High Visibility Protective Fabric
a protective fabric and high-visibility technology, applied in the field of fabric and garments, can solve the problems of reducing the personal protection per weight of fabri
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
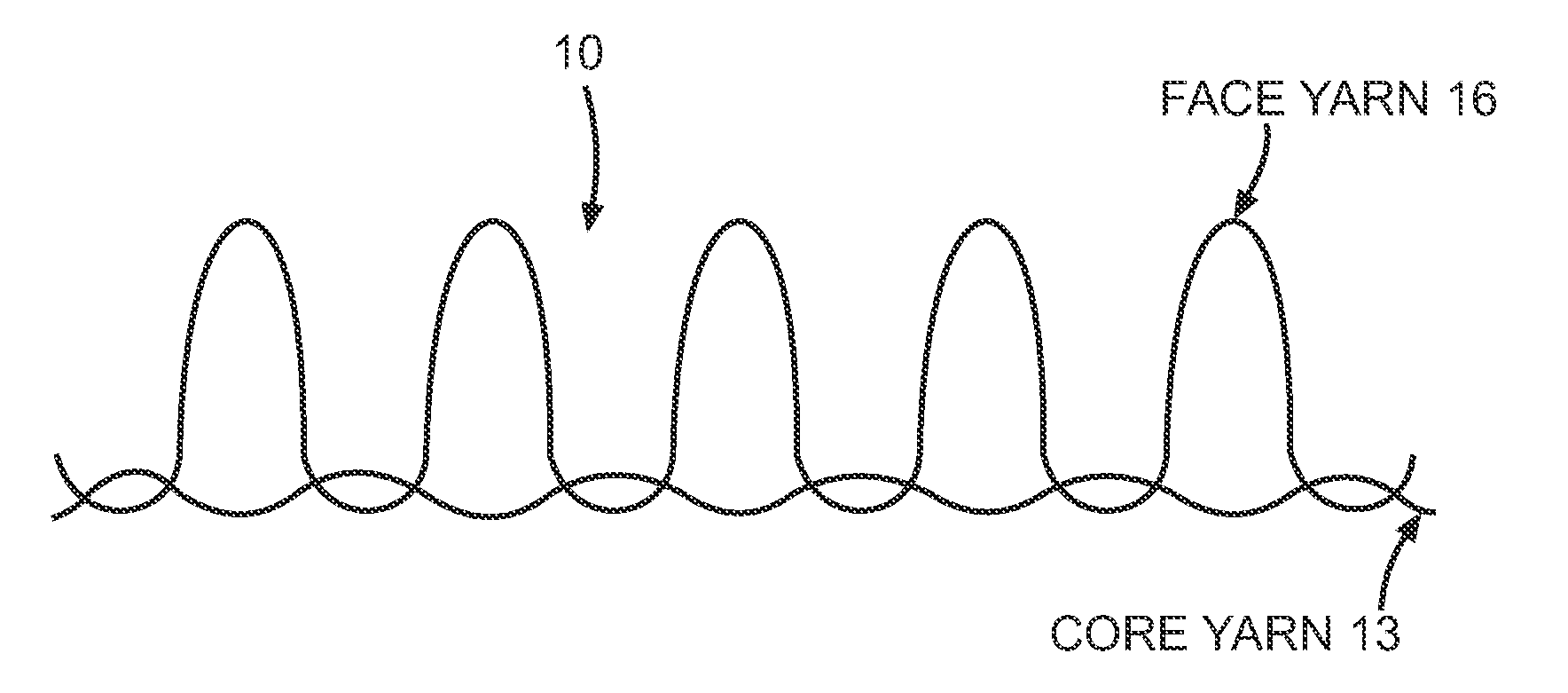
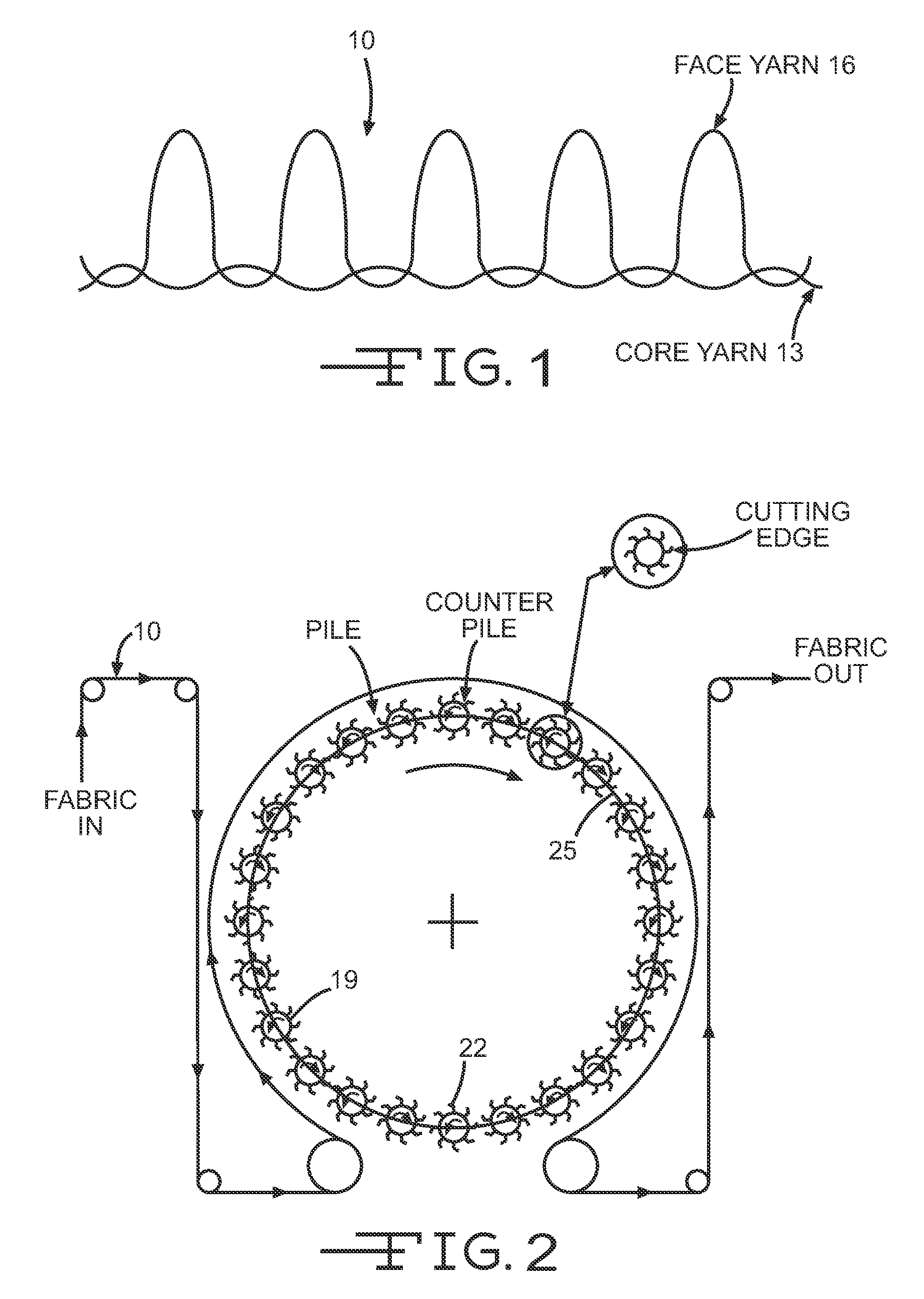
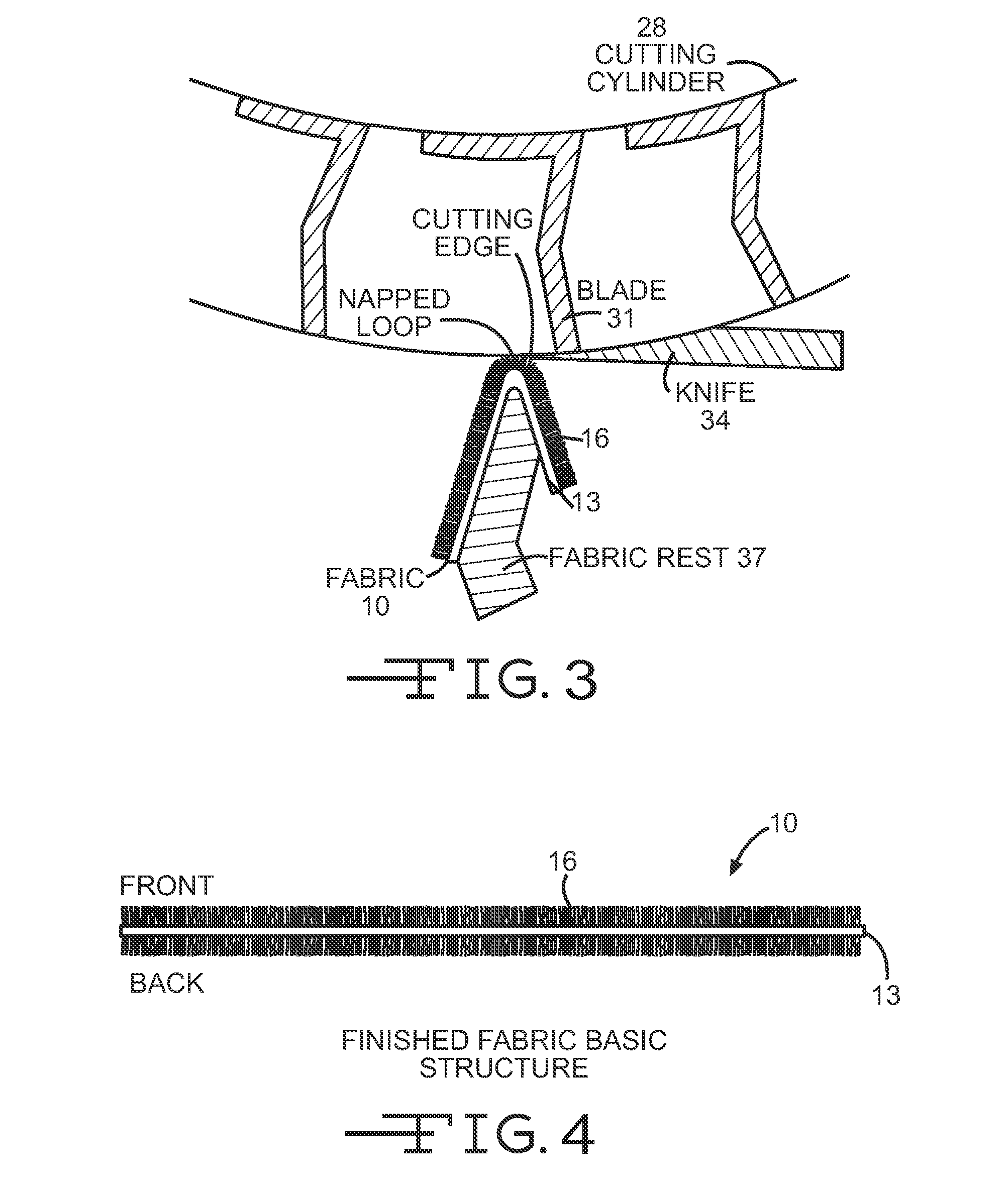
[0025]The present invention may be used to provide a high visibility fabric, which may be used to make garments. Furthermore, the present invention may be used to make a garment that is not only highly visible but is also fire resistant and / or protective with respect to electric arcs, and which also provides insulation to the wearer in cold weather. One embodiment of the invention is a fabric formed from at least two yarns. FIG. 1 depicts features of such a fabric 10. The fabric 10 has a first yarn 13 that is used to make a core, and a second yarn 16 that is used to make a face of the fabric 10. The face yarn 16 forms the outside appearance of the fabric 10. The face yarn 16 may be used on two sides of the core structure, so that the appearance of the fabric 10 is uniform. The face yarn 16 may substantially overlay the yarn 13 that is used for the core so that the core is not visible. The face yarn 16 is formed from a yarn that can be dyed to make the fabric 10 highly visible, and t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com