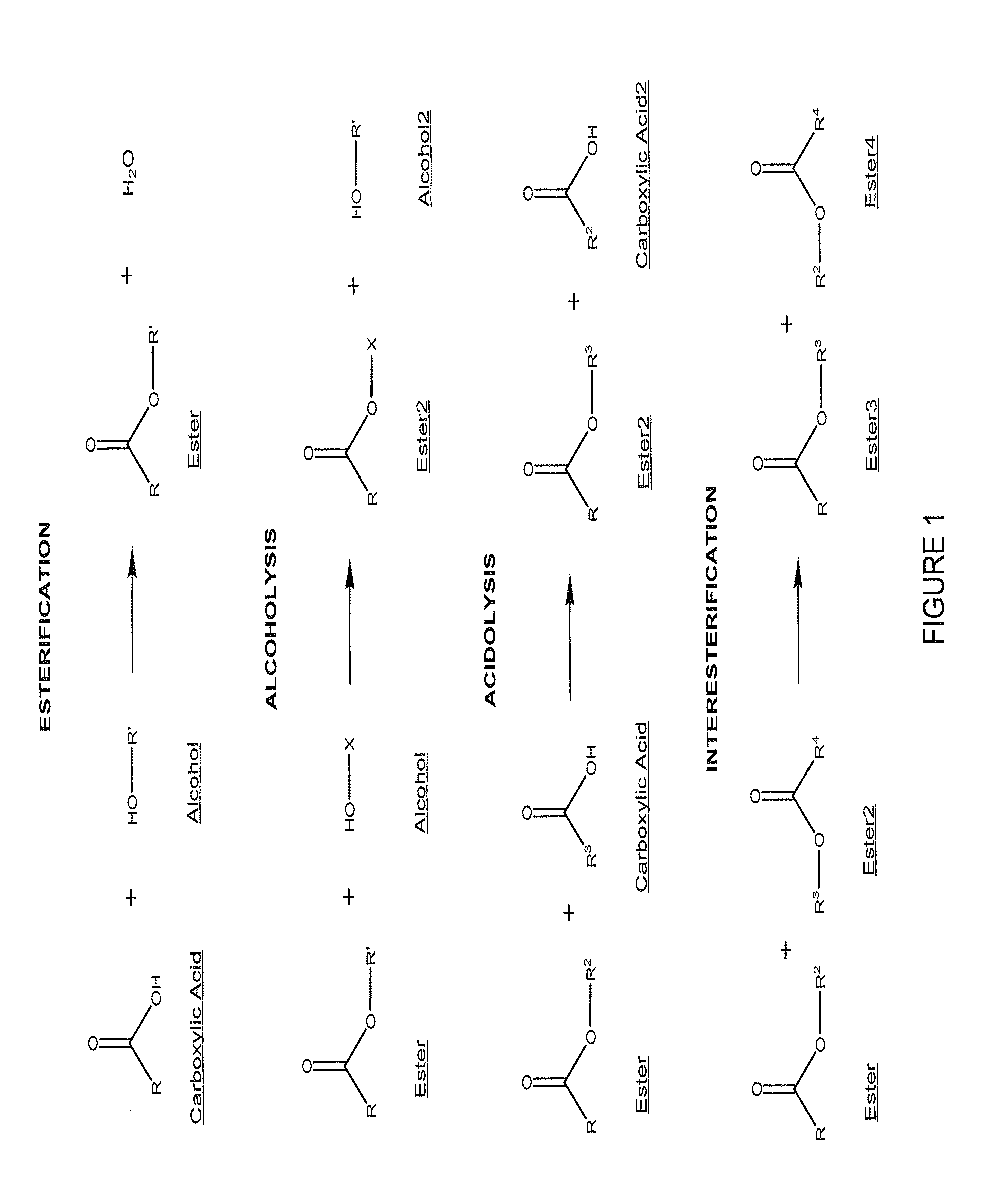
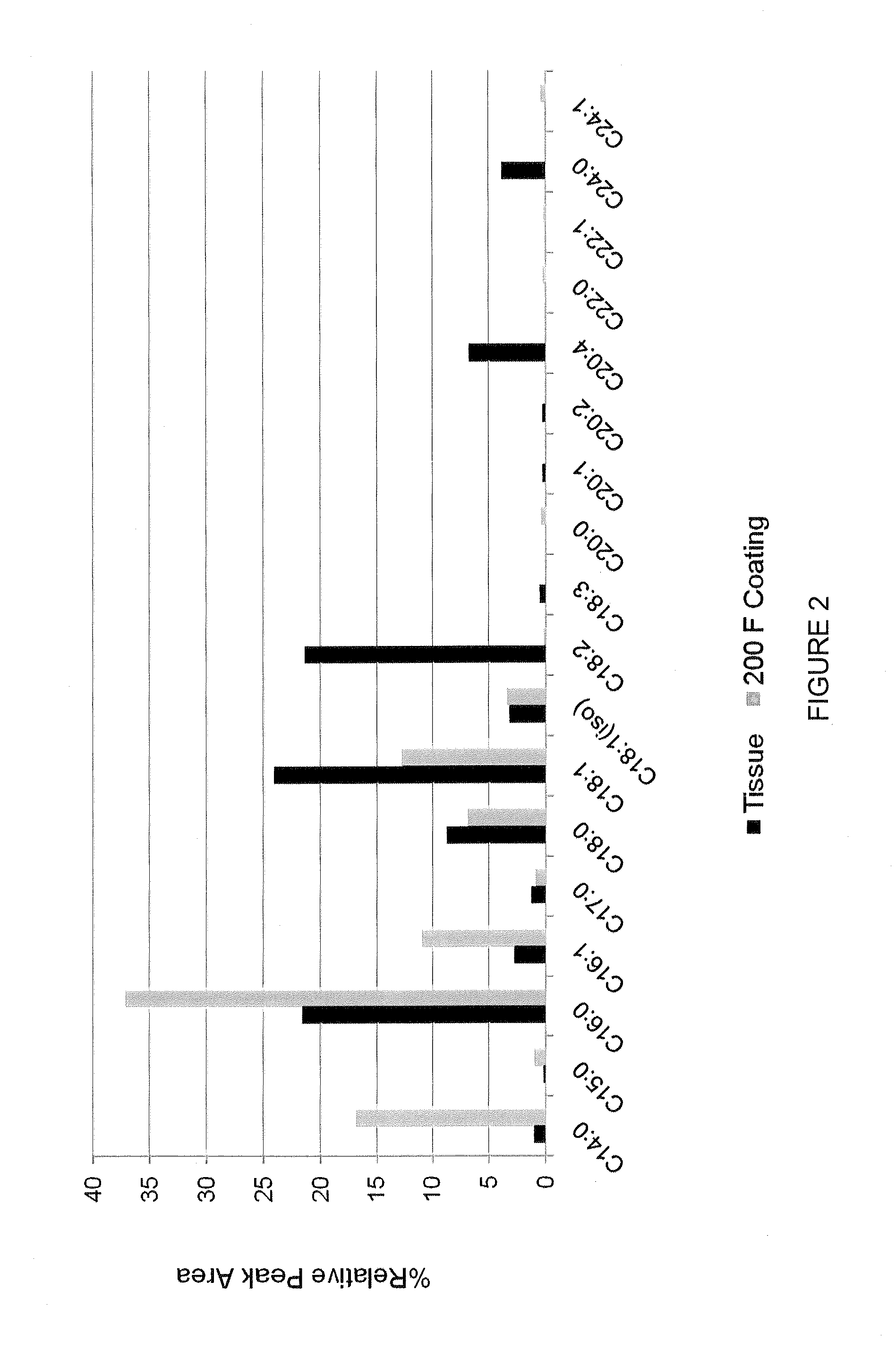
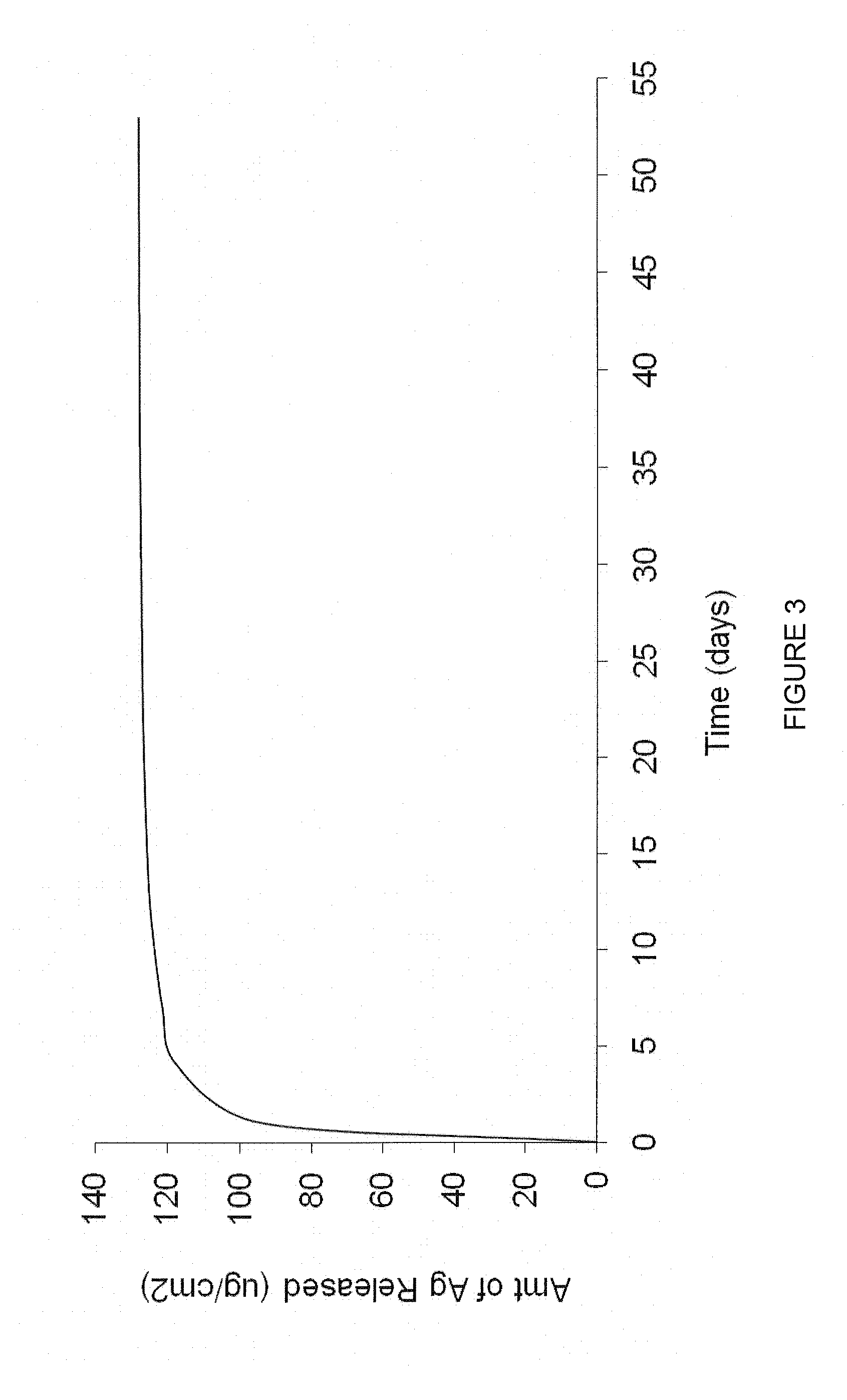
Anti-infective antimicrobial-containing biomaterials
a biomaterial and antimicrobial technology, applied in the field of antimicrobial antimicrobial-containing biomaterials, can solve the problems of increasing medical costs, increasing the risk of infection of patients, and increasing the risk of morbidity and mortality of patients, so as to prevent or diminish chronic inflammation and reduce infection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Silver Fatty Acid Salts within the Fatty Acid-Derived Biomaterial
[0145]In accordance with the present invention, silver in its aqueous form was used to hydrate a fatty acid-derived biomaterial sample. One possible mechanism for the formation of the antimicrobial-containing biomaterial hydrated in aqueous silver is as follows: fish oil (triglycerides) absorbs oxygen into the oil; oxidation of the C═C bonds in the oil occurs; fatty acid and glycerides (a mixture of mono, di- and tri) are formed; continued curing results in dehydration of neighboring carboxyl and hydroxyl functional groups; lactone / ester cross-links are formed between fatty acids and glycerides; the oil solidifies into a bioabsorbable gel containing cross-linked fatty acids and glycerides; the cross-linked fatty acid biomaterial is immersed in an aqueous Ag solution; and the hydrated silver coated fatty acid biomaterial is dried to evaporate the solvent.
[0146]The silver hydrated fatty acid-derived biomaterial was prepa...
example 2
Fatty Acid-Derived Biomaterial Surface Coated with Silver
[0150]In a different embodiment of the present invention, silver was coated onto the surface of a fatty acid-derived biomaterial. Sample preparation was done as follows. Silver nitrate was massed and dissolved in methanol to a final concentration of 0.02M. In addition, a fatty acid biomaterial was prepared by encapsulating polypropylene mesh with approximately 100 mg of fish oil per inch2 then thermally curing the fish oil cast onto the polypropylene mesh at a temperature of 200° F. for 24 hours to form a solid fatty acid- derived coating. To incorporate silver on the surface, a 1 inch2 sample of the fatty acid biomaterial was then sprayed onto the surface with the 0.02M silver nitrate solution and allowed to dry to evaporate off the methanol solvent. One possible mechanism for the formation of the antimicrobial-containing biomaterial coated with aqueous silver is as follows: fish oil (triglycerides) absorbs oxygen into the oi...
example 3
Formation of Reduced Silver within the Fatty Acid-Derived Biomaterial
[0153]In this example, a different method of forming a silver coated fatty acid-derived material is described. The method of preparation is as follows:
[0154]Three components are used to make up a silver-containing fatty acid emulsion formulation which is then thermally cured onto polypropylene mesh to form a solid reduced silver fatty acid-derived biomaterial coating. The three components that make up the emulsion include an aqueous silver solution, native fish oil and partially cured fish oil that has a viscous consistency. An aqueous silver solution was prepared by massing silver nitrate or silver acetate and dissolving it in water to give final concentrations of 0.07M and 0.06M respectively. Separately, partially cured fish oil was prepared by exposing native fish oil to temperatures of approximately 90° C. in the presence of oxygen for 16 hours which results in a partially cured fish oil component with a viscou...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com