Wind turbine and vibration damping method thereof
a technology of wind turbine and vibration damping, which is applied in the direction of rotors, vessel construction, marine propulsion, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the fatigue load of a structural material reducing the life of the wind turbine, and the vibration induced by the fluctuation of the wind speed flowing into the wind turbine cannot be ignored, so as to achieve a large damping effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
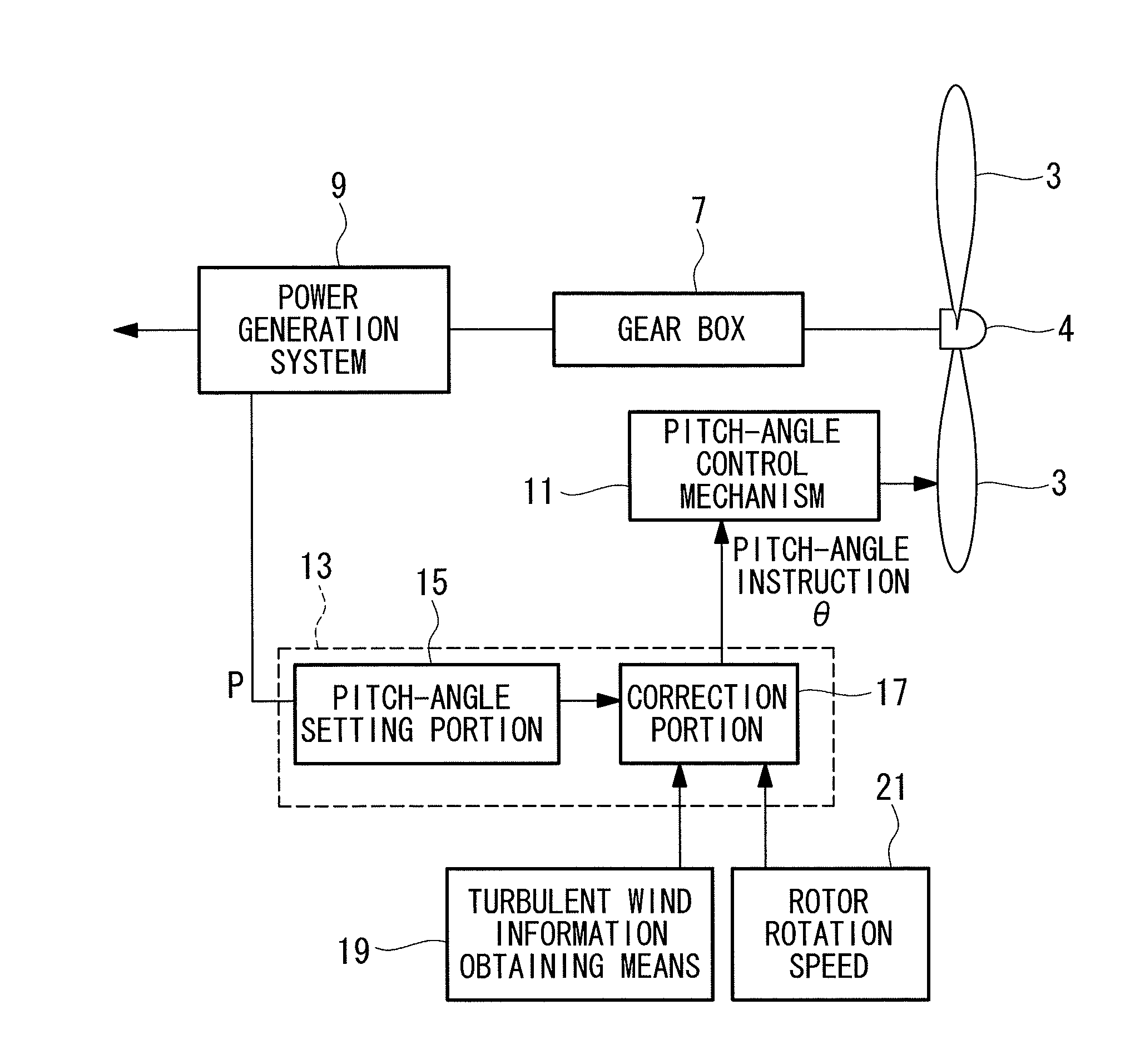
[0043]An embodiment according to the present invention will be described below by referring to the attached drawings.
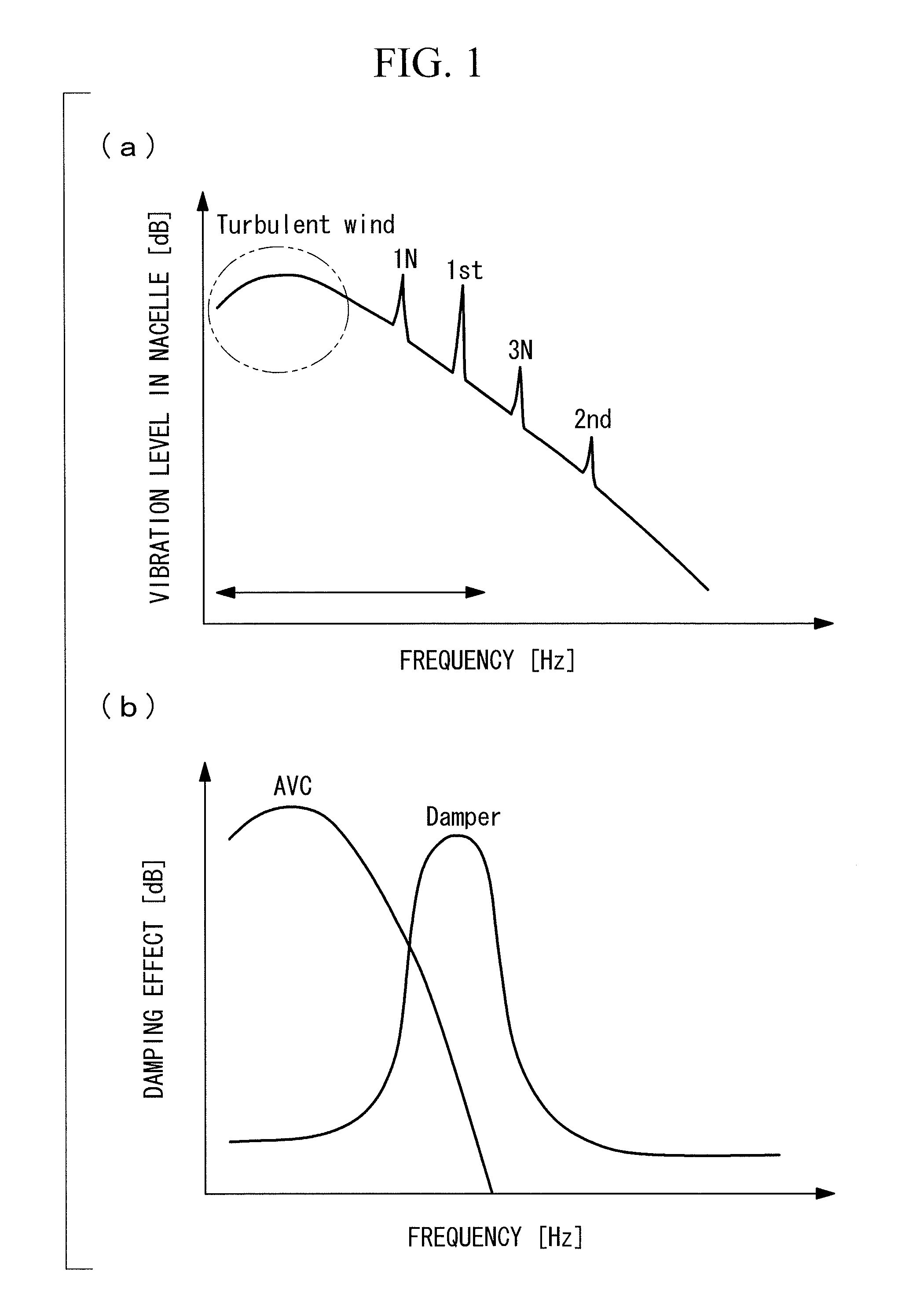
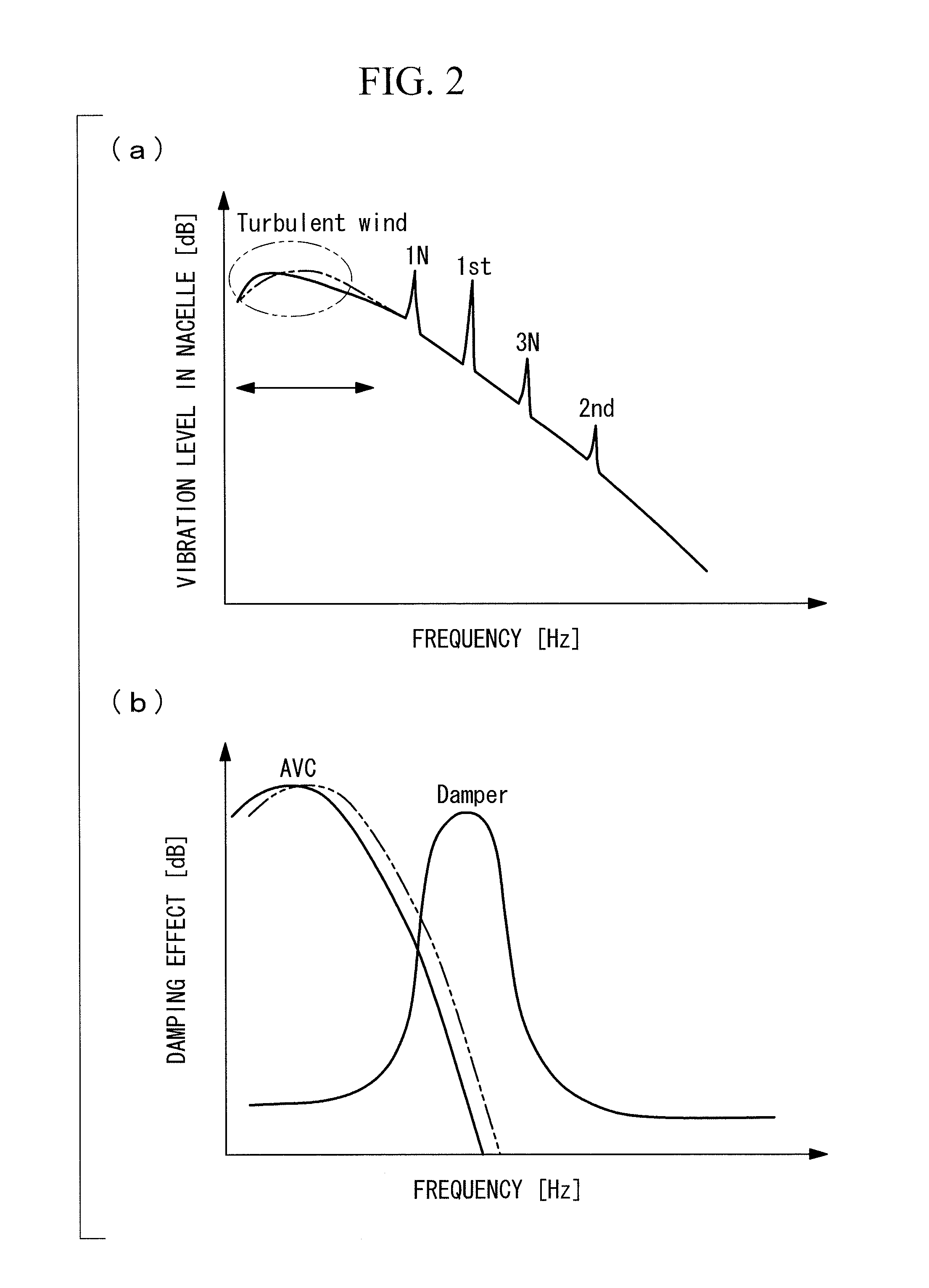
[0044]FIG. 1 illustrates a basic idea of vibration damping of the present invention. The lateral axis of FIG. 1(a) indicates a frequency [Hz], and the vertical axis indicates a vibration level [dB] in a nacelle installed on an upper part of a tower of a wind turbine. As illustrated in FIG. 1(a), vibration caused by a frequency component of turbulent wind, vibration in a rotor rotation speed (1N), vibration in a primary component (1st) of a natural vibration frequency of the wind turbine itself, vibration in a rotation speed (3N) three times of the rotor rotation speed, and vibration in a secondary component (2nd) of the natural vibration frequency of the wind turbine itself appear in the order from the low-frequency side. The relationship between the frequency in the rotor rotation speed (1N) and the primary natural vibration frequency (1st) might be opposite dependin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com