Mixture, dissolving solution and pharmaceutical agent each comprising thermophilic microorganism
a technology of thermophilic microorganisms and pharmaceutical agents, which is applied in the direction of bacteria based processes, immunological disorders, metabolism disorders, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to achieve the advantageous effect of enhancing muscle-building effects of conventional techniques at the same time, and not being able to disclose direct effects in patent documents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
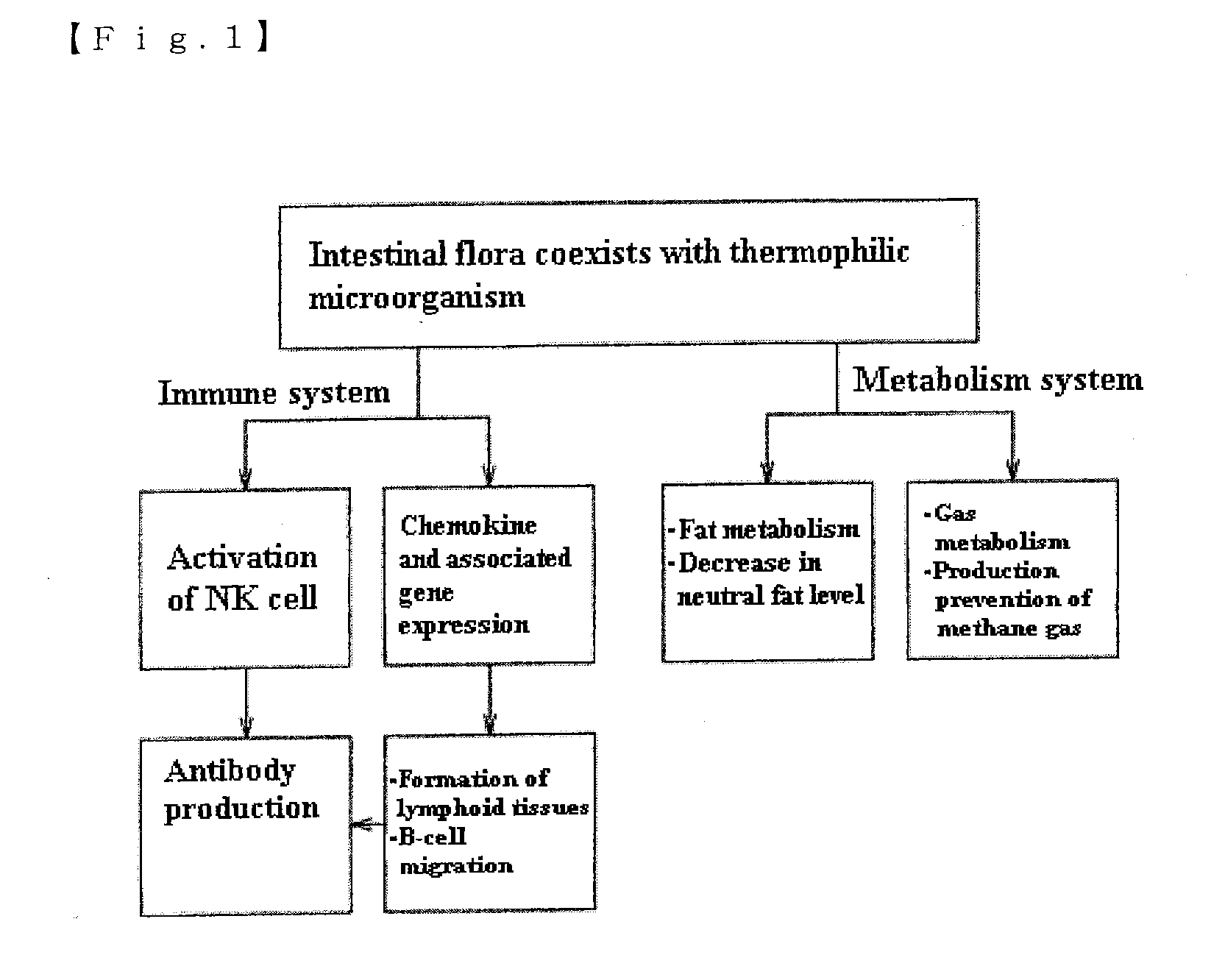
Image
Examples
example 1
(1-1) Preparation of Dissolving Solutions 1-A and 1-B
[0058]A dissolving solution 1-A was prepared using a high-temperature fermentation product reported by Niisawa et al. (Niisawa C, Oka S, Kodama H, Hirai M, Kumagai Y, Mori K, Matsumoto J, Miyamoto H, Miyamoto H (2008) Microbial analysis of composted product of marine animal resources and isolation of antagonistic bacteria to plant pathogen from the compost. J Gen Appl Microbiol 54: 149-158) such that the product was diluted 200 times by weight and then subjected to aeration by diffused air at 60 to 70° C. for 6 hours or more. Furthermore, a dissolving solution 1-B was prepared by co-cultivating thermophilic microorganisms included in the dissolving solution 1-A with PTA-1773.
(1-2) Analysis of Microorganisms in Dissolving Solution 1-A
[0059]The dissolving solution 1-A includes various kinds of thermophilic microorganisms, and thermophilic mixed bacteria BP-1051 as the dominant bacterial species. Their base sequences (16SrDNA sequenc...
example 2
(2-1) Preparation of Dissolving Solution 2
[0068]A dissolving solution 2 was prepared by fermenting an organic material containing marine residues with microorganisms included in the dissolving solution 1-B in an air permeable three-staged fermenter installed in Miroku Co., Ltd at 70° C. or more and 90° C. or less, diluting the final fermentation product 100 times with water, and dissolving it therein at 60° C. or less for 10 hours or more under aeration conditions.
(2-2) Analysis of Microorganism Dominant in Cecal Feces of Germ-Free Mouse with Administration of Dissolving Solution 2
[0069]A dissolving solution 2 at a concentration of 0.5% was administered to aseptically breeding Balb / c mice (male, 10 weeks of age) for three weeks, and the base sequences (16SrDNA sequences) of microorganisms isolated from cecal feces of the mice were then analyzed. Here, the above Balb / c mice were bred in isolators (manufactured by ICM Co., Ltd.) in a breeding room controlled at a room temperature of 2...
example 3
(3-1) Verification Experiment [1] for Dissolving Solution 1-A
[0077]An experiment for verifying a regulatory effect of the dissolving solution 1-A on expression of gene cluster by administration of the dissolving solution 1-A to Wistar rats (male, 3 weeks of age) (obtained from Kyudo Co., Ltd.). In this experiment, the following three groups were prepared and compared with one another.
Group (1-A): A normal feeding group (controls)
Group (1-B): A group in which the dissolving solution 1-A was added to drinking water.
Group (1-C): A group in which the dissolving solution 1-A (but sterilized with 0.02 μm) was added to drinking water.
[0078]Here, the Wistar rats used in the experiment were preliminarily bred in groups (1-A) to (1-C) for five days. Furthermore, the Wistar rats were divided into five animals per group and each was bred in its own gauge (manufactured by Natsume Seisakusyo Co., Ltd.). Furthermore, the feed used was one sterilized by radiation (product name MF, manufactured by O...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com