Methods and Compositions for Treating Neuroblastoma
a neuroblastoma and composition technology, applied in the field of neuroblastoma, can solve the problems of difficult replication and lack of tractable molecular target approaches, and achieve the effect of increasing alk mfi
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Methods
SUMMARY
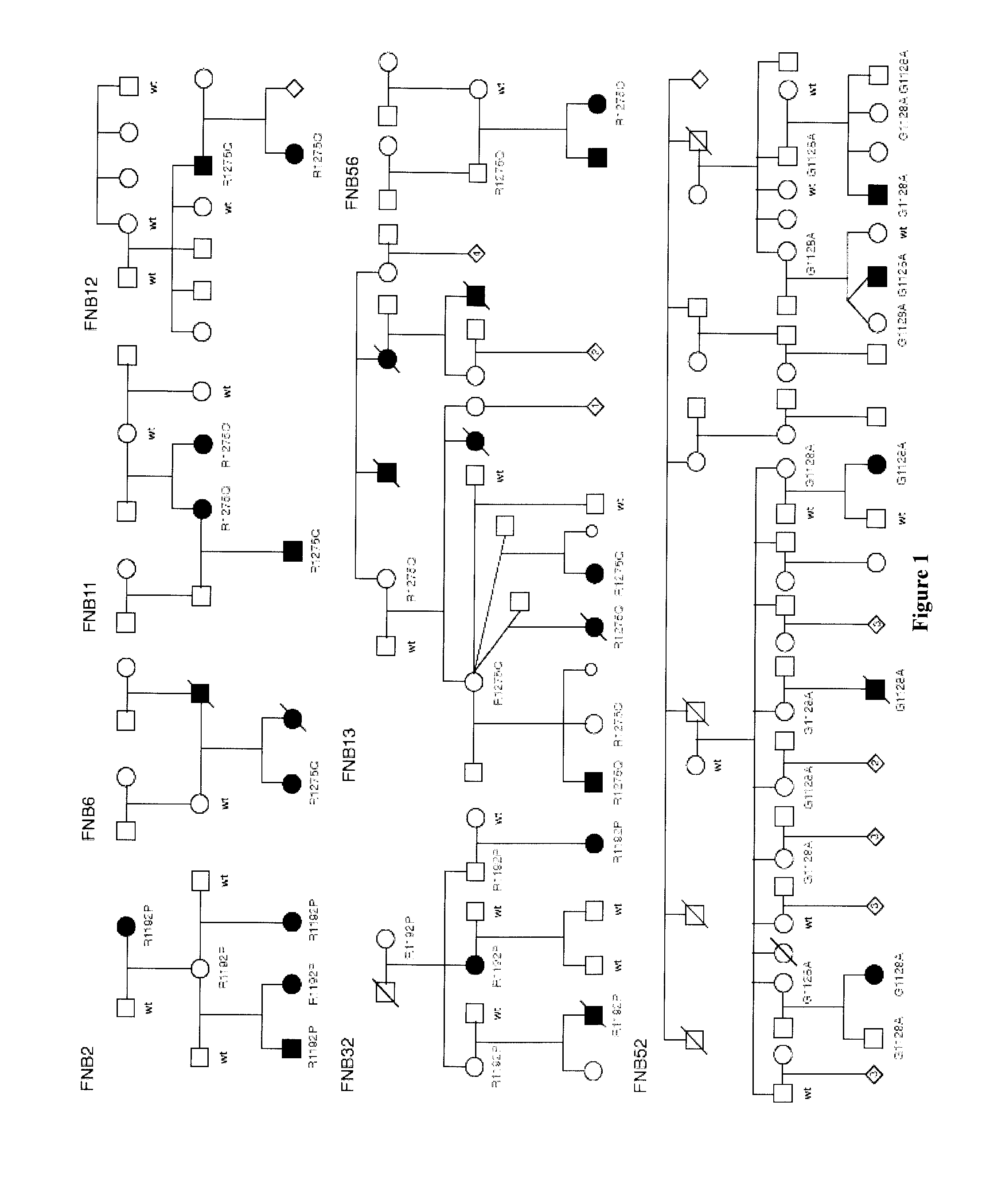
[0092]Twenty probands with neuroblastoma and a family history of the disease were identified for study. Eight pedigrees had 3 or more affected individuals; six pedigrees contained only two affected individuals, but of first degree relation; and six pedigrees consisted of only two affected individuals, but of second, third, or >fourth degree relationship. A total of 176 individuals (49 affected with neuroblastoma) were genotyped genome-wide, and two families were excluded due to insufficient DNA for genotyping. Marker data was simulated under a model of genetic homogeneity and autosomal dominant inheritance, and the data was analyzed using an affected-only approach comparable to the model-free approach used in the actual linkage analysis. Genotype data were checked for Mendelian inconsistencies using PEDSTATS (Wigginton et al. (2005) Bioinformatics, 21:3445-7), and analyzed for linkage using MERLIN (Abecasis et al. (2002) Nat. Genet., 30:97-101) and LAMP (Li et al. (200...
example 2
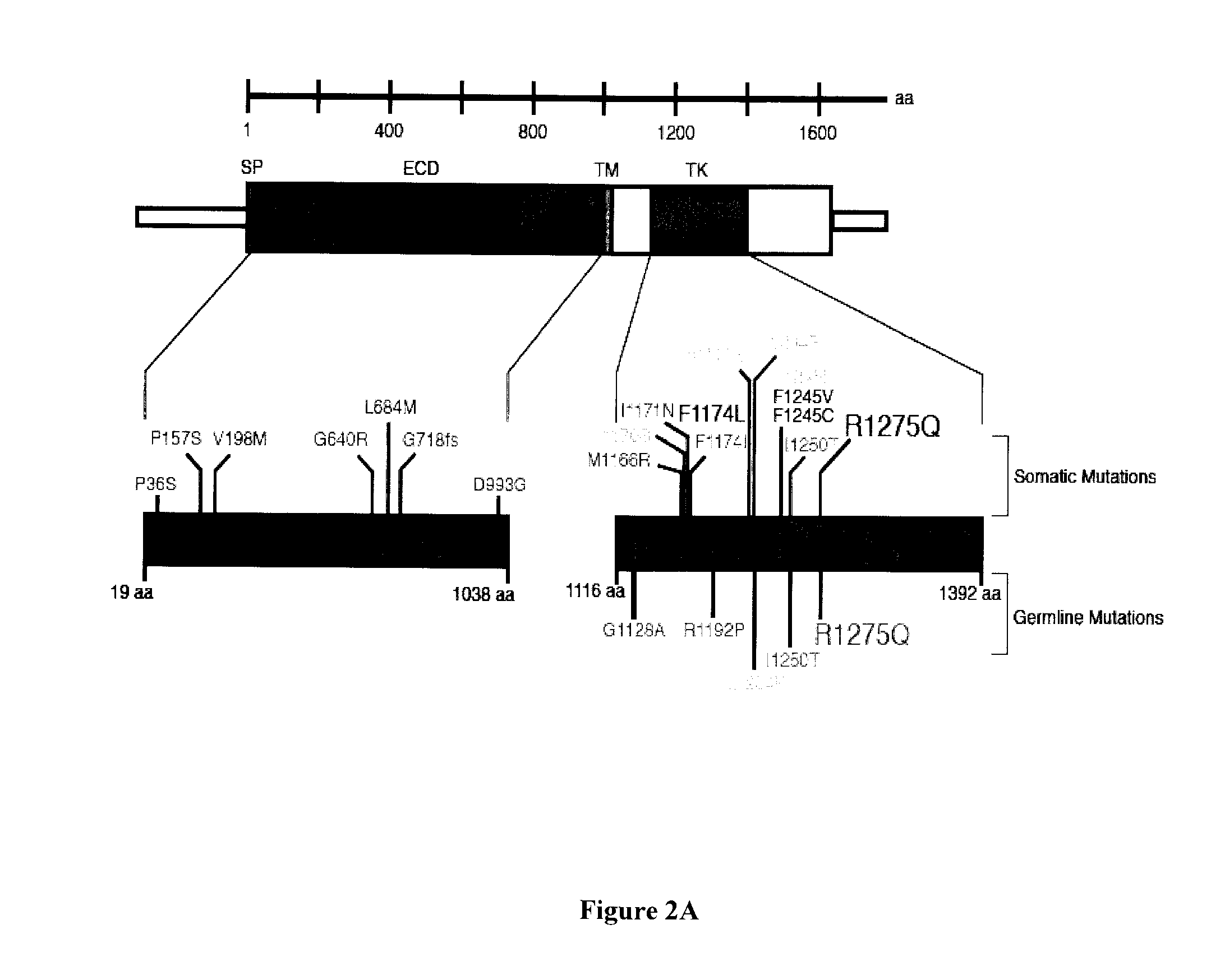
[0116]ALK is a tractable target for pharmacologic inhibition, but sensitivity depends on mutation type. FIG. 6A is a graph of a dose response curve and FIG. 6B is a graph of the % growth inhibition with PF066 at 333 nM. FIG. 7 shows the expression of pALK, pAKT, pSTAT3, and pMAPK3. For FIG. 6A, the human-derived neuroblastoma cell lines NB1643 (R1275Q), NB1 (ALK amplified), and NBSD (Fl 174L) were screened for evidence of anti-tumor activity to ALK inhibitor PF-02341066 in vitro. A quantitative assay to evaluate growth inhibition in a multi-well was used in a parallel format to screen for cellular cytotoxicity. Inhibition of substrate adherent growth during log-phase was then screened using the 96×6 RT-CES™ system (Real-Time Cell Electronic Sensing; ACEA Biosciences; San Diego, Calif.) with cells plated in triplicate for each assay, allowing for relatively high throughput and real-time assessment of alterations in growth kinetics, assaying for potential cytostatic or cytotoxic respo...
example 3
[0118]Neuroblastoma is a cancer of early childhood that arises from the developing autonomic nervous system. It is the most common malignancy diagnosed in the first year of life and shows a wide range of clinical phenotypes with some patients having tumors that regress spontaneously (D′Angio et al. (1971) Lancet 1:1046-1049), whereas the majority of patients have aggressive metastatic disease (Maris et al. (2007) Lancet 369:2106-2120). Neuroblastoma remains an important clinical problem as it continues to be a leading cause of childhood cancer mortality despite dramatic escalations in dose-intensive chemoradiotherapy, and long-term survivors experience significant treatment related morbidity (Oeffinger et al. (2006) N. Engl. J. Med., 355:1572-1582; Hobbie et al. (2008) Pediatr. Blood Cancer 51:679-683). To improve outcome and make paradigm-shifting advances in this disease, it is necessary to discover the key oncogenic drivers of the malignant process and exploit these therapeutical...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compositions | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| protein structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com