System and method for server security and entitlement processing
a server and entitlement processing technology, applied in the field of server security mechanisms, can solve the problems of customer and system integrator frustration, security mechanism not suited to easy modification of rules, and little or no understanding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
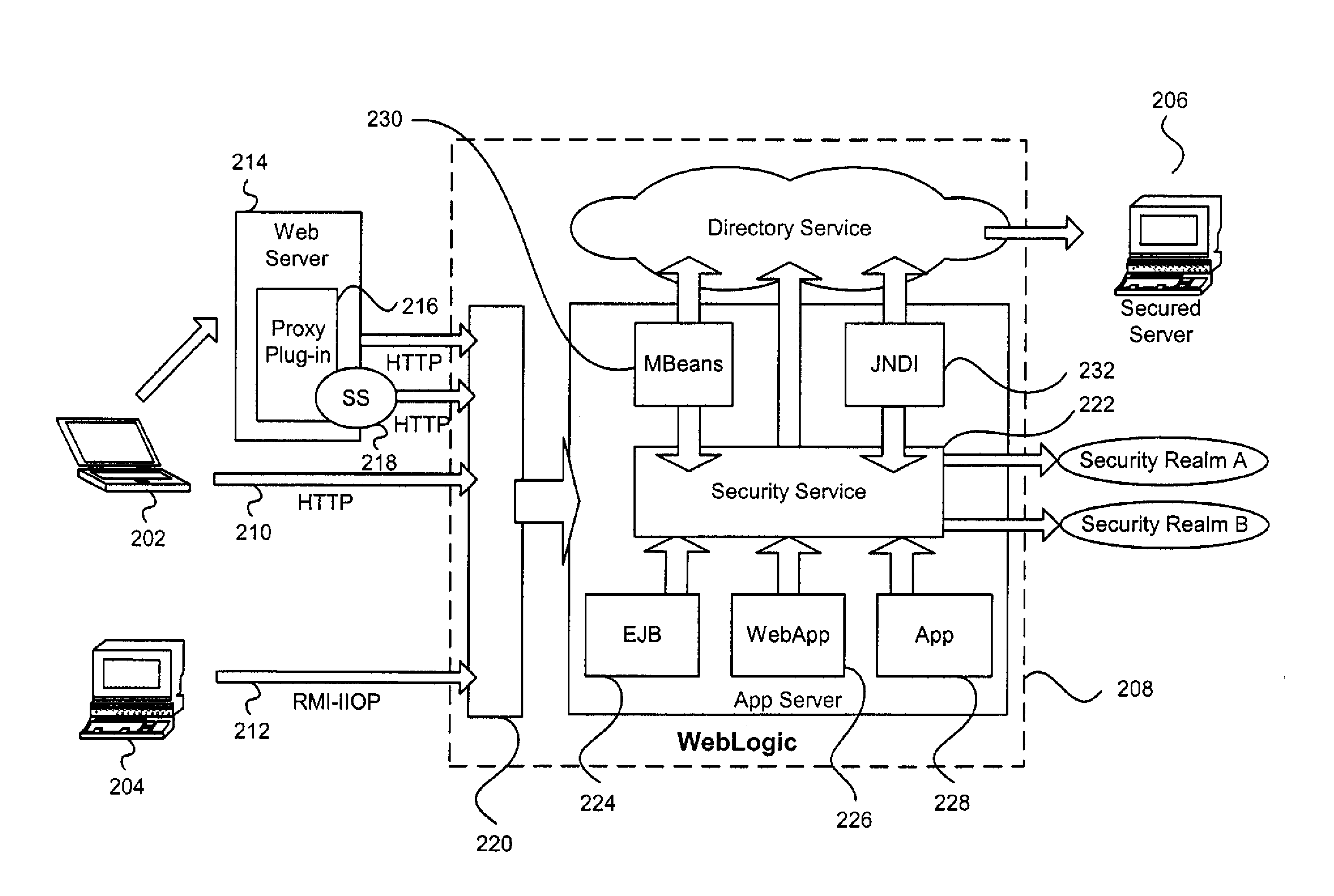
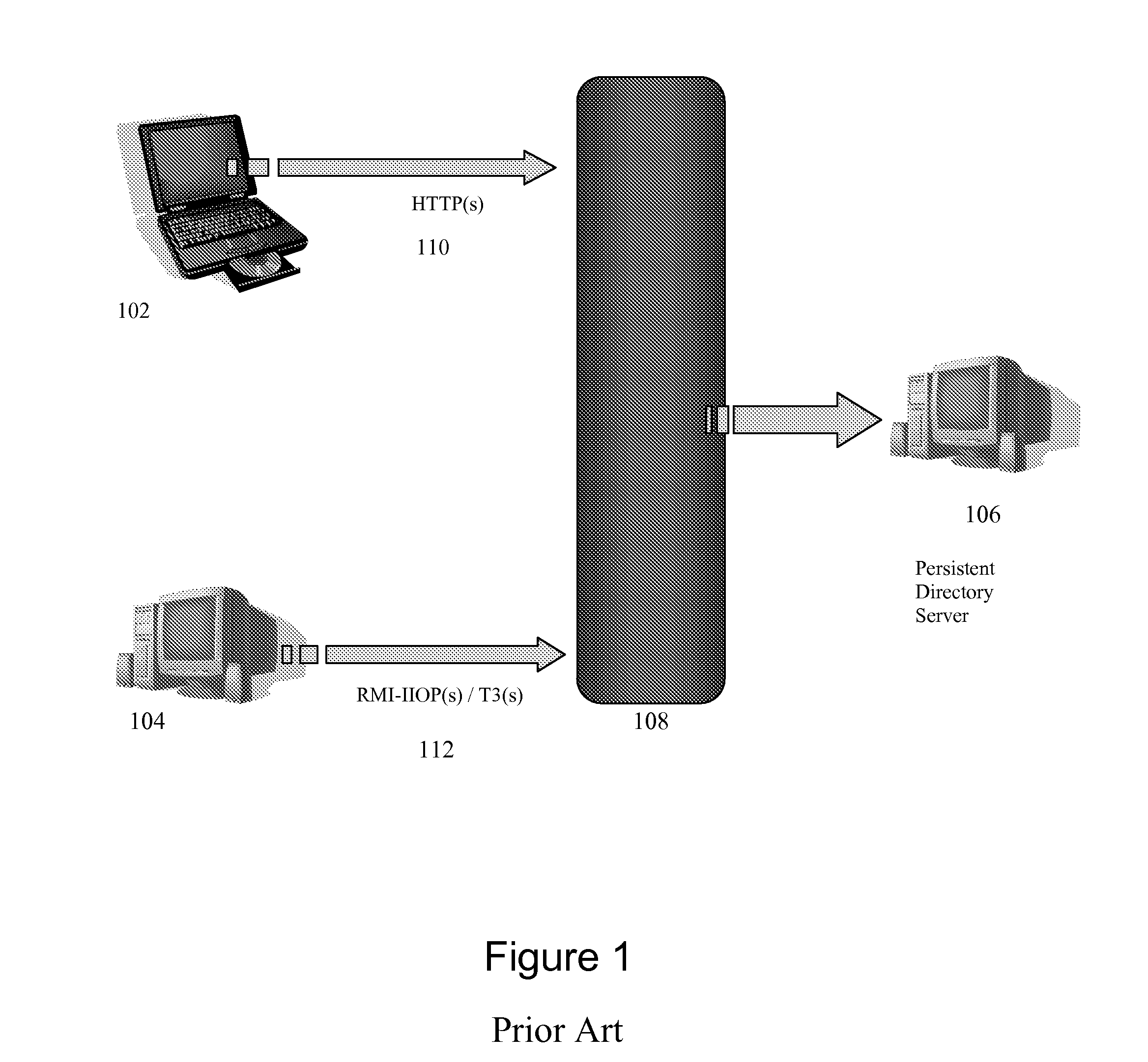
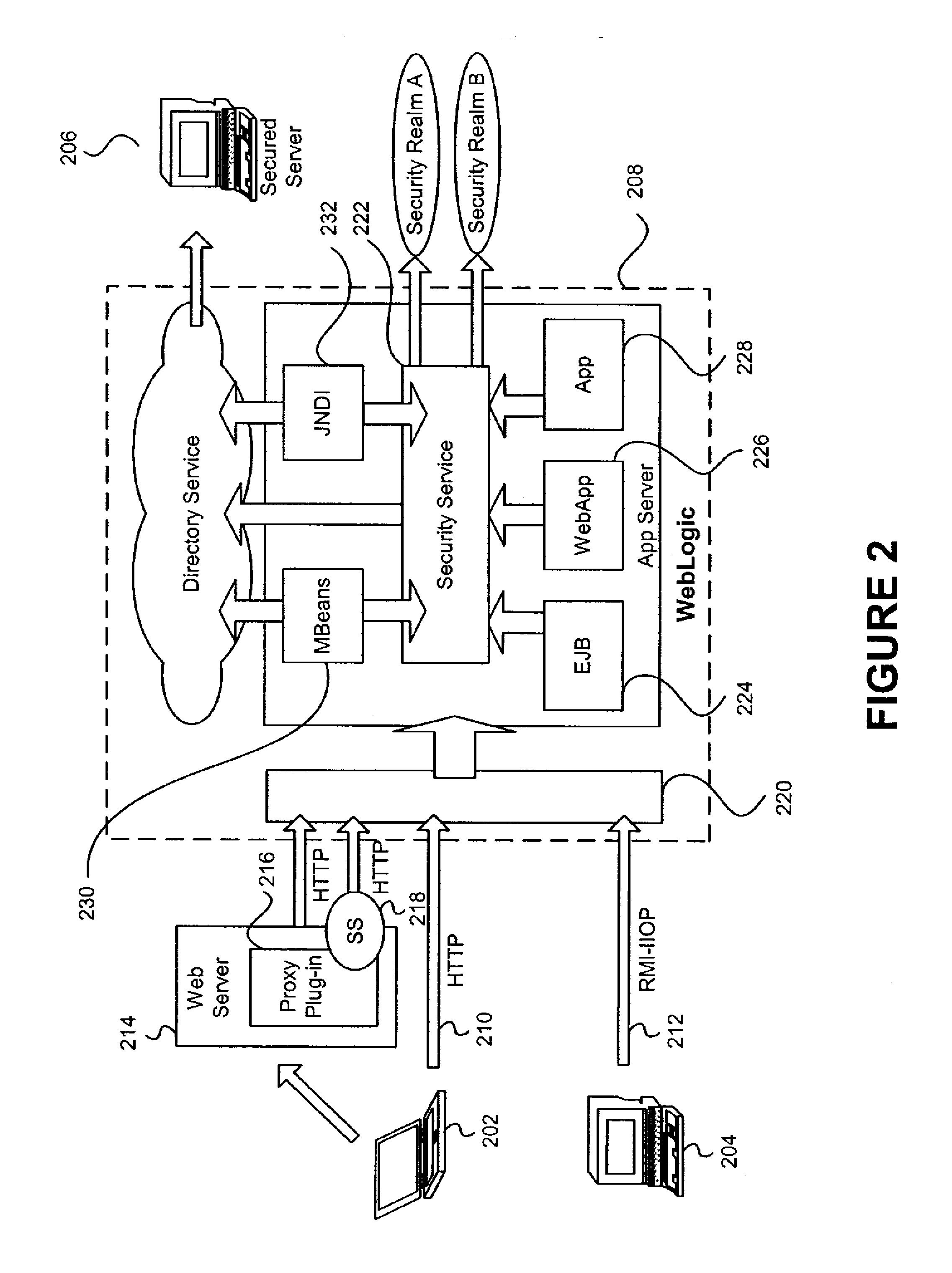
[0035] An embodiment of the invention includes a security architecture that provides for server security and entitlement processing, that allows security and business logic plugins to be inserted into a security service hosted by a server, and that can be used to control access to one or more secured resources on that server, on another server within the security domain or realm, or between security realms. The security service acts as a focal point for security enforcement and access rights determination, and information used within one login process can flow automatically to other login processes, allowing for single sign or security enforcement.
[0036] Except for the new terms that are defined below, the terms used in this document are consistent with terminology as defined in standard texts on Java, Enterprise Java Beans, WebLogic Server, and other generally accepted security concepts. [0037] access control—the restriction of access to resources to prevent its unauthorized use. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com