Interventional medical closure device
a medical closure and medical technology, applied in the field of interventional medical closure devices, can solve the problems of prolonging the time, affecting the healing effect of patients, and affecting the healing effect of patients, and achieve the effect of reducing the trauma caused upon creation and being simple yet effectiv
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
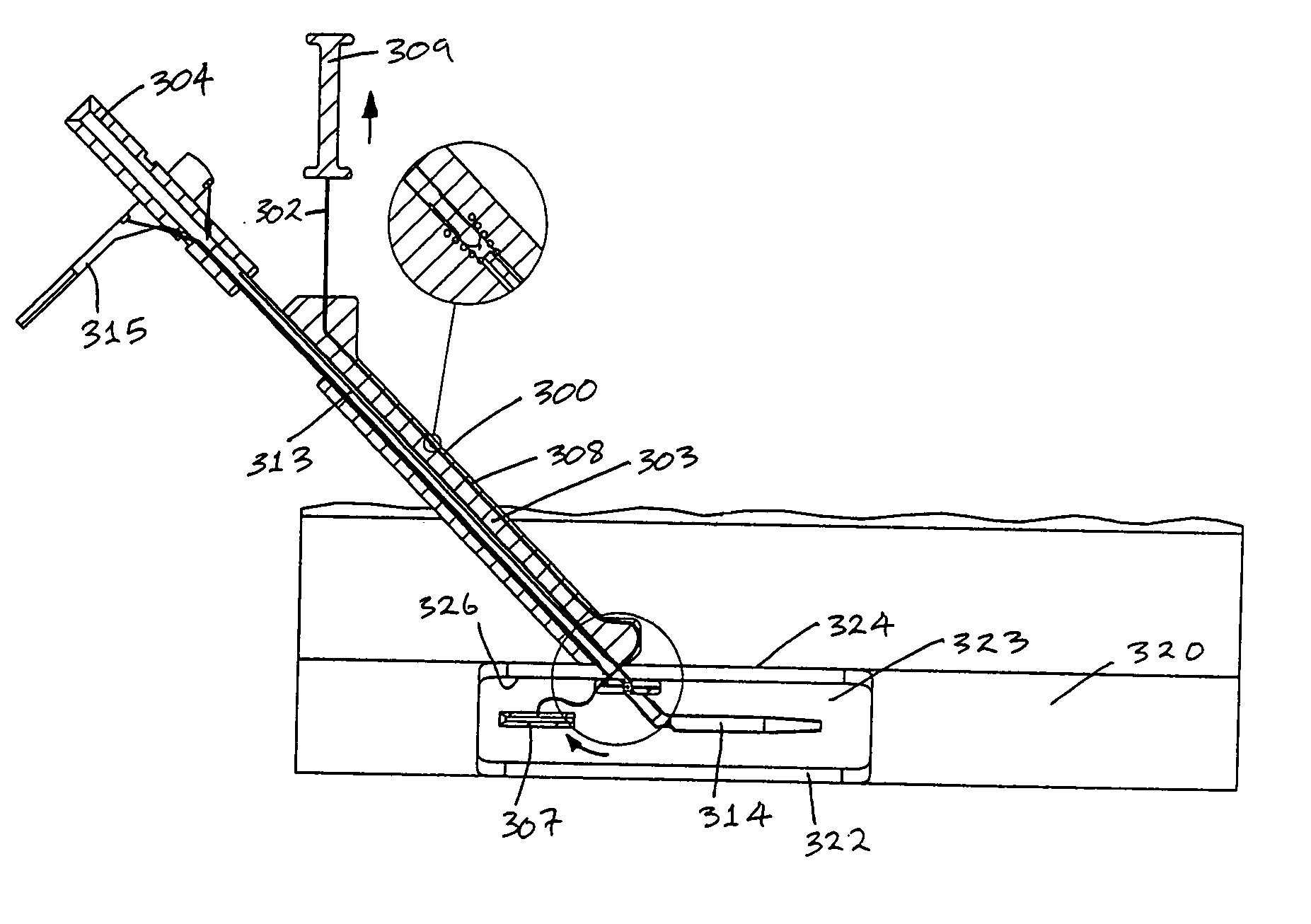
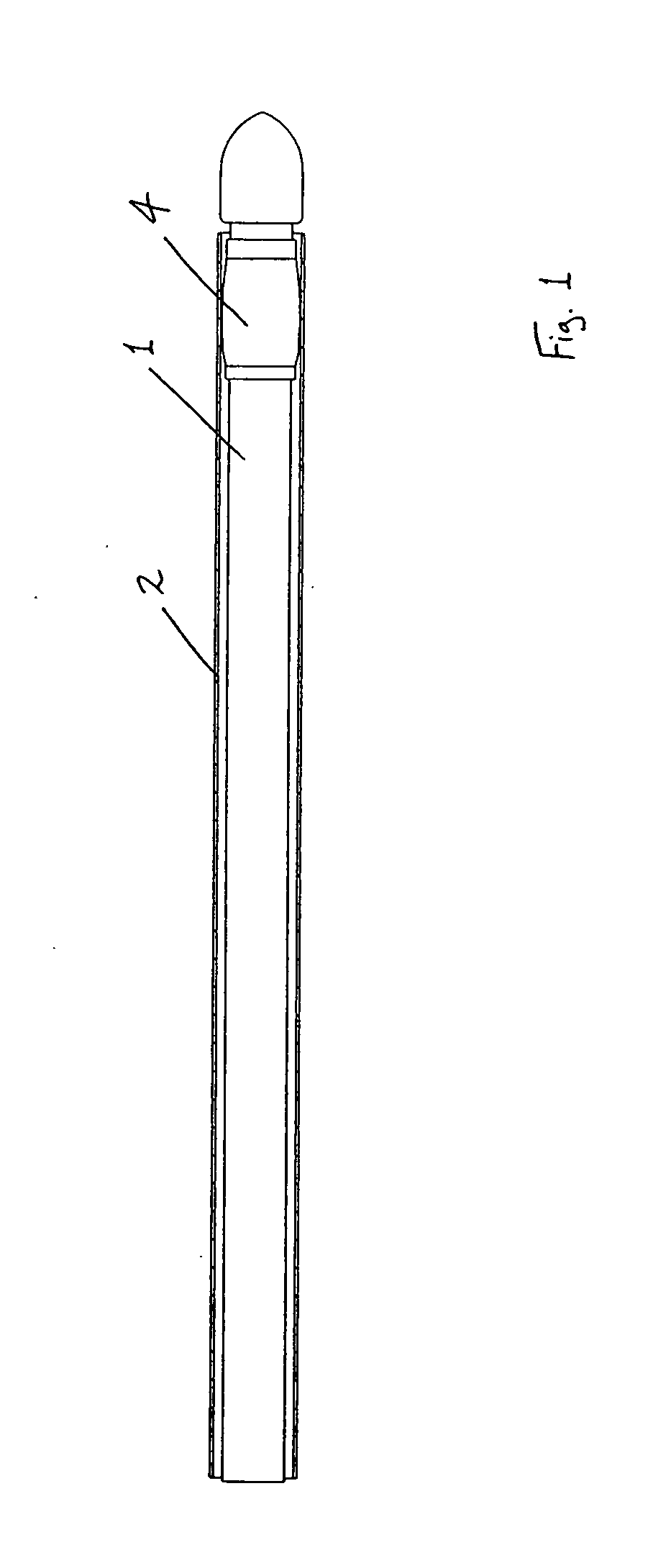
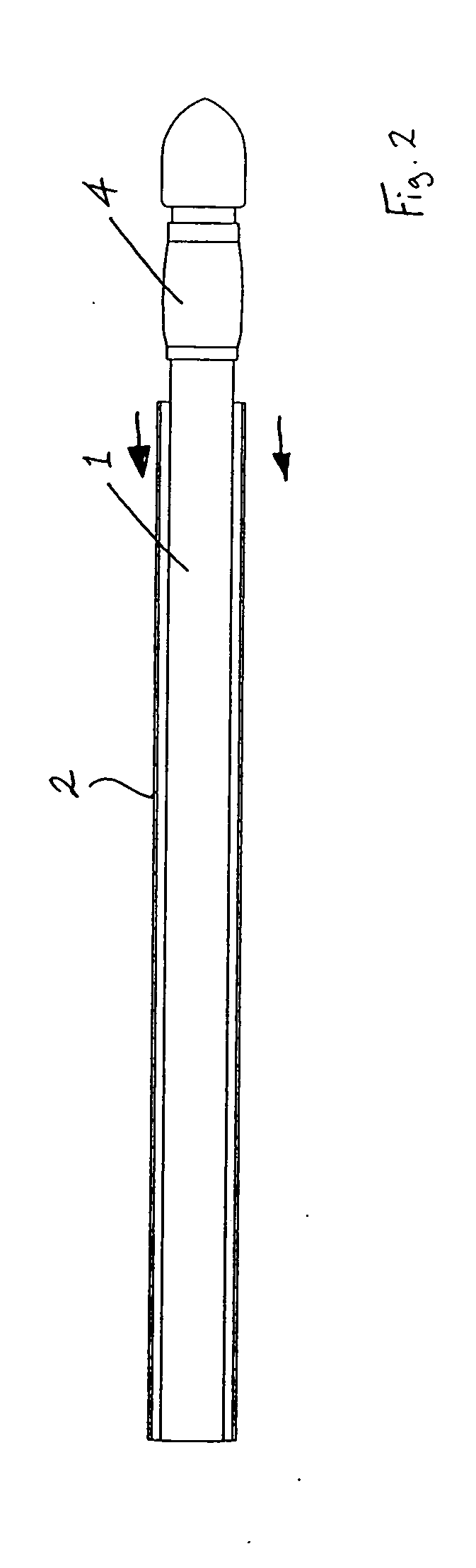
[0183] Referring to the drawings and initially to FIGS. 1 to 35(a) thereof, there is illustrated a medical device according to the invention, which is suitable for use in accessing an interior of a body part. The device is particularly suitable for accessing the interior of a blood vessel 6. The medical device comprises an elongate engagement element 1, a protective sheath 2, as illustrated in FIGS. 1 to 5, and an incising element 3, as illustrated in FIGS. 6 to 9.
[0184] The engagement element 1 comprises a retaining element, which is provided in this case as a balloon part 4, which is expandable, in this case inflatable, from a low-profile delivery configuration (FIGS. 1 and 2) to a deployed configuration (FIGS. 3 and 4), and is returnable, in this case deflatable, from the deployed configuration to the delivery configuration (FIG. 5). In the delivery configuration, the engagement element 1 is piercable through a flap 7 of tissue wall and through a wall 8 of the blood vessel 6. In...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com