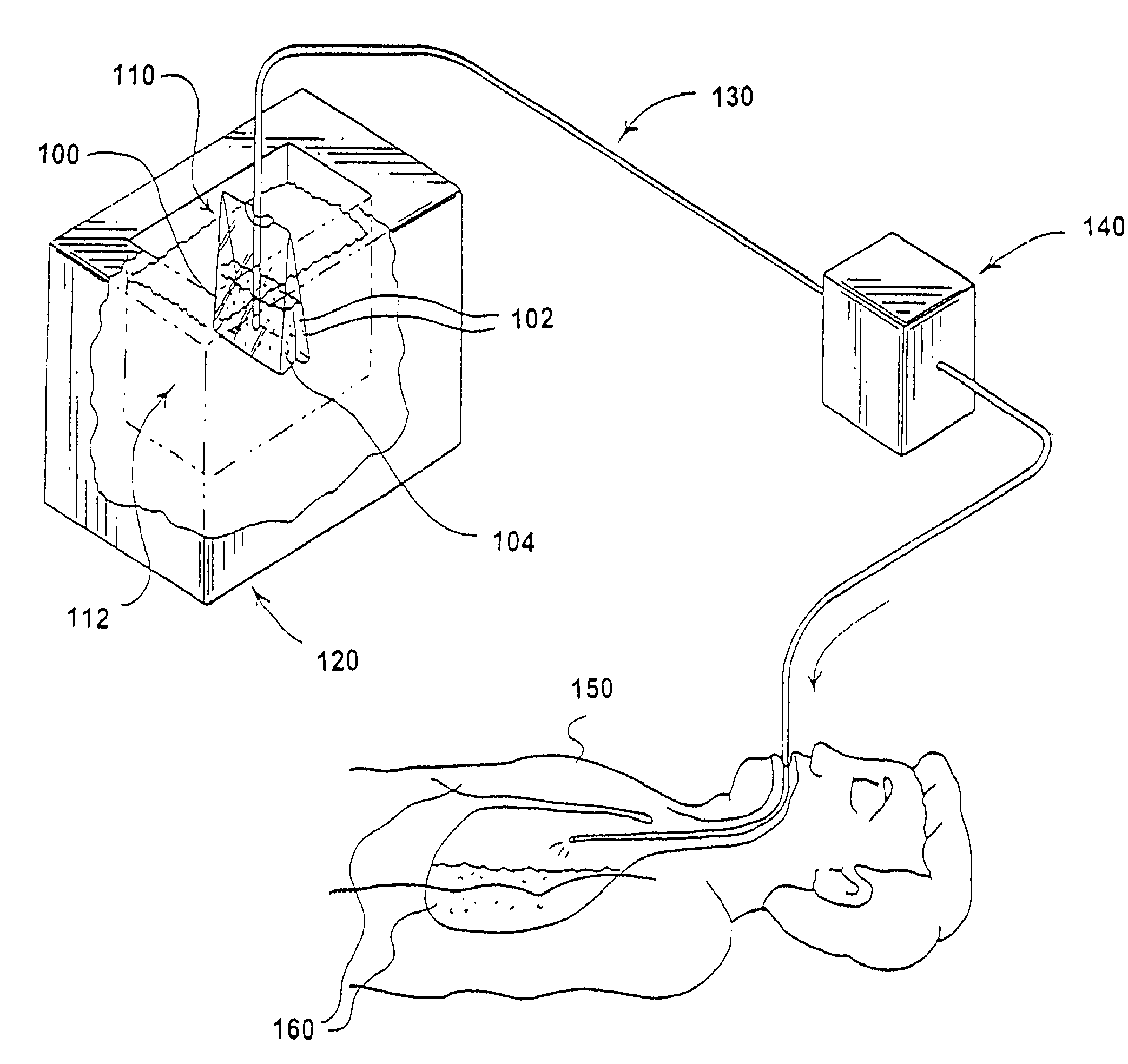
Method for inducing hypothermia
a hypothermia and hypothermia technology, applied in the field of hypothermia induction, can solve the problems of rapid and significant cooling, less than 2-4% survival rate of cardiac arrest patients, and tissue damage postponement of hypothermia, etc., to achieve rapid induction, improve patient outcome, and high protective
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0056]The first example is an ice slurry made from medical grade sodium chloride saline solution. This slurry is used to cool major blood vessels which flow to the head and the heart as with the aortic flush and neck injections described above. The movement of the slurry and the transport of cooled blood into the critical zones is enhanced by chest compressions.
[0057]The sodium chloride in aqueous solution serves as a freezing point depressant and alters the nature of the ice crystals formed in solution when the solution is cooled to its freezing point. Using about a 0.9% saline solution, a slurry is formed in a saline solution confined in a container or in a saline solution directly in a plastic medical injection bag ensuring sterility for the patient and convenience for the suppler. The solution is cooled to the point where ice crystals form. The freezing point for a 0.9% concentration, for example, of sodium chloride is −0.3° C. In contrast to pure water, the saline solution in t...
example 2
[0065]In another embodiment, cooling of the heart is achieved by charging the lungs with a phase-change slurry. Due to the almost intimate contact of the lungs with one side of the heart, charging the lungs greatly improves the rate of cooling of the heart. One example of a phase-change ice slurry used for the lungs is in the form of liquid perfluorocarbon or sodium chloride solution either of which may be used as the carrier of ice particles into the lungs. When oxygenated, the sodium chloride solution or perfluorocarbon liquid can also serve as a liquid ventilator or oxygen transporter.
[0066]During cardiac arrest, the lungs are effectively a dead air space and behave as an insulating layer that significantly reduces heat transfer to and from the heart, impeding cooling applied externally to the chest. Because the heart lies immediately behind the lungs, with only a thin membrane layer separating the two regions, the heart can be more rapidly cooled by using a coolant delivered to ...
example 3
[0083]Ham: surface cooling / no blood flow
[0084]As a means of obtaining an indication of a cool-down rate associated with external surface cooling only of a large tissue mass of size and surface area similar to the head, an experiment was conducted on a 9.8 pound ham (shank portion) with an imbedded bone mass. The ham was cooled down from an initial temperature of 29.4° C. to 16.7° C. in 30 minutes by direct full immersion in a tightly packed ice slush water bath at 0° C. with a thermocouple imbedded 3.5 inches into the thickest part of the ham. The resulting core cool-down rate was 0.42° C. / min. These results confirm that surface cooling only, in the absence of blood flow, falls far short of achieving the desired cooling.
[0085]FIG. 5 shows the results of the sphere heat conduction model applied to the ham compared with the measured ham core temperature history based on a sphere of radius b=3.5 inches for thermal diffusivities ranging from 1.5 to 5.0×10−7 m2 / S.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com