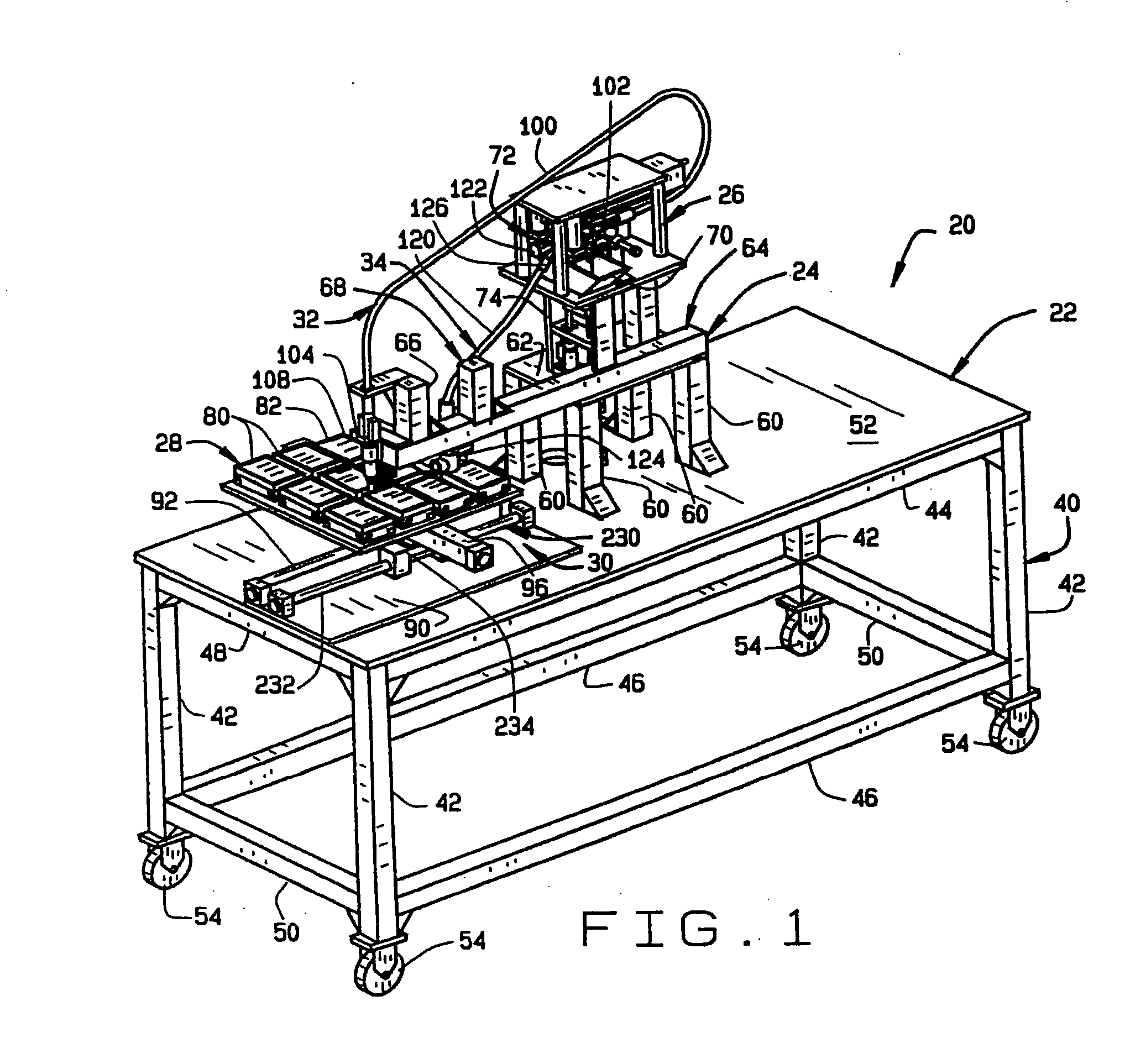
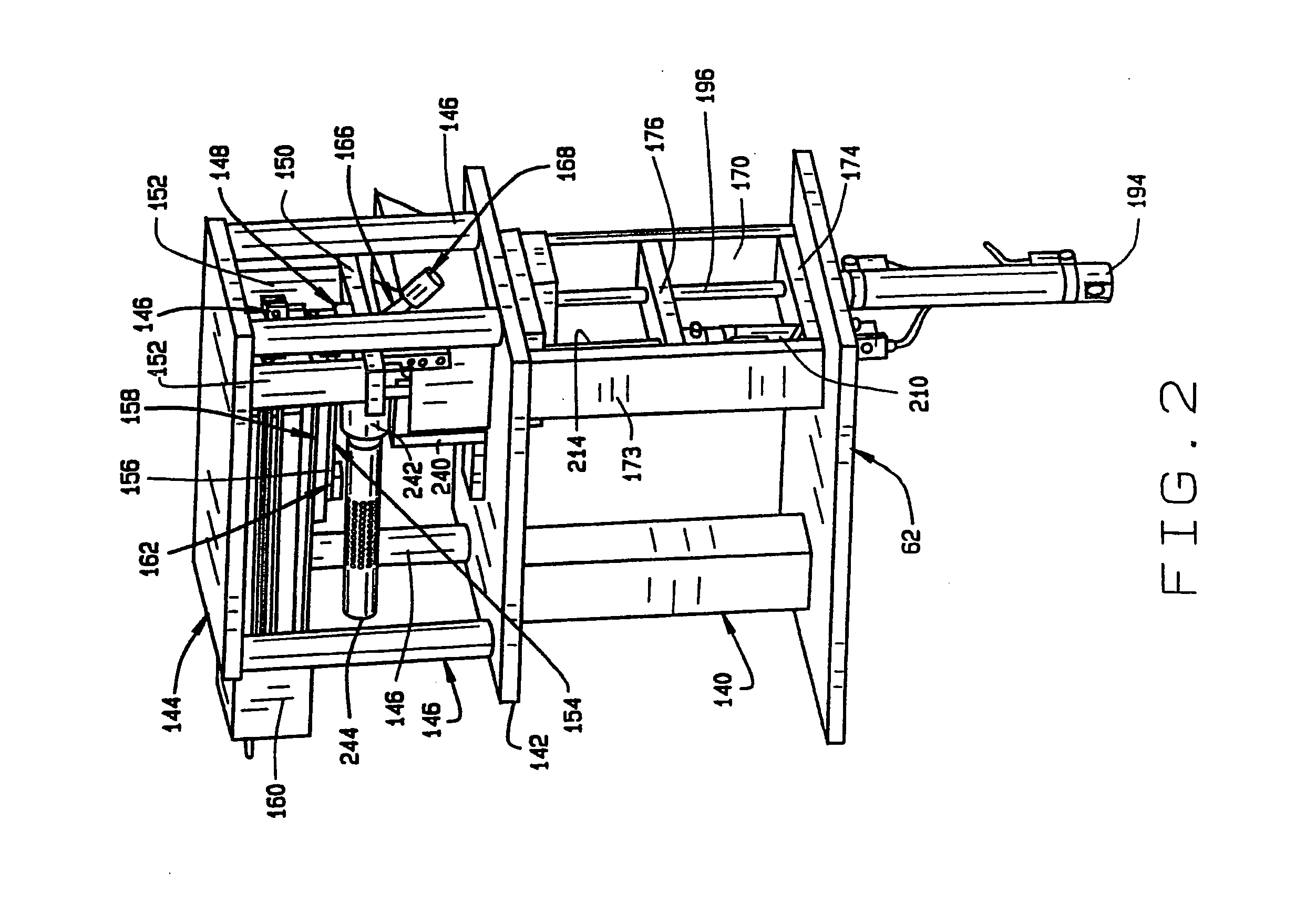
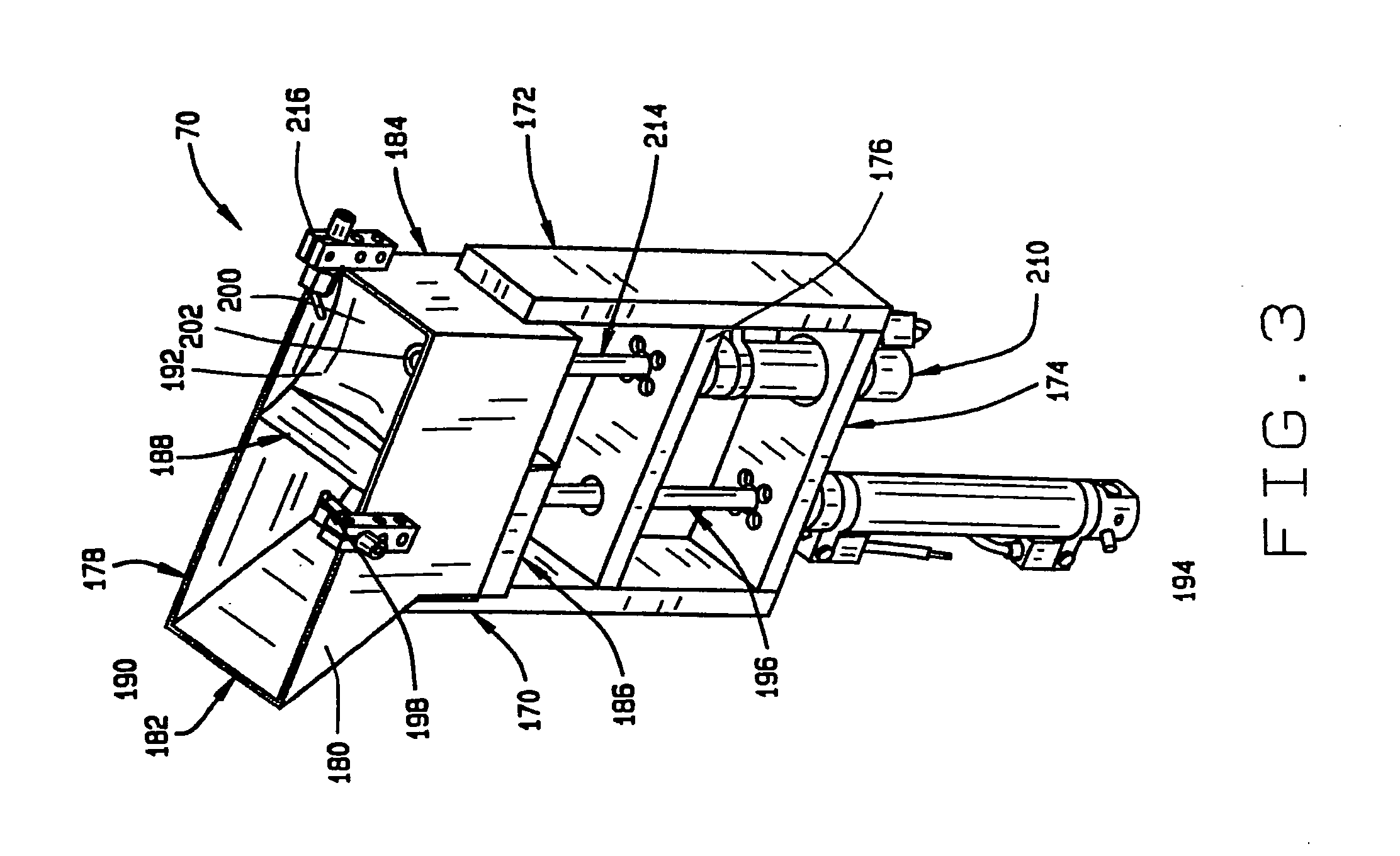
High throughput screening of fatty acid composition
a fatty acid composition, high throughput technology, applied in the direction of instruments, material analysis, sorting, etc., can solve the problems of laborious and time-consuming, and achieve the effect of reducing labor intensity, accelerating the process of evaluating a population, and facilitating the selection process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0109] This example demonstrates the use of the screening methods of the present invention in a program for selection and bulking of Low Linolenic Acid soybeans.
[0110] Soybean is the most valuable legume crop, with many nutritional and industrial uses due to its unique chemical composition. Soybean seeds are an important source of vegetable oil, which is used in food products throughout the world. The relatively high level (usually about 8%) of linolenic acid (18:3) in soybean oil reduces its stability and flavor. Hydrogenation of soybean oil is used to lower the level of linolenic acid (18:3) and improve both stability and flavor of soybean oils. However, hydrogenation results in the production of trans fatty acids, which increases the risk for coronary heart disease when consumed. The development of low linolenic acid soybeans has been complicated by the quantitative nature of the trait. The low linolenic acid soybean varieties that have been developed have been found to yield po...
example 2
[0116] This example demonstrates the use of the screening methods of the present invention in a program for selecting and bulking of Stearidonic Acid (SDA) soybeans.
[0117] Tissue samples were collected from soybean varieties identified as 0% SDA, 15% SDA, 20% SDA, and 30% SDA. The tissue samples were contacted with solvent to produce a mixture of fatty acid esters and the fatty acid esters were then separated and analyzed using fast gas chromatography as described in Example 1. The fatty acid profiles of the SDA soybeans are shown in Table 3.
TABLE 3Fast GC Method and SDA SoybeansFatty acid (% relative)0% SDA15% SDA20% SDA30% SDAC14 Myristic acid00.30.30.3C16 Palmitic acid11.912.512.713.1C18 Steric acid3.83.73.73.7C18:1n9 Oleic acid20.31517.115.3C18:2n6 Linoleic acid50.83228.217C18:3n6 gamma Linolenic—3.84.84.6C18:3 Linolenic acid7.711.110.512.2C18:4n3—131626.8OctadecatetraenoicC20 Arachidonic acid0.60.80.60.7C20:1n9 Eicosenoic acid0.20.40.30.4C22 Behenic acid0.30.30.30.4C24 Ligno...
example 3
[0118] This example demonstrates the use of the screening methods of the present invention in a program for selection and bulking of High Stearic Acid soybeans.
[0119] Tissue samples were collected from soybean varieties identified as high stearic acid soybeans. The tissue samples were contacted with solvent to produce a mixture of fatty acid esters and the fatty acid esters were then separated and analyzed using fast gas chromatography as described in Example 1. The fatty acid profiles of the high stearic acid soybeans are shown in Table 4.
TABLE 4High Stearic Acid SoybeansFatty acid (% relative)Fast GC methodC14 Myristic acid0C16 Palmitic acid8.9C18 Steric acid20.3C18:1n9 Oleic acid21.4C18:2n6 Linoleic acid37.8C18:3 Linolenic acid3.1C20 Arachidonic acid1.8C20:1n9 Eicosenoic acid0.1C22 Behenic acid1.0C24 Lignoceric acid0.2
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| oblique angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| fatty acid composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com