Road Roller Skates
a technology of roller skates and rollers, which is applied in the direction of roller skates, skate boards, skating, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in learning technique, impractical holding or stopping position of these types of skates, and inability to roll on ordinary roads with rough surfaces. , to achieve the effect of reducing energy loss, facilitating movement, and efficient use of skates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
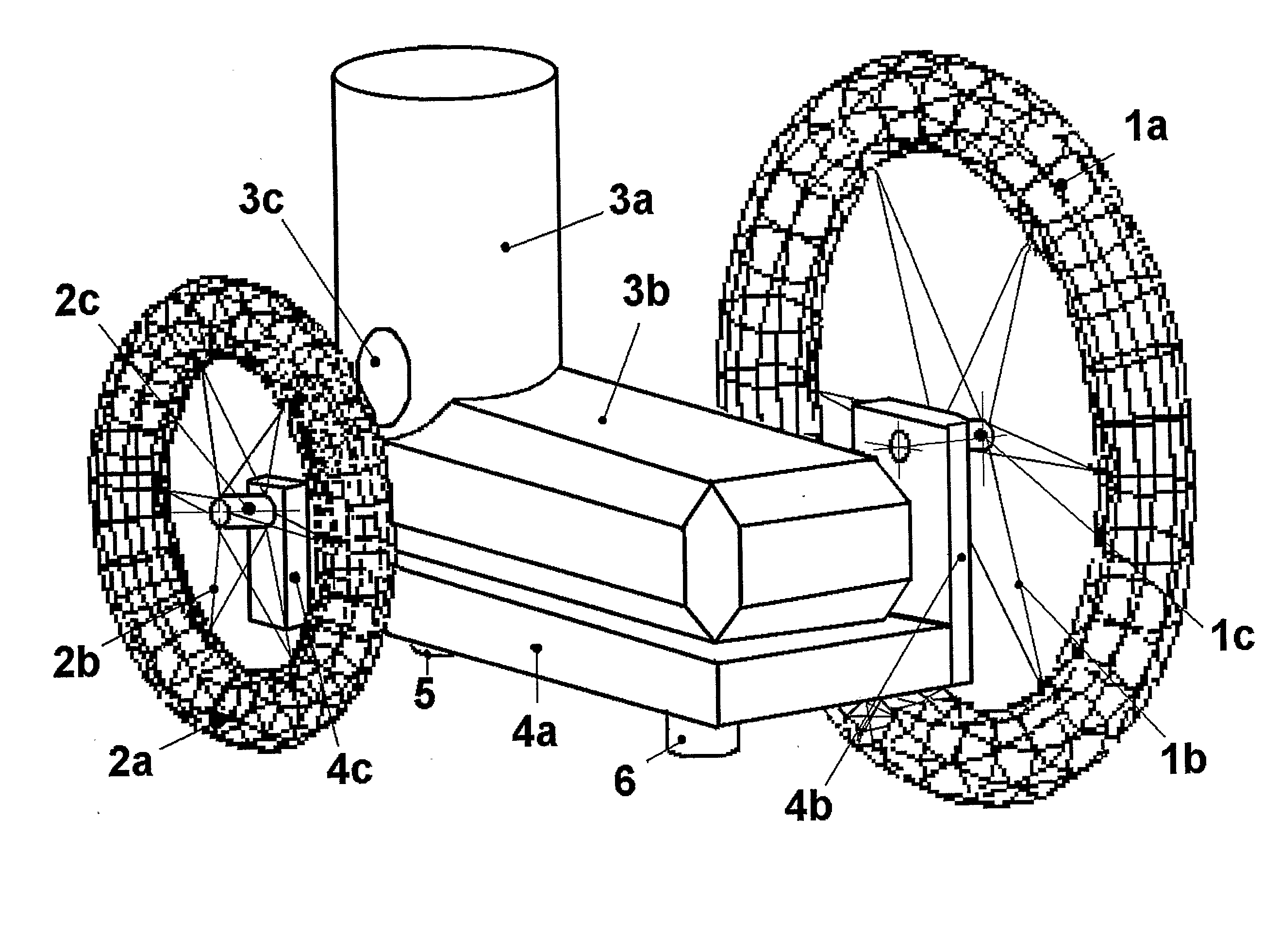
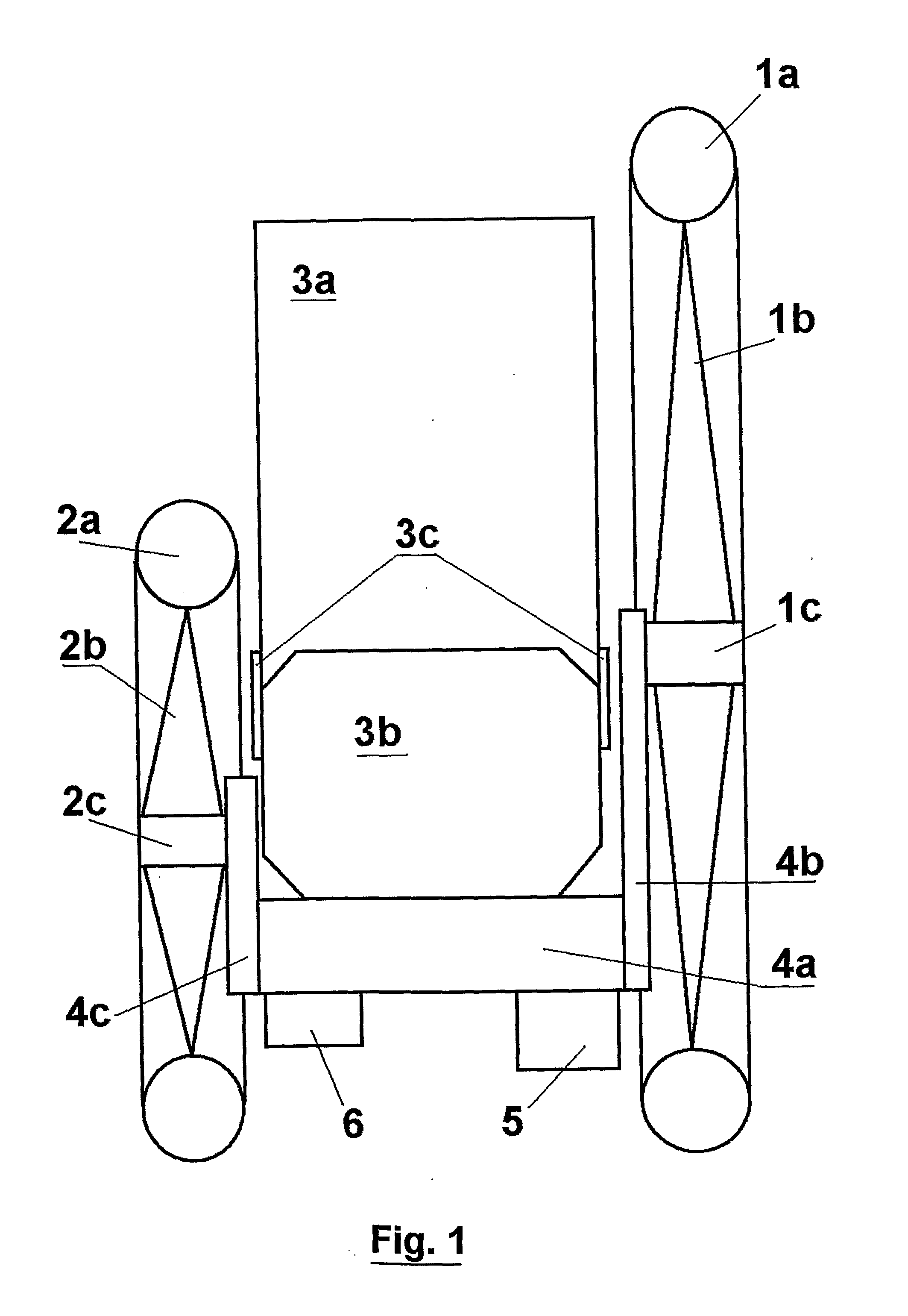
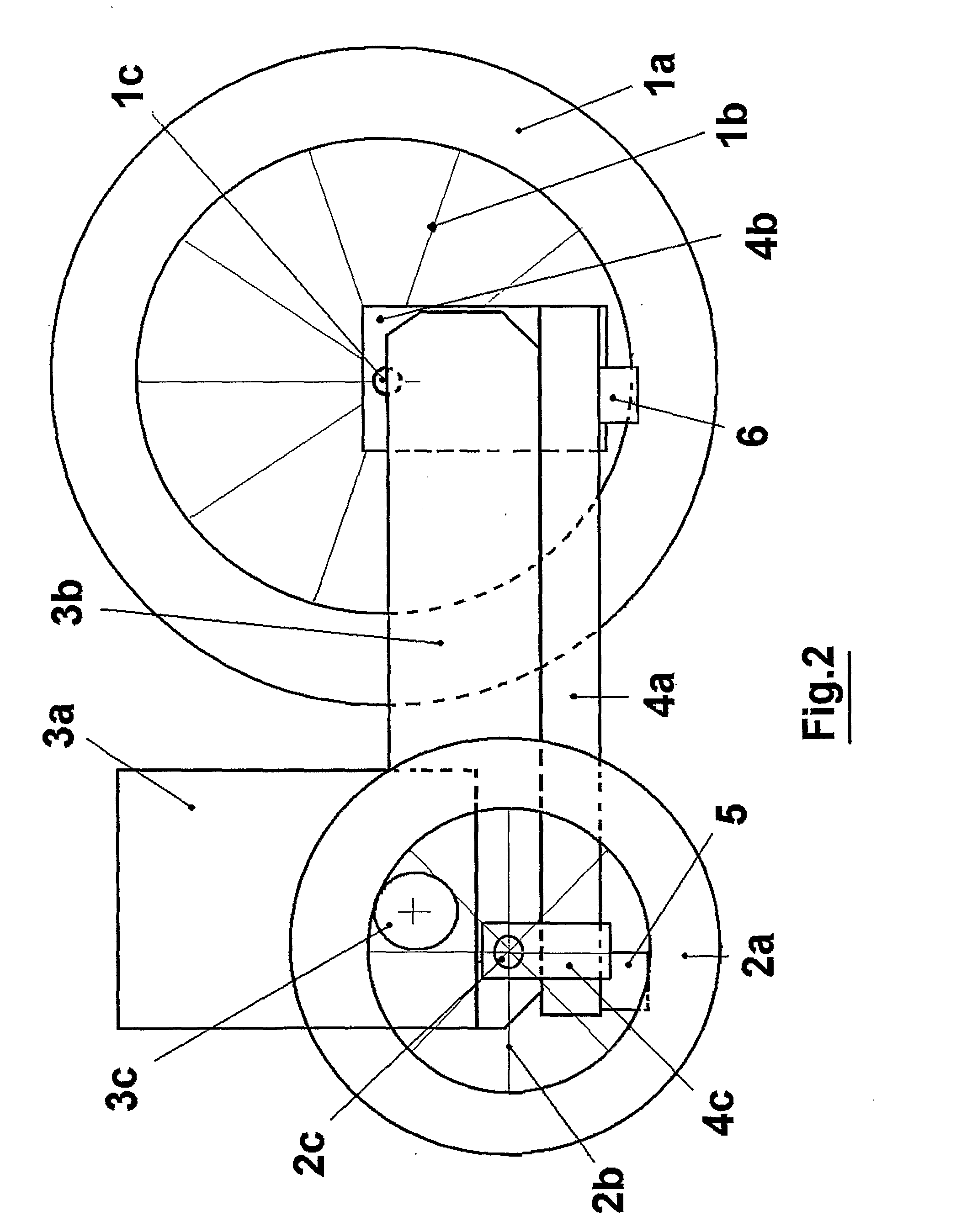
[0044]A typical way to manufacture the invention, for a skate with a front wheel of 200 mm and a rear wheel of 125 mm, consists of:
[0045]One commercial semi rigid shoe (3) molded in plastic material with cloth lining. The shoe is fixed with rivets onto the sole (4).
[0046]A support sole (4) in a light aluminum alloy molded by injection with reinforcement fins on the bottom, or made of carbon fiber. The sole is about 27 cm long, 8 cm wide and 7 mm thick. The angle brackets (4b) and (4c) are either of the same material and molded directly with the sole, or made in steel sheet 2 mm thick (with addition of reinforcements for rigidity 8 mm wide obtained by folding / stamping) and fixed by screws under the sole. This way angle bracket (4b) will have the following dimensions: a / base plate fixed under the sole 30×45 mm, b / triangular part normal to the sole and going up until the axis of the wheel: width 45 mm on the bottom and 25 mm at the level of the wheel's axis, height between base plate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com