Method for making ultra-lightweigh structual metals
a technology of structual metals and metals, applied in the field of porous metallic objects, can solve the problems of poor rigidity of materials, high cost, and difficult to achieve complex three-dimensional shapes, and achieve the effect of better than expected physical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
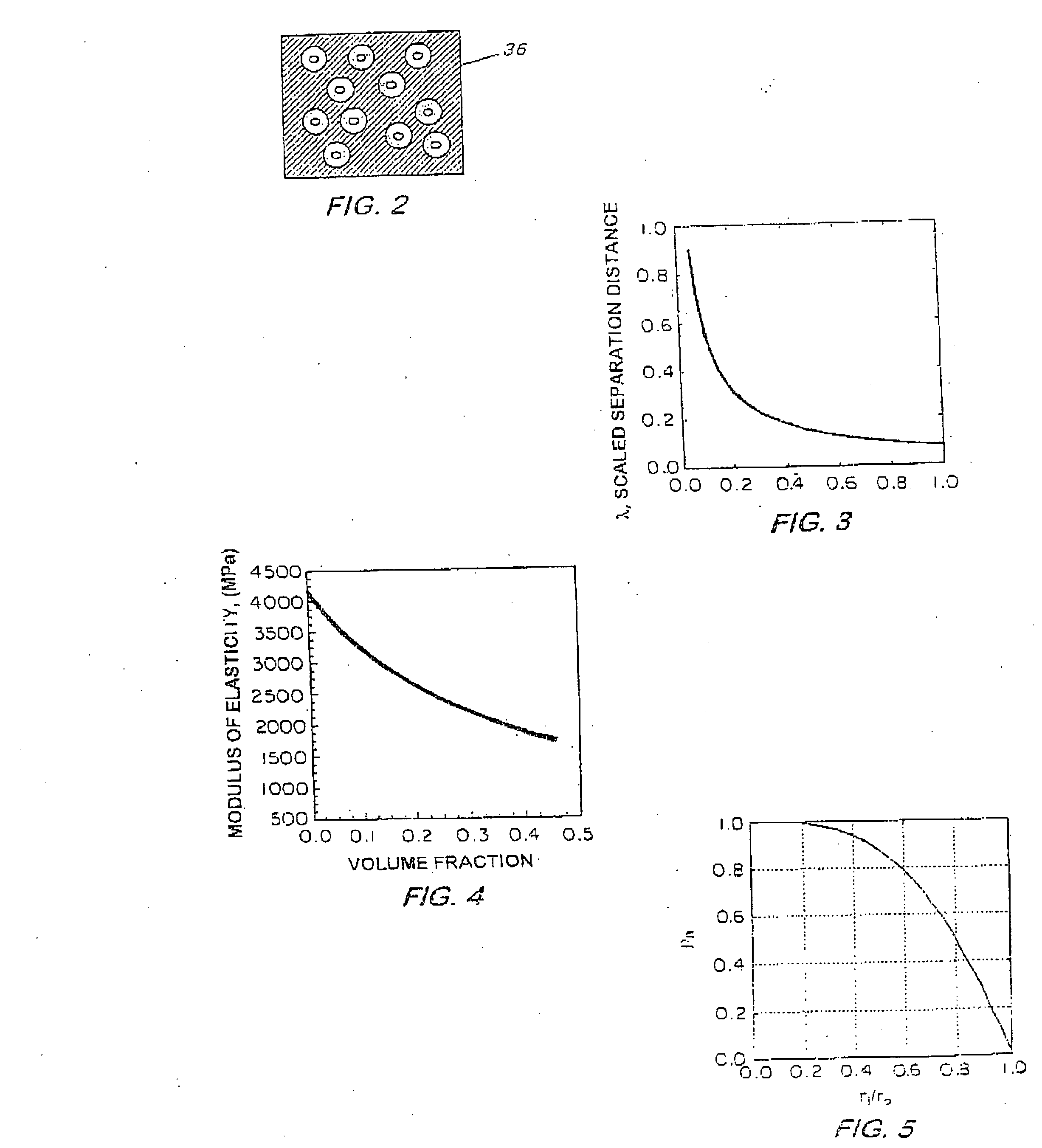
[0016]This invention pertains to a method for making a lightweight porous metallic product and to the product itself for eutectic, peritectic and monotectic systems, although only the eutectic case is discussed herein.
[0017]The invention is a novel approach for making under-dense or lightweight or porous metallic materials, especially into a net shape. The method involves mixing nanoscopic or microscopic hollow spheres into a metal alloy of at least two components during processing. The spheres are typically ceramic since most ceramics have a higher melting point than a metallic alloy. The spheres, however, can be non-ceramic, such as metallic, wherein the metal the sphere is made of has a melting point that is higher, and preferably substantially higher, such as several times higher, than the melting point of the matrix metal alloy and is generally immiscible in the matrix metal alloy. The hollow spheres can be ceramic coated with a metal or they can be metallic coated with a ceram...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com