System and method for packet delivery backtracking
a packet backtracking and packet technology, applied in the field of system and method for packet backtracking, can solve problems such as undeliverable flagging, and achieve the effect of maximizing the chance of transmission success
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024]A preferred embodiment of the present invention will be set forth in detail with reference to the drawings, in which like reference numerals refer to like elements or steps throughout.
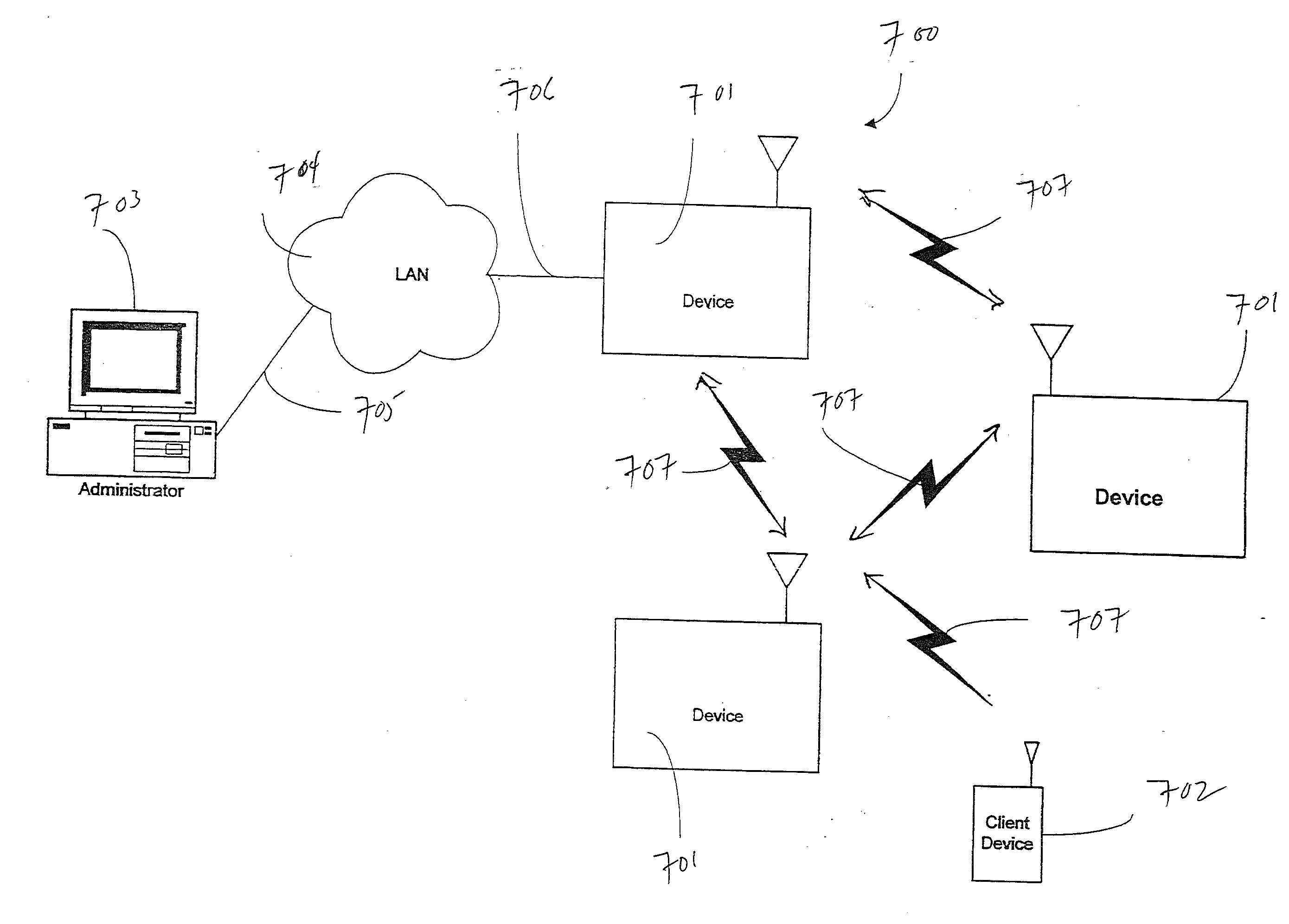
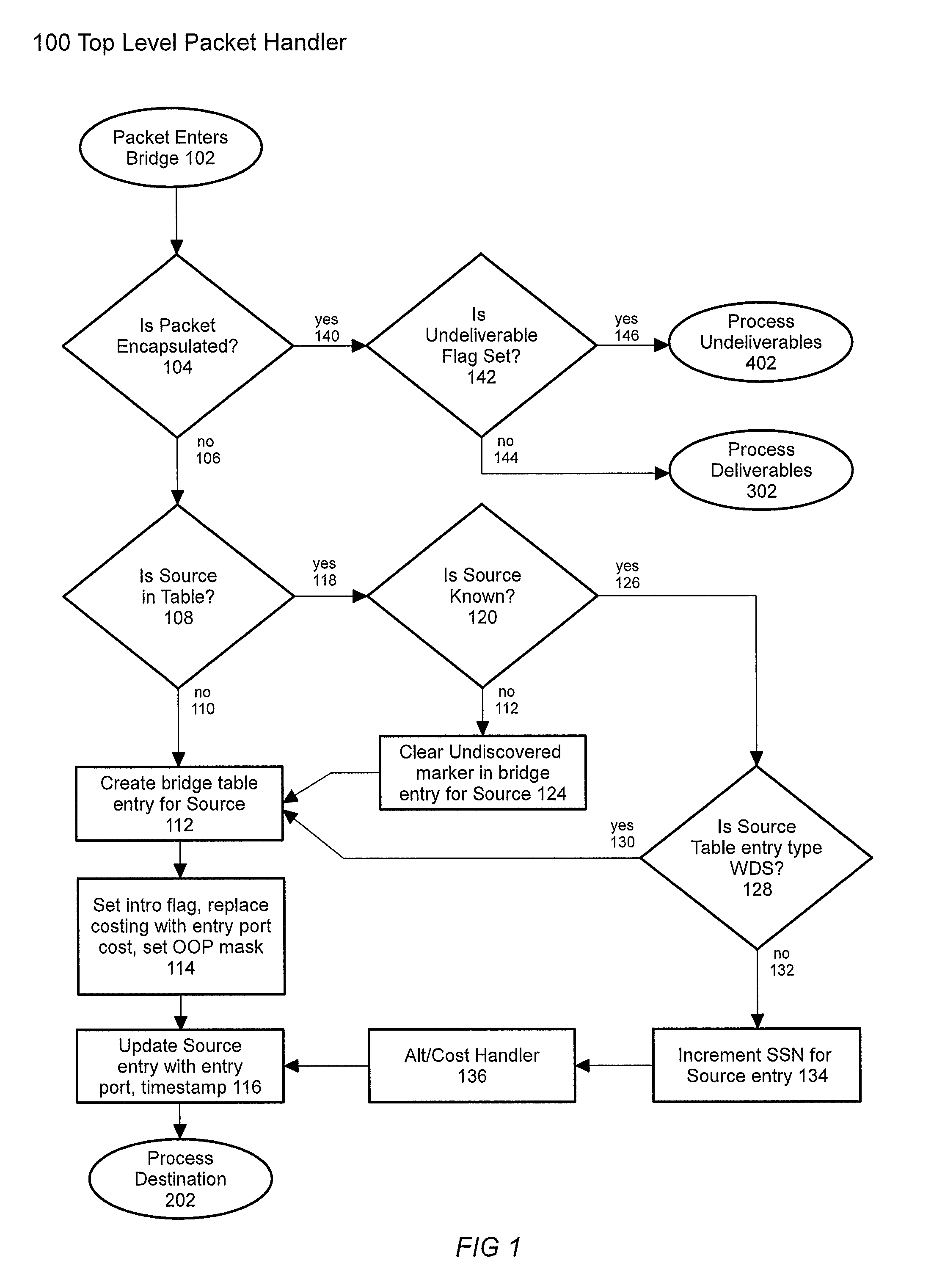
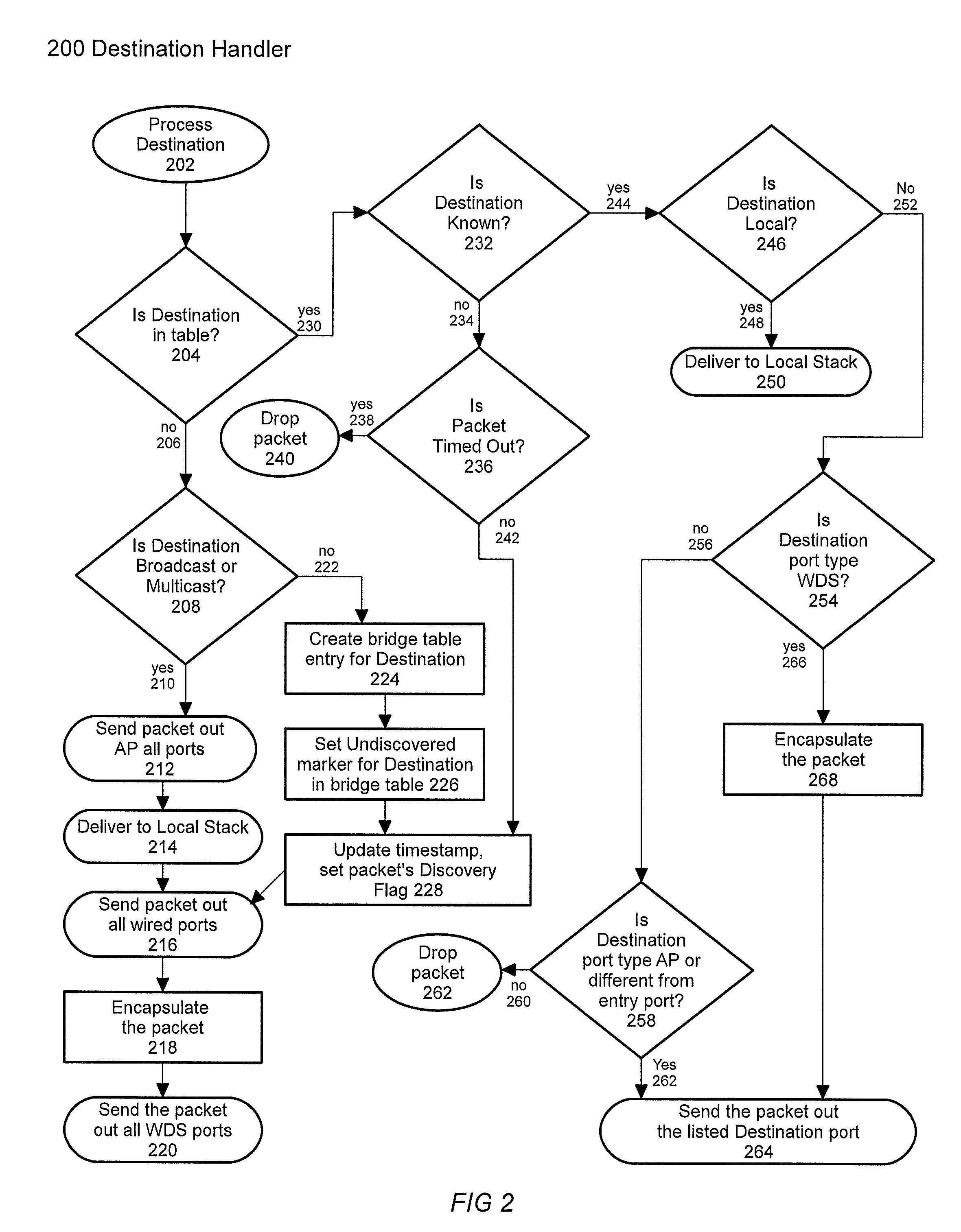
[0025]FIG. 1 illustrates the top level of the Bridge Handler 100. A packet enters this handler 102 and is then checked for encapsulation 104. If the packet is not encapsulated 106, its source is checked in the bridge table 108. If the source is not known 110, an entry for it is created in the bridge table 112, a random sequence number is added 113, default settings are applied to that table entry 114, and the entry is timestamped 116 and delivered to its destination 202.
[0026]If the source is already in the table 108, 118, it is checked for whether it was previously known 120. If it is known 122, the Undiscovered flag is cleared 124, sequence number applied 113, flags initialized 114, timestamped 116, and the packet is delivered 202. If the source was known, a check is done 128 for whether it is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com