Serological markers of inflammatory bowel disease phenotype and disease progression
a inflammatory bowel disease and serological marker technology, applied in the field of serological markers of inflammatory bowel disease phenotype and disease progression, can solve the problems of limiting the ability to predict clinical disease behavior and outcome, difficult diagnosis of ibds, and substantial morbidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Determining Anti-GM-CSF Antibody Activity for Classification of Subtypes
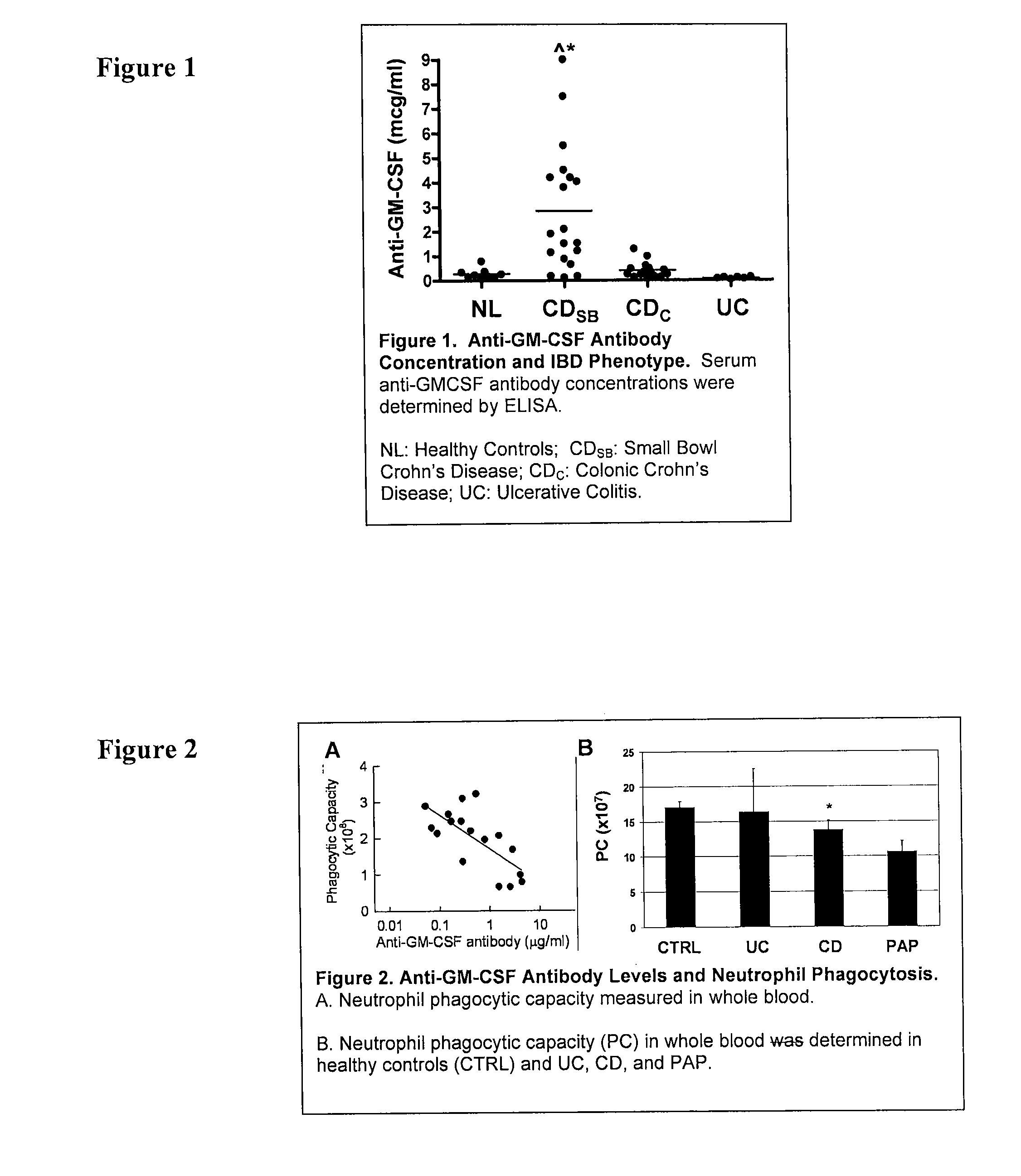
[0100]GM-CSF concentration in whole blood or serum samples obtained from a patient suspected of having an inflammatory bowel disease is determined using the methods as described in Uchida, et al. Blood, 2004, incorporated herein by reference, and described herein.
[0101]Anti-GM-CSF antibodies are assayed using serum samples that are either immediately obtained or previously collected and stored at—70° C. until analysis. Anti-GM-CSF antibody concentration of a serum sample from an individual of interest is then measured. The serum sample is diluted 1:100, 1:1000 and 1:3000 with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing 1% bovine serum albumin and 0.1% Tween 20. Separate 50 μl aliquots of diluted serum and the affinity-purified anti-GM-CSF antibody isolated from the serum of patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis as a standard (0-50 ng / ml) were incubated at room temperature for 40 minutes in ELISA plates pre...
example ii
Anti-GM-CSF Concentration as a Predictor of Disease Behavior
[0102]The methods of Example 1 are carried out essentially as described above. Following performance of the above-described methods, the values obtained from the assay are then used to classify the individual as either having colonic, or ileal or ileo-colonic. Values greater than or equal to about 2 mcg / ml indicate that the disease behavior is less likely to be only colonic (L2), less likely to be non-stricuring, non-penetrating (B1), and more likely to be treated with a surgery. Assessment of the presence or absence of the CARD 15 mutation is not necessary for this determination.
example iii
Determining CD11b Stimulation Index for Classification of Subtypes
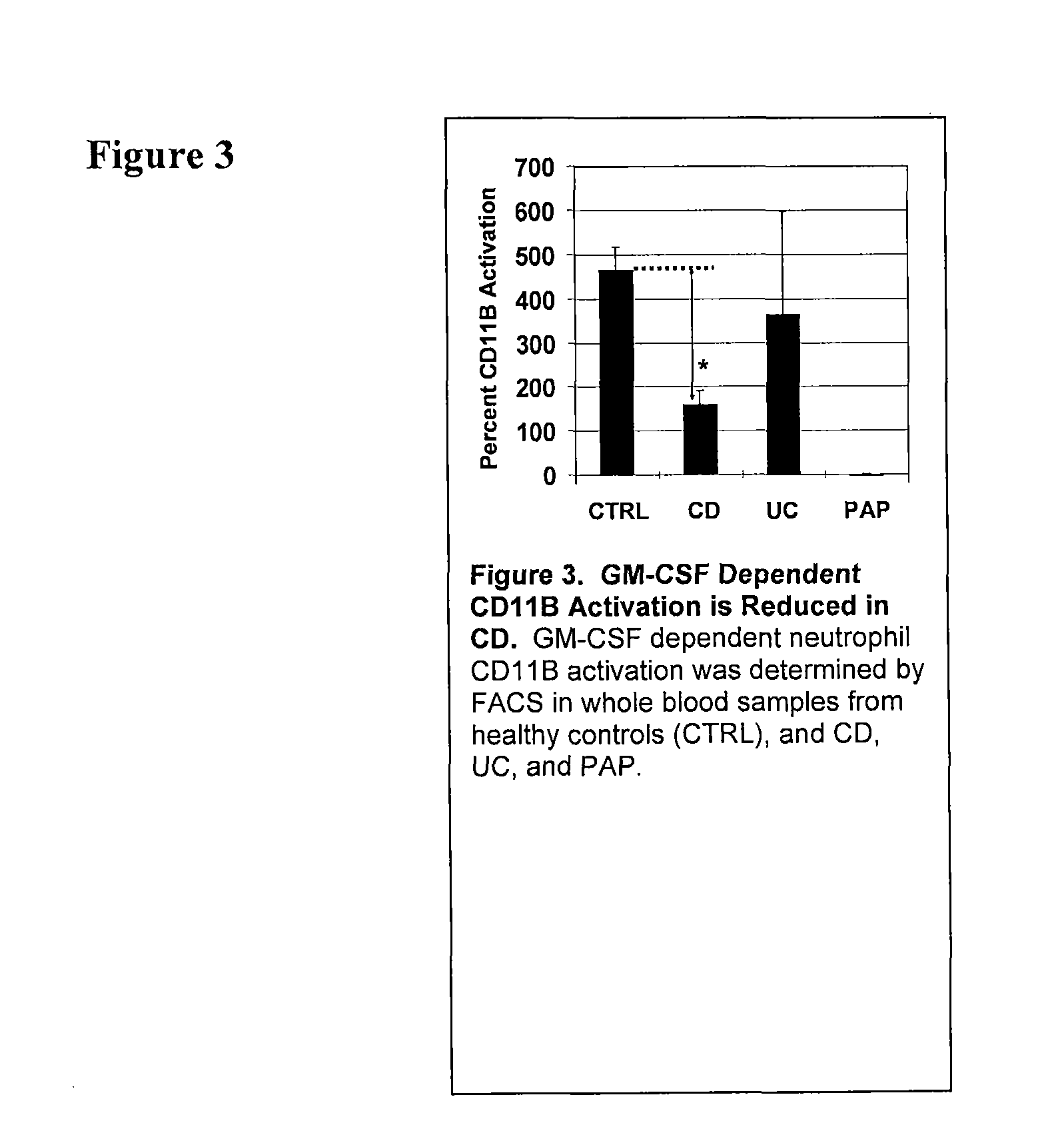
[0103]The CD11b Stimulation Index on neutrophils from whole blood samples obtained from an individual suspected of having an inflammatory bowel disease is determined using the methods as described in Uchida, et al. NEJM, 2007, incorporated herein by reference, and described herein. Briefly, this assay is performed using whole blood samples from IBD patients or healthy controls in the absence or presence of stimulation with exogenously added GM-CSF and then cell surface CD11b is quantified on neutrophils (and / or also on monocytes and eosinophils) is then measured by flow cytometry. Neutrophils can be identified with the high expression level of CD16 determined by fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated anti-CD16 antibody. Monocytes can be determined APC-conjugated anti-CD14 antibody. Eosinophils can be determined moderate expression of CD16 and specific cell size and complexity. This assay provides a method to qua...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| fluorescent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com