Method of forming an article
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
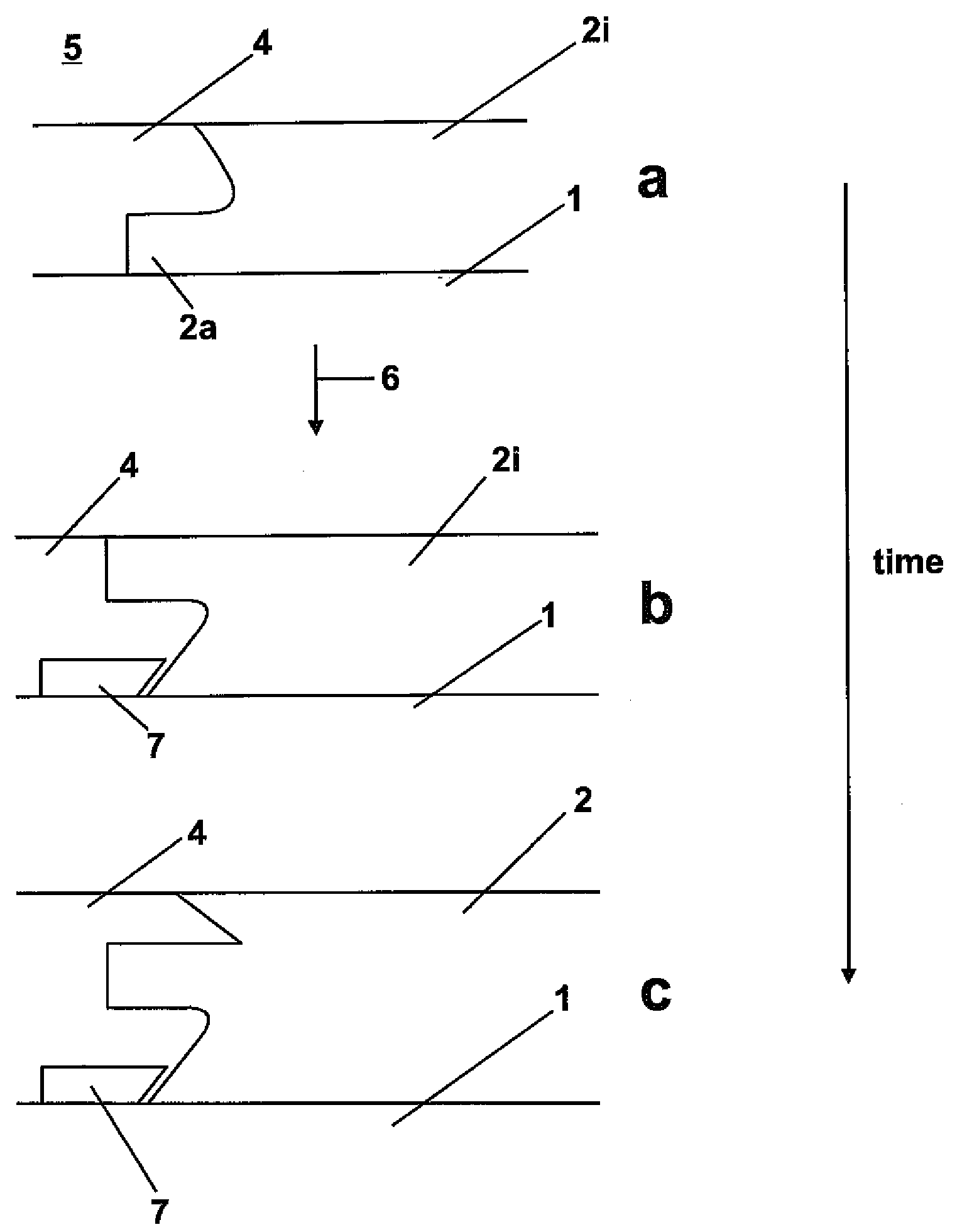
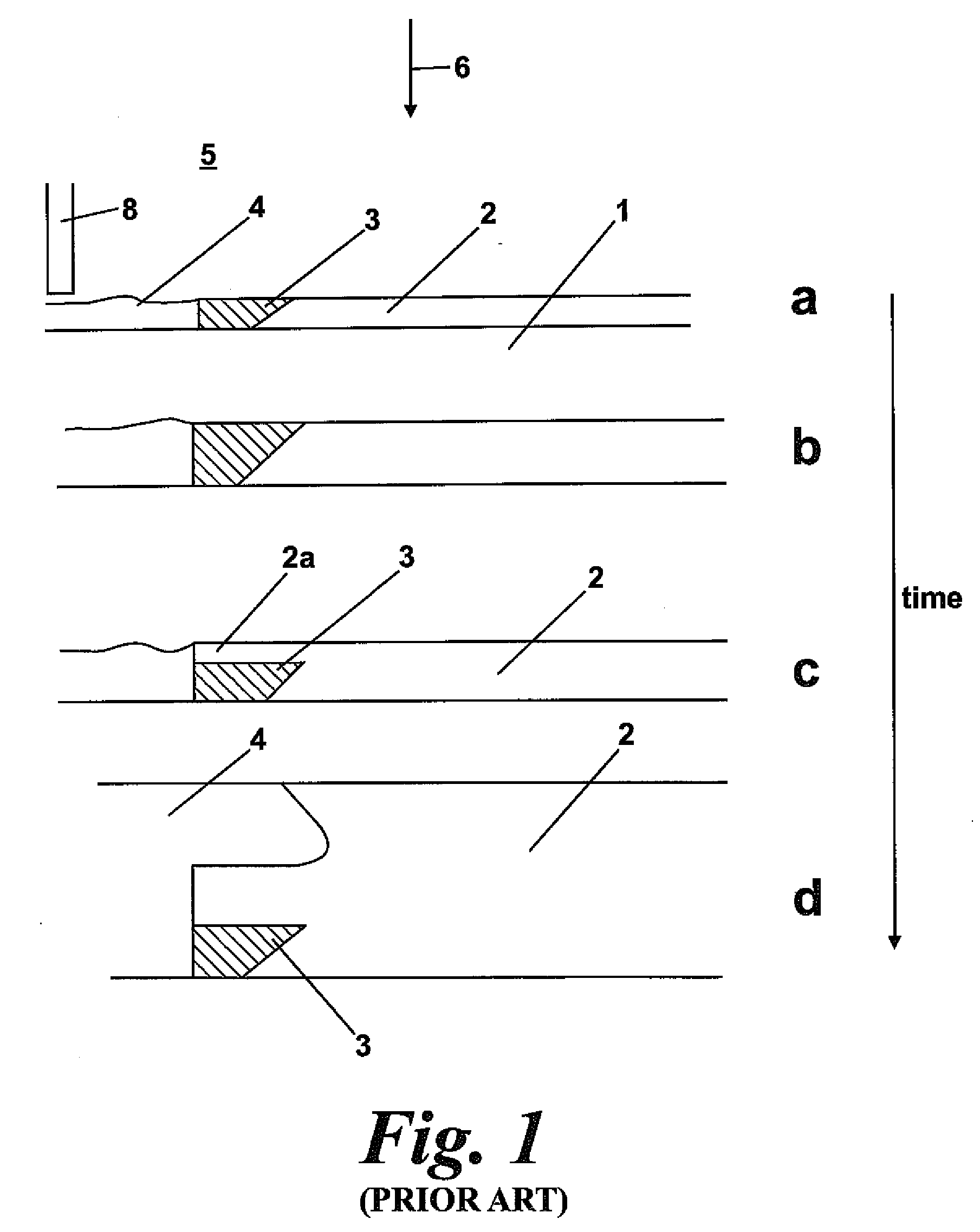
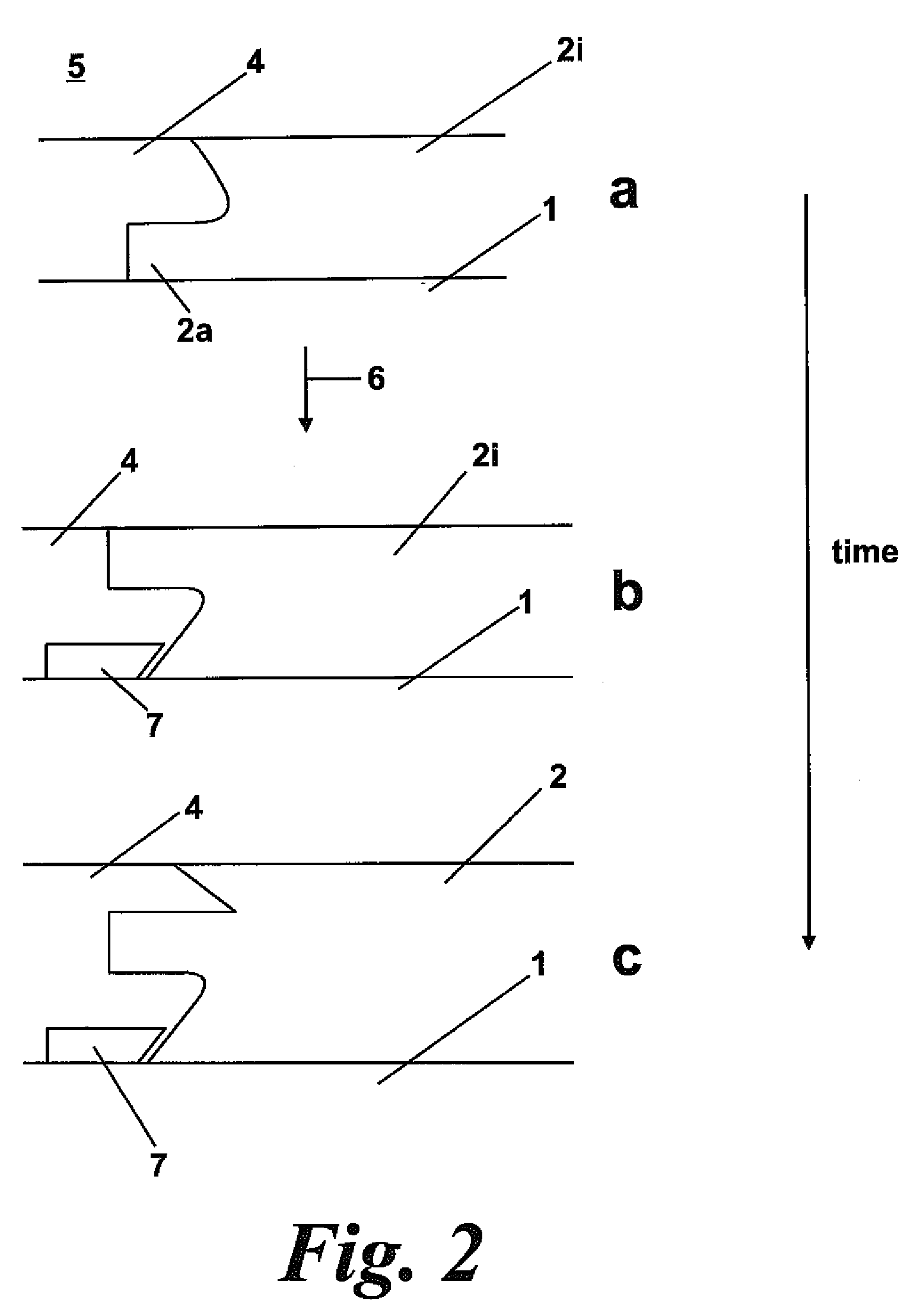
[0044]FIGS. 1a and b show intermediate stages of the powder bed SLS / SLM process. The start point is a base plate 1 and powder 4. A thin layer of powder is placed by various means familiar to those familiar with these machines across the base plate—e.g. by pushing powder from a powder source bin with a re-coater blade 8. A point source of energy 6 such as a laser beam is directed at the powder causing it to fuse to form a solid 2 being part of a desired 3 dimensional solid object. The base plate is indexed downwards and a fresh layer of powder created across the base plate and the solid 2 in build. The ambient 5 is an inert gas such as argon or is de-oxygenated air. Typically the base plate 2 is warmed to above ambient to enable easy thermal control. At 3 a support structure is being built. This is not a desired part of the solid object but is required by a subsequent part of the building process. Such supports can be custom designed or generated automatically by “Magics” software fr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Dimension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com