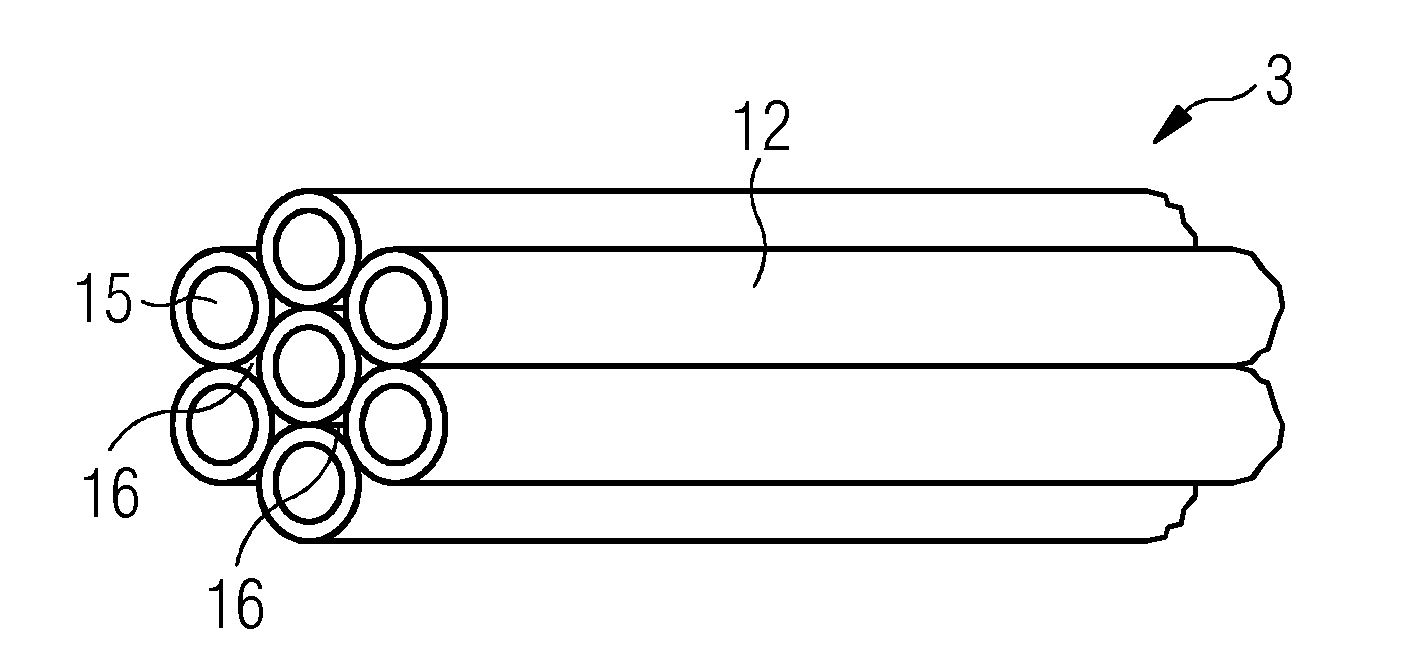Sandwich core material
a core material and sandwich technology, applied in the direction of wind motors with parallel air flow, liquid fuel engine components, wind energy generation, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming and labor-intensive, and achieve the effect of reducing the total weight of the core material layer, reducing the space between the core material elements, and reducing the weight of the core material
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
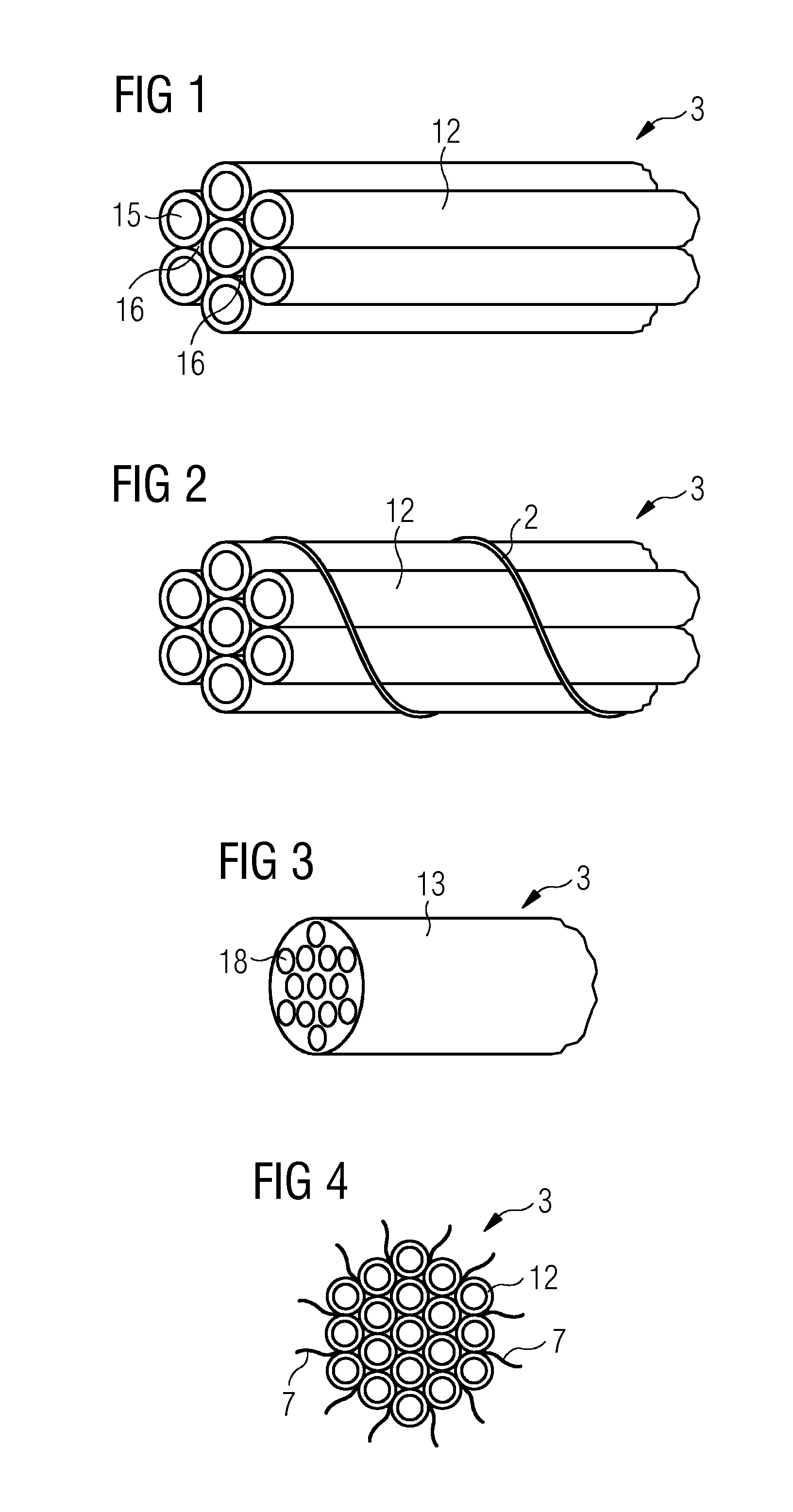
[0046]FIG. 1 shows a perspective view of a flexible core material element 3 comprising seven tubes 12 made of a polymer material. Each tube 12 is constructed with a hollow tube cross section 15. The seven tubes 12 are arranged in the form of a tow, wherein the tow comprises one tube 12 in the middle and six tubes 12 around this one middle tube 12 in the cross section of the tow. The six outer tubes 12 are bound to the tube 12 in the middle and to each adjacent tube 12 by melting the surface of the polymeric material and bonding them to each other at their respective contact points.
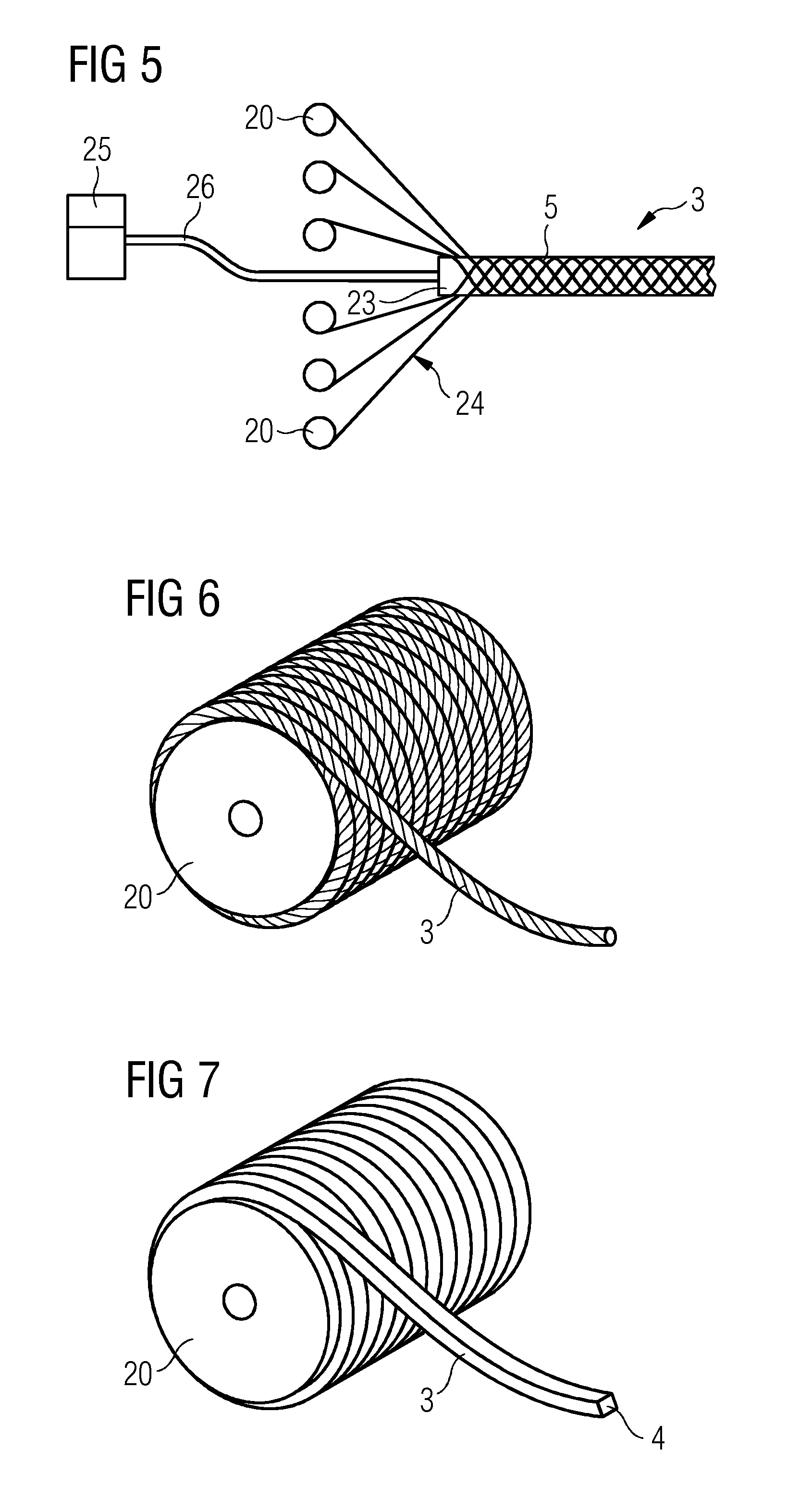
[0047]This tow may by used as a flexible core material element 3 because of its specific flexibility that allows winding it around a bobbin or roll for storage, transportation and delivery to a mould. Thus, the delivery into the mould may be done automatically by means of a respective robot device by using the sandwich core element delivered on a bobbin.
second embodiment
[0048]FIG. 2 shows a similar flexible core material element 3 according to a In this embodiment, seven hollow tubes 12 are arranged in a similar manner as shown in FIG. 1, but are fixed together by circumferential threads 2. Those threads 2 may be made of a plastic or fibre material which may be elastic so that it may easily be wound around the tow in a helical manner. Instead of helical threads 2, a plurality of threads wound at distinct distances from the beginning of the tow may be arranged for fixedly combining the tubes 12 to a tow. The threads 2, thus, function as external connecting means of the tubes 12.
[0049]Of course, the bonding by molten resin as explained in the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1 (an internal connection) may be combined with this external connection.
third embodiment
[0050]FIG. 3 shows a perspective view of a flexible core material element 3 according to a The core tow of this embodiment comprises a hose 13 filled with a lightweight material 18. The material of the hose 13 may be permeable to an injection resin used in order to allow an intrusion of the resin into the hose material and, thus, a fixation in the surrounding core material layer or the surrounding sandwich laminate layers. The material 18 filled into the hose 13 may be impermeable in order to avoid an intrusion of high amount of heavy weight resins. In FIG. 3, the hose 13 is filled with micro balloons 18 which are lightweight due to the high amount of air or another gas filled into the balloons. Alternatively, other lightweight materials may be used instead of the micro balloons 18, such as hollow fibres, tubes, foams or the like.
[0051]In FIG. 4, a flexible core material element 3 according to a fourth embodiment is shown in its cross section. The core tow 3 has reinforcement fibre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com