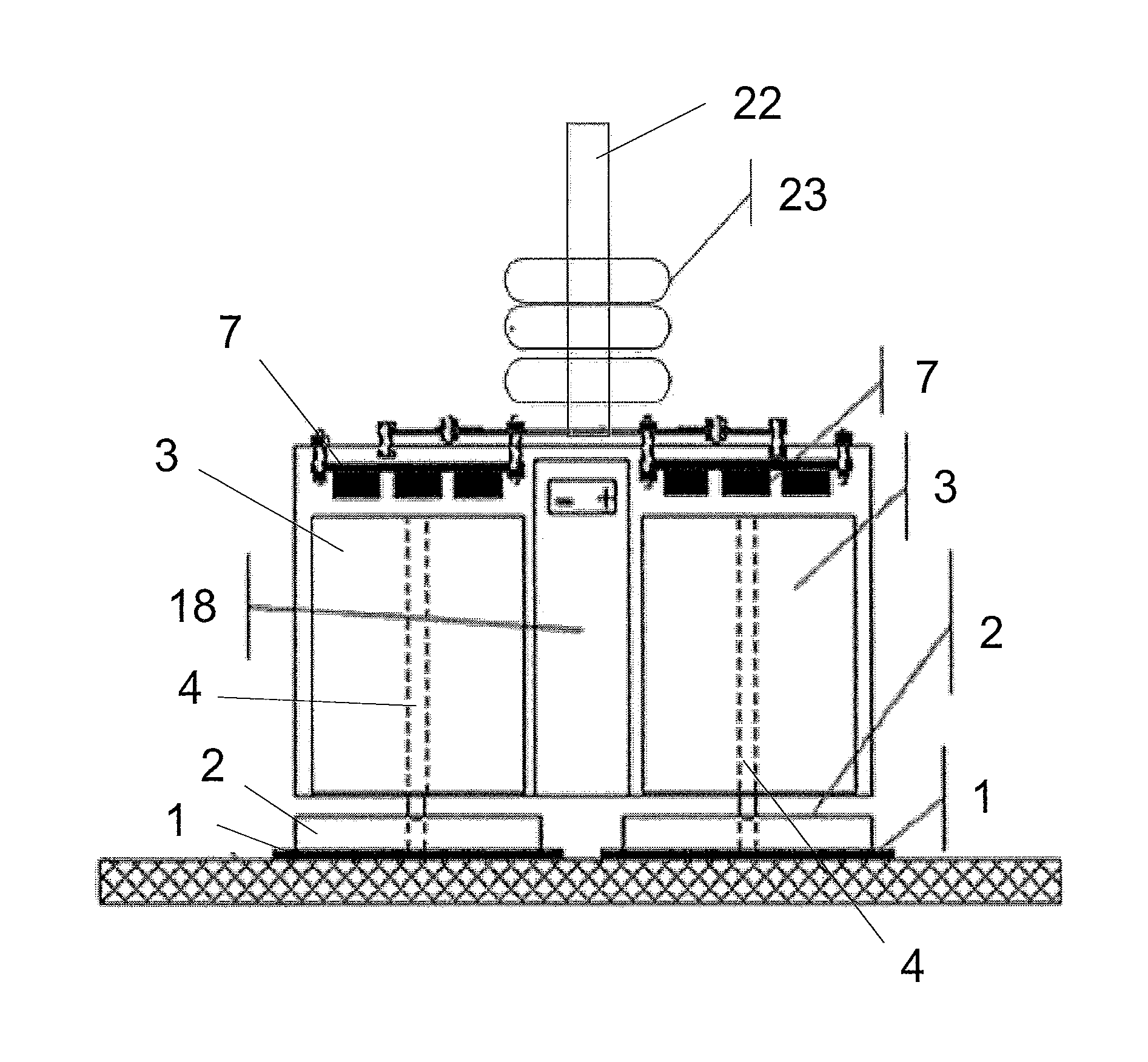
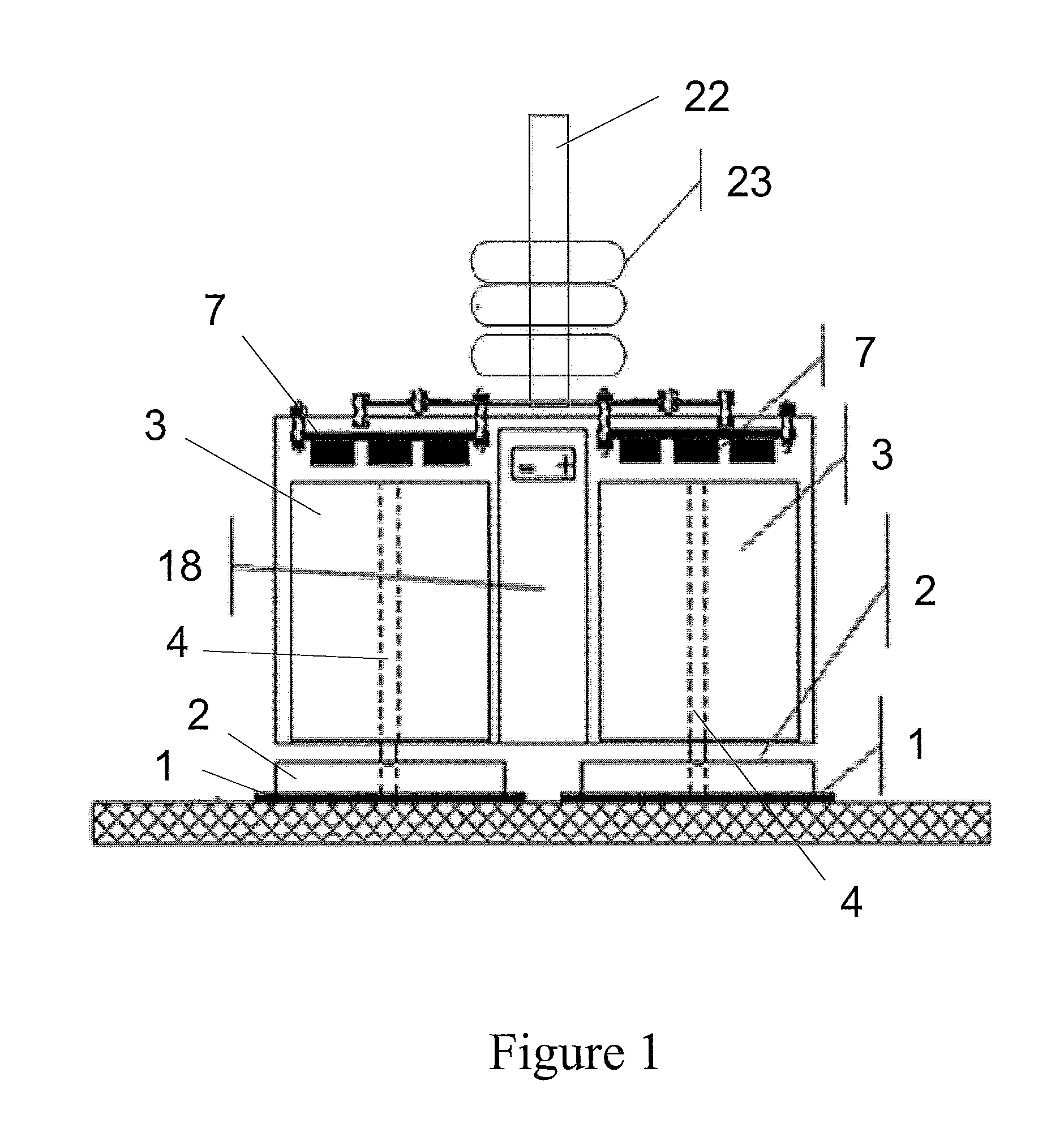
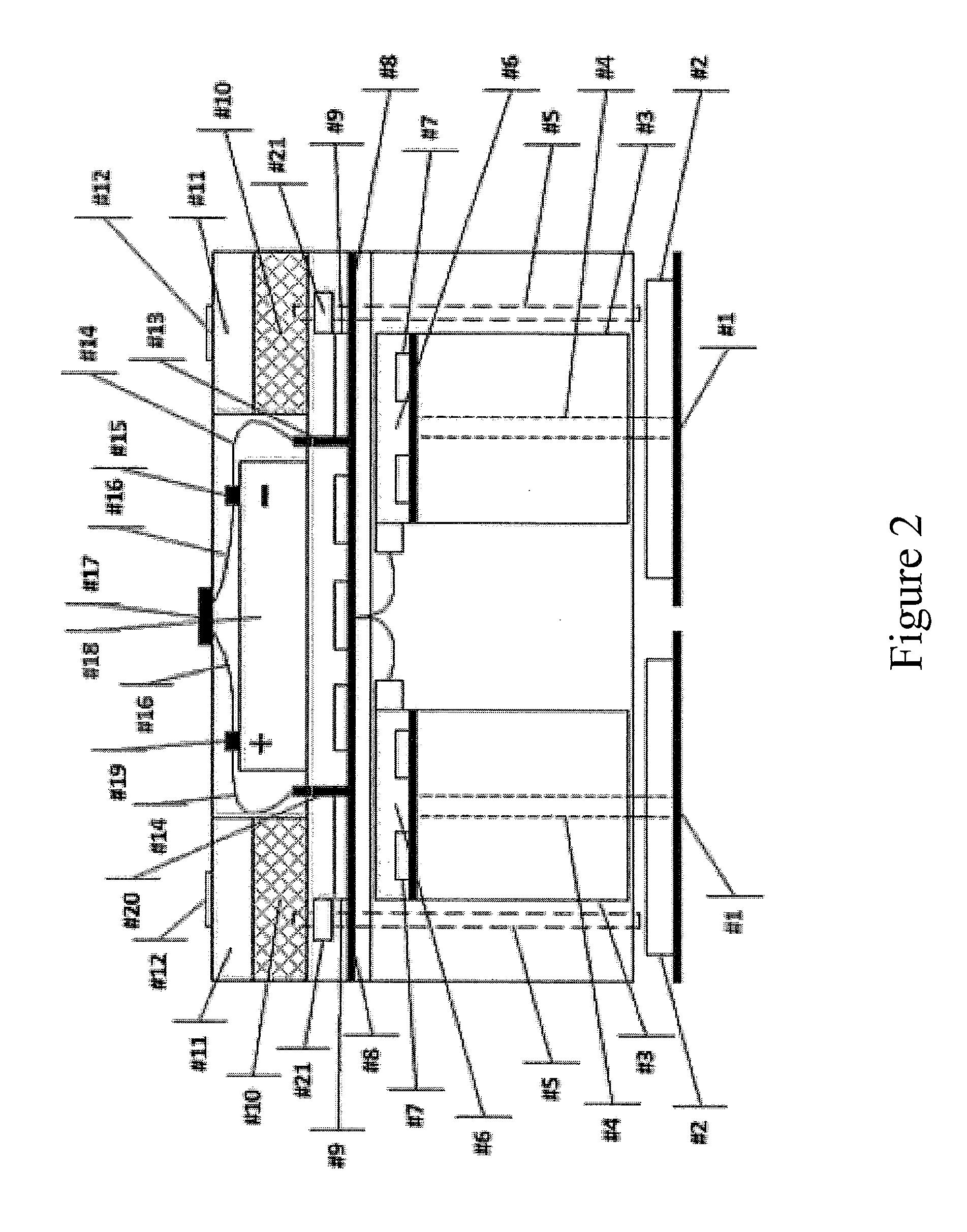
[0030]The present invention is directed to, in general, a robotic surface treatment device and, in particular, a robotic surface treatment device with floor pads rotationally actuated to treat a surface. Certain preferred and non-limiting em...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com