III-V Hemt Devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
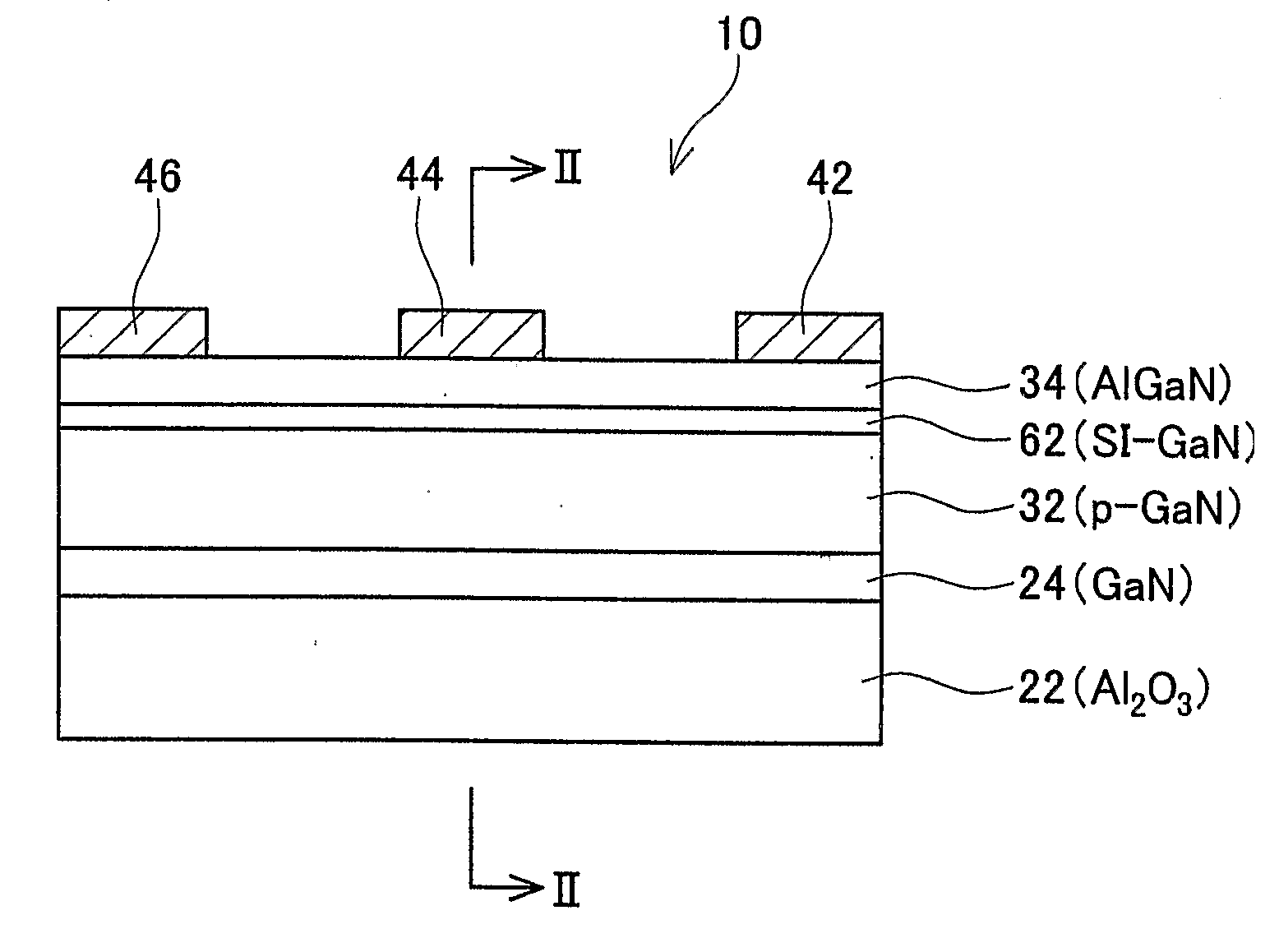
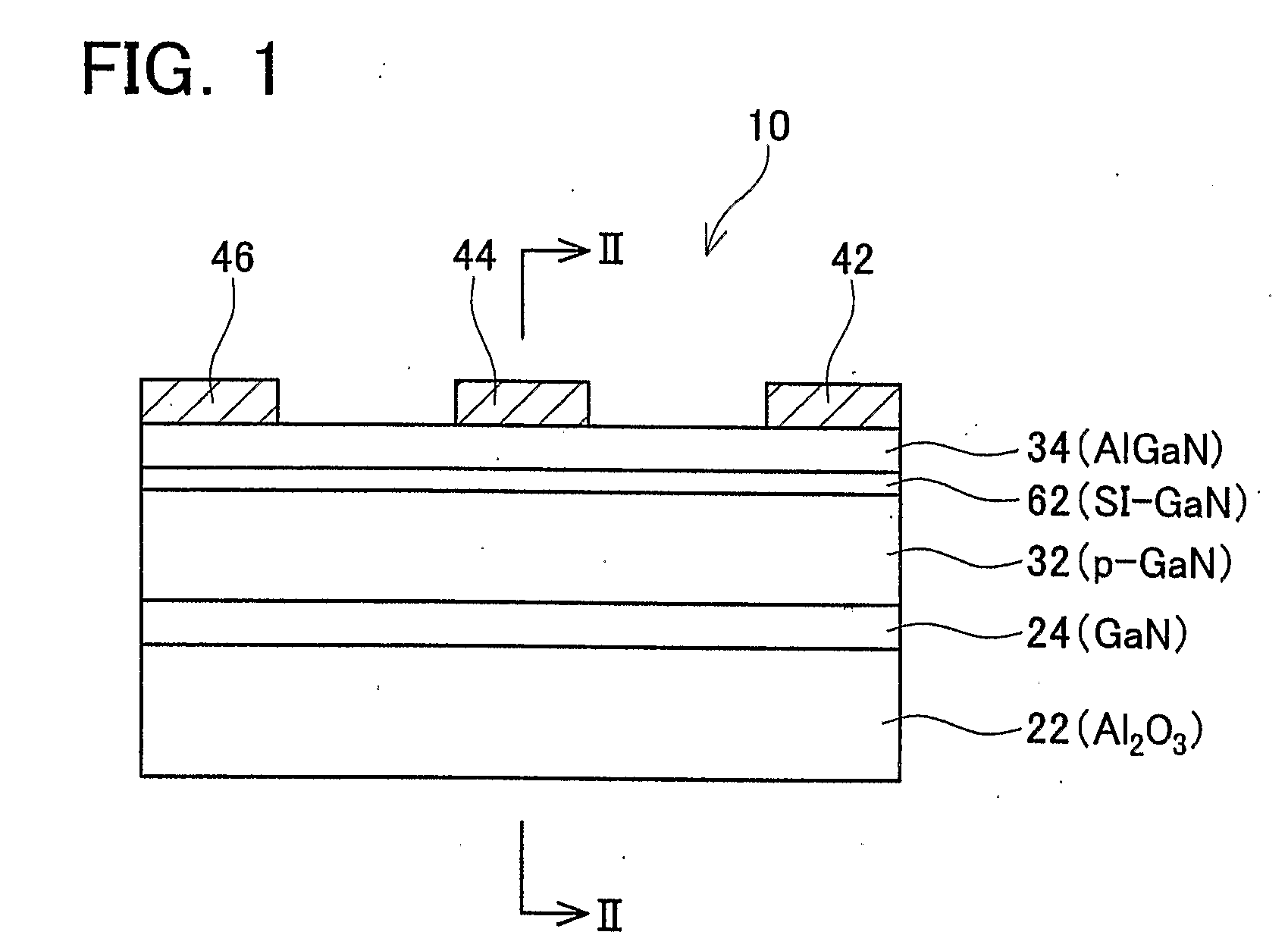
[0072]FIG. 1 schematically shows a cross-sectional view of essential parts of a semiconductor device 10 of the first embodiment.
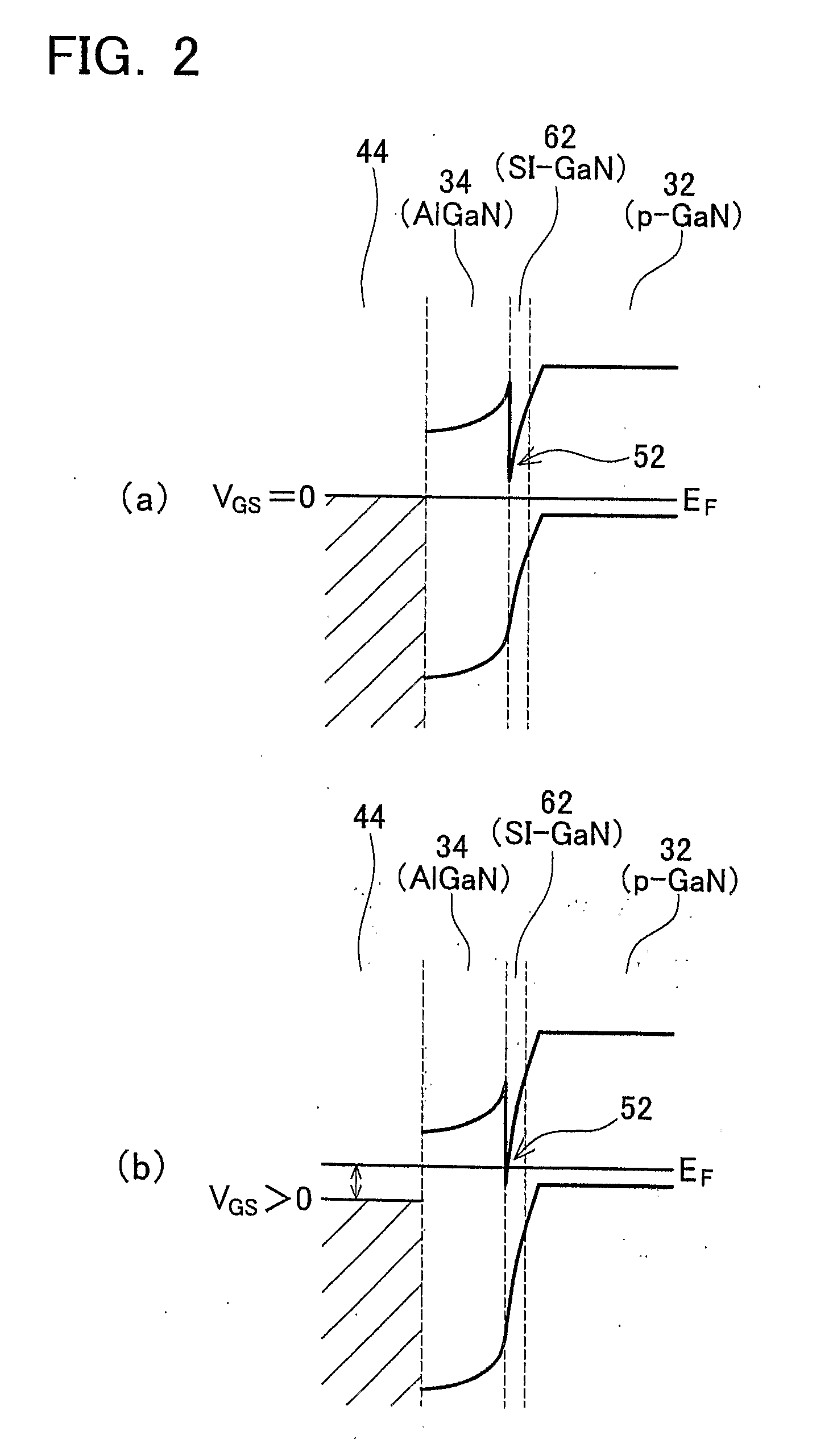
[0073] The semiconductor device 10 comprises a substrate 22 formed from sapphire (Al2O3) at the bottom side. Instead of sapphire, silicon carbide (SiC), gallium nitride (GaN), etc. may be used to form the substrate 22. A buffer layer 24 formed from gallium nitride (GaN) is formed on the substrate 22. A p-GaN layer 32 (an example of a first layer), an SI (Semi Insulated)-GaN layer 62 (an example of a middle layer), and an AlGaN layer 34 (an example of a second layer), are stacked on the buffer layer 24.
[0074] The SI-GaN layer 62 is located between the p-GaN layer 32 and the AlGaN layer 34. The p-GaN layer 32 has been doped with magnesium (Mg). Semiconducting crystals of the AlGaN layer 34 contain aluminum (Al), and the AlGaN layer 34 has a wider band gap than the p-GaN layer 32 and the SI-GaN layer 62.
second embodiment
[0094]FIG. 3 schematically shows a cross-sectional view of essential parts of a semiconductor device 100.
[0095] The semiconductor device 100 comprises a substrate 122 formed from sapphire (Al2O3) at the bottom side. Instead of sapphire, silicon carbide (SiC) or gallium nitride (GaN) may also be used to form the substrate 122. A buffer layer 124 formed from gallium nitride (GaN) is formed on the substrate 122. A GaN layer 132 (an example of a first layer), and an n-AlGaN layer 134 (an example of a second layer), are stacked on the buffer layer 124.
[0096] The n-AlGaN layer 134 has been doped with silicon (Si). Semiconducting crystals of the n-AlGaN layer 134 contain aluminum (Al), and the n-AlGaN layer 134 has a wider band gap than the GaN layer 132.
[0097] A gate electrode 144 (an example of an electrode) formed from a stacked structure of nickel (Ni) and gold (Au) is disposed at a center, relative to the page, of a top surface of the n-AlGaN layer 134. The gate electrode 144 direc...
third embodiment
[0113]FIG. 5 schematically shows a cross-sectional view of essential parts of a semiconductor device 200 of a third embodiment.
[0114] The semiconductor device 200 comprises a substrate 222 formed from sapphire (Al2O3) at a bottom side. Instead of sapphire, silicon carbide (SiC) or gallium nitride (GaN) may also be used to form the substrate 222. A buffer layer 224 formed from gallium nitride (GaN) is formed on the substrate 222. A p-GaN layer 232 (an example of a first layer), an n-AlGaN layer 233 (an example of a second layer), and a p-AlGaN layer 235 (an example of a surface layer), are stacked on the buffer layer 224.
[0115] The p-GaN layer 232 and the p-AlGaN layer 235 have been doped with magnesium (Mg). The n-AlGaN layer 233 has been doped with silicon (Si). Semiconducting crystals of the n-AlGaN layer 233 and the p-AlGaN layer 235 contain aluminum (Al), and the n-AlGaN layer 233 and the p-AlGaN layer 235 have a wider band gap than the p-GaN layer 232.
[0116] A gate electrode...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com