Wind turbine blade, wind turbine and method for manufacturing a wind turbine blade
a technology of wind turbine blades and wind turbine blades, which is applied in the direction of wind motors with parallel air flow, non-positive displacement fluid engines, liquid fuel engine components, etc., can solve the problems of lightning current following the electrical cables to a ground potential instead of the down conductor, time-consuming and costly repair of the sensor system, and difficult protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
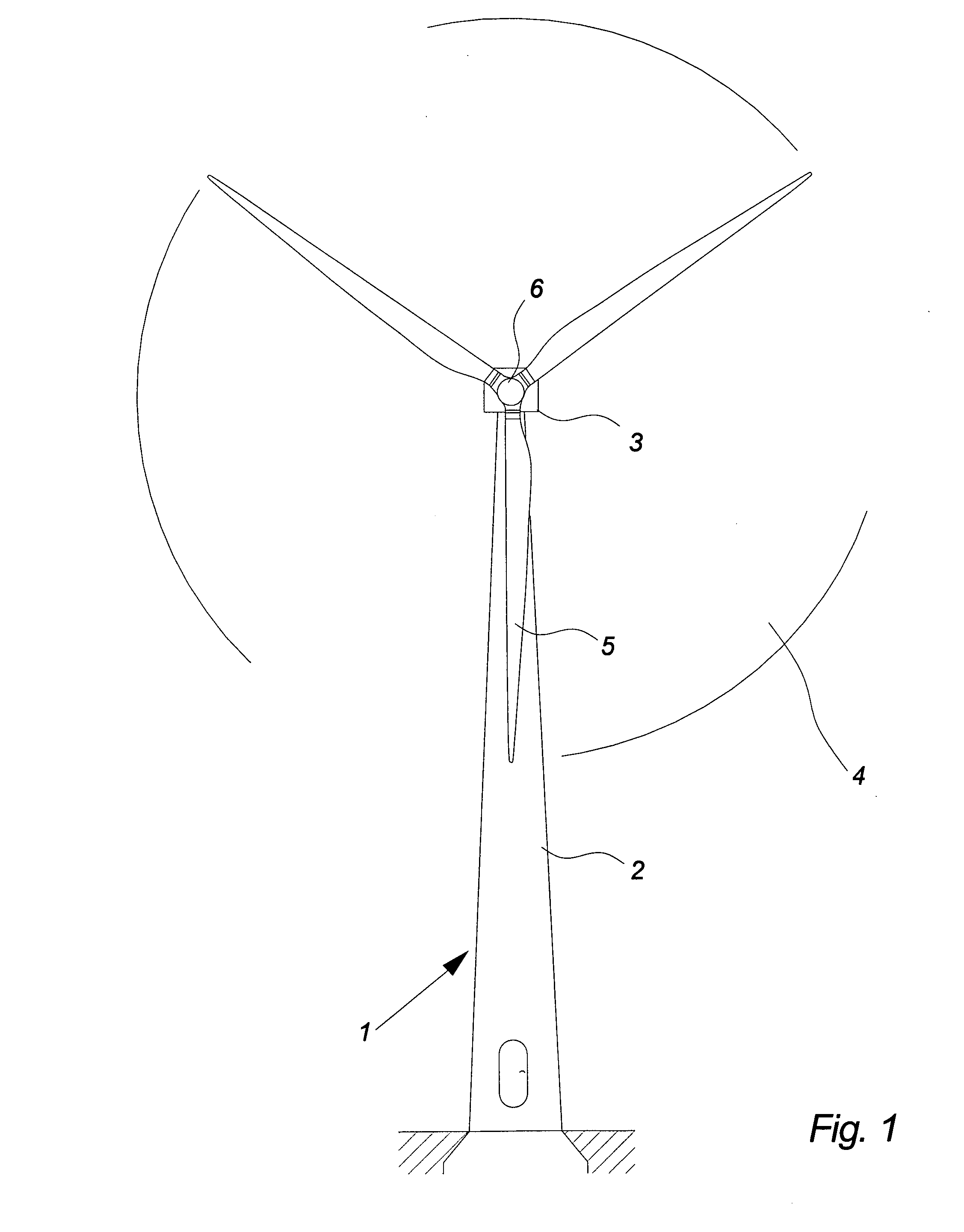
[0042]FIG. 1 illustrates a wind turbine 1, comprising a tower 2 and a wind turbine nacelle 3 positioned on top of the tower 2. The wind turbine rotor 4 comprises at least one wind turbine blade e.g. three wind turbine blades 5 as illustrated in the figure. The rotor is mounted on a hub 6, which is connected to the nacelle 3 through the low speed shaft extending out of the nacelle front.
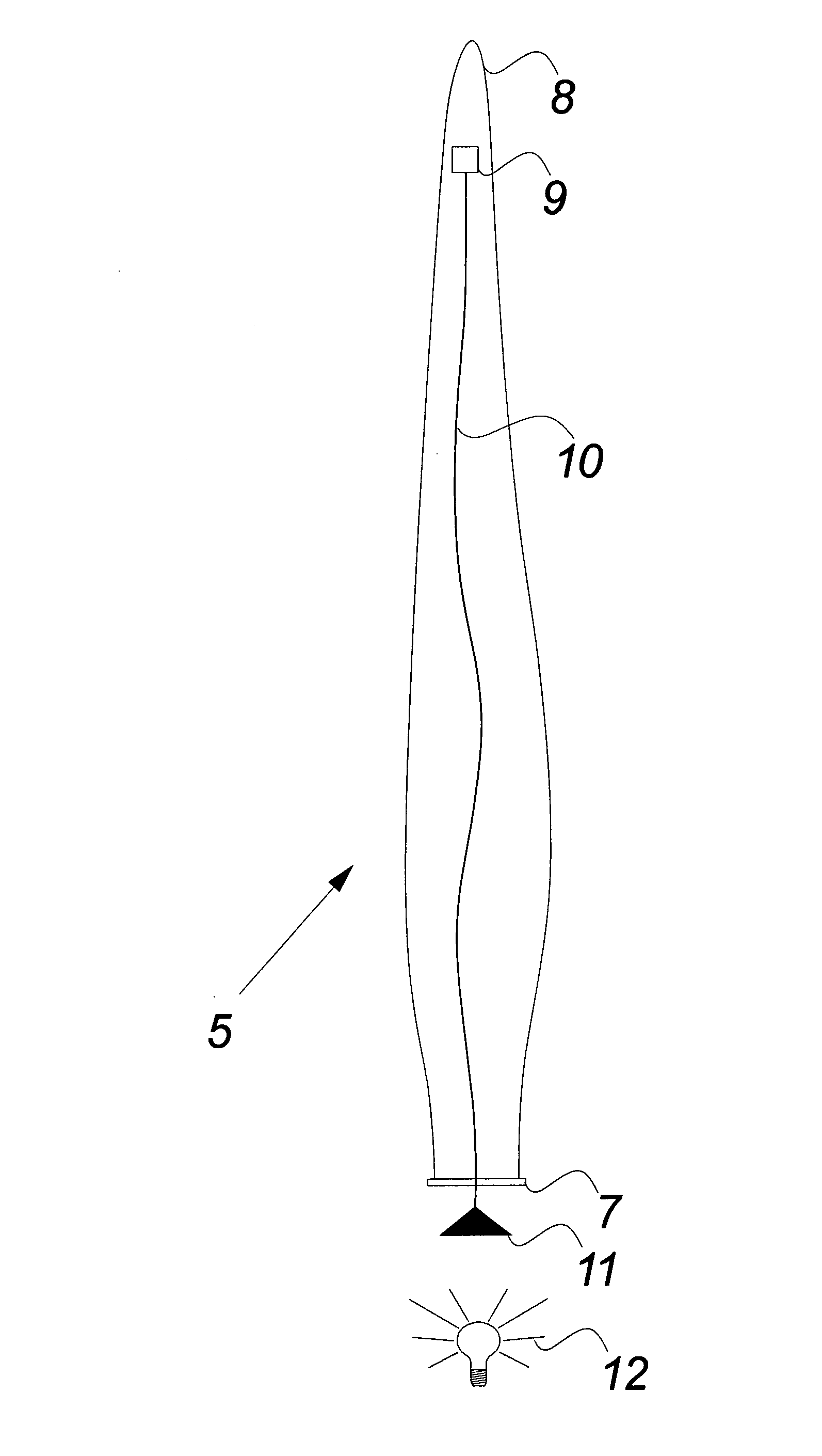
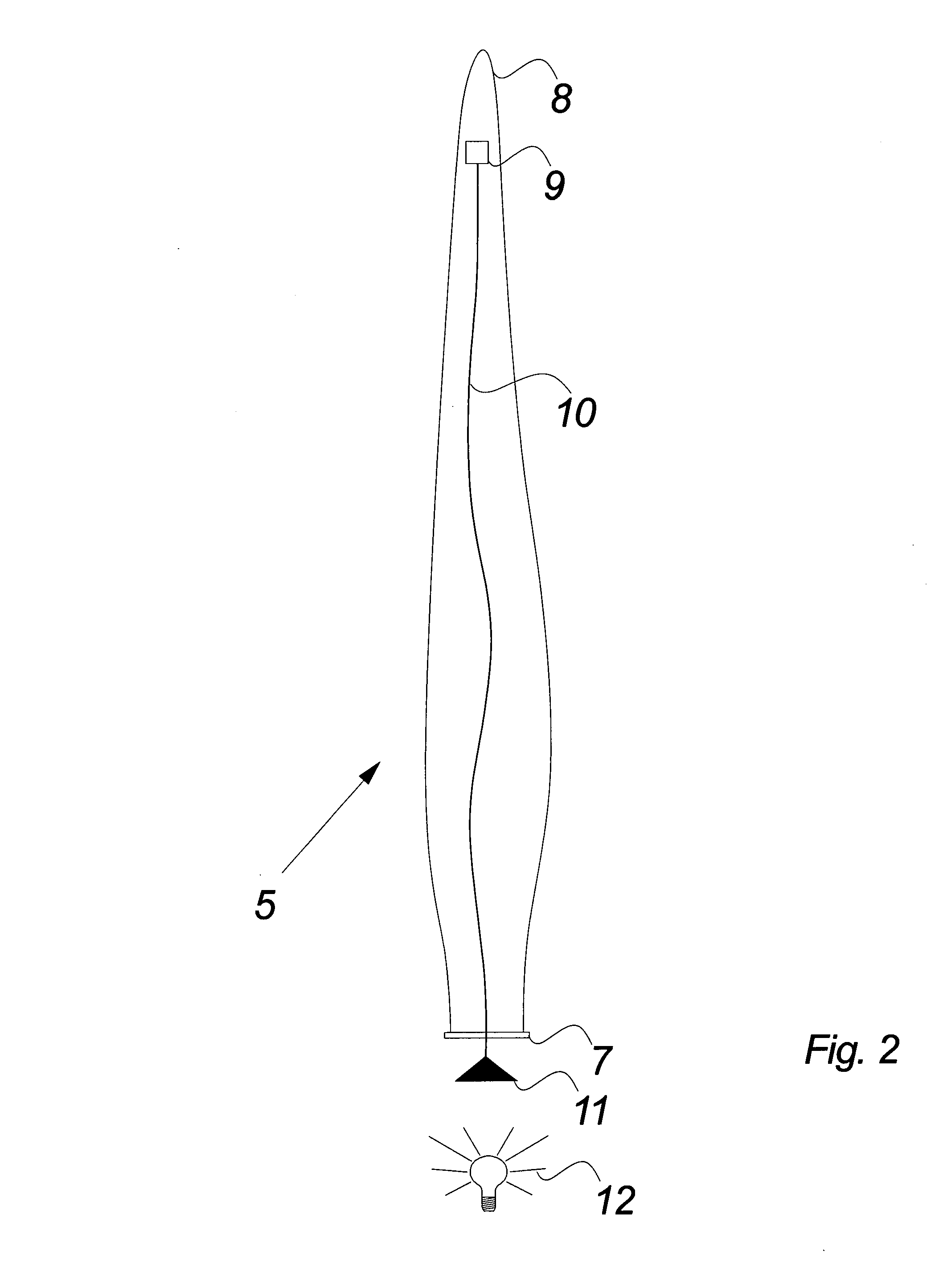
[0043]FIG. 2 illustrates schematically a wind turbine blade according to the invention.
[0044]The figure especially illustrates the optical fibre connection 10 between a light source 12 positioned outside the wind turbine blade 5 and an electric powered module 9 positioned in or inside the wind turbine blade 5.
[0045]The light source 12 may for example be positioned in the hub 6 or in the nacelle 3 (not illustrated in the figure) and facing one end 11 of the optical fibre 10. The light source may be any kind of light source with the possibility of emitting light of a certain and defined power density e....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Transmission | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com