Nucleolin-mediated cancer diagnostics and therapy
a cancer and nucleotide technology, applied in the field of nucleotide-mediated cancer diagnostics and therapy, can solve the problems of unclear function of endostatin, and achieve the effects of increasing the receptiveness of a target cell, enhancing the anti-angiogenesis effect of angiogenesis inhibitor, and increasing the efficacy of angiogenesis inhibitors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example one
[0083] Nucleolin is an Endostatin-Binding Protein
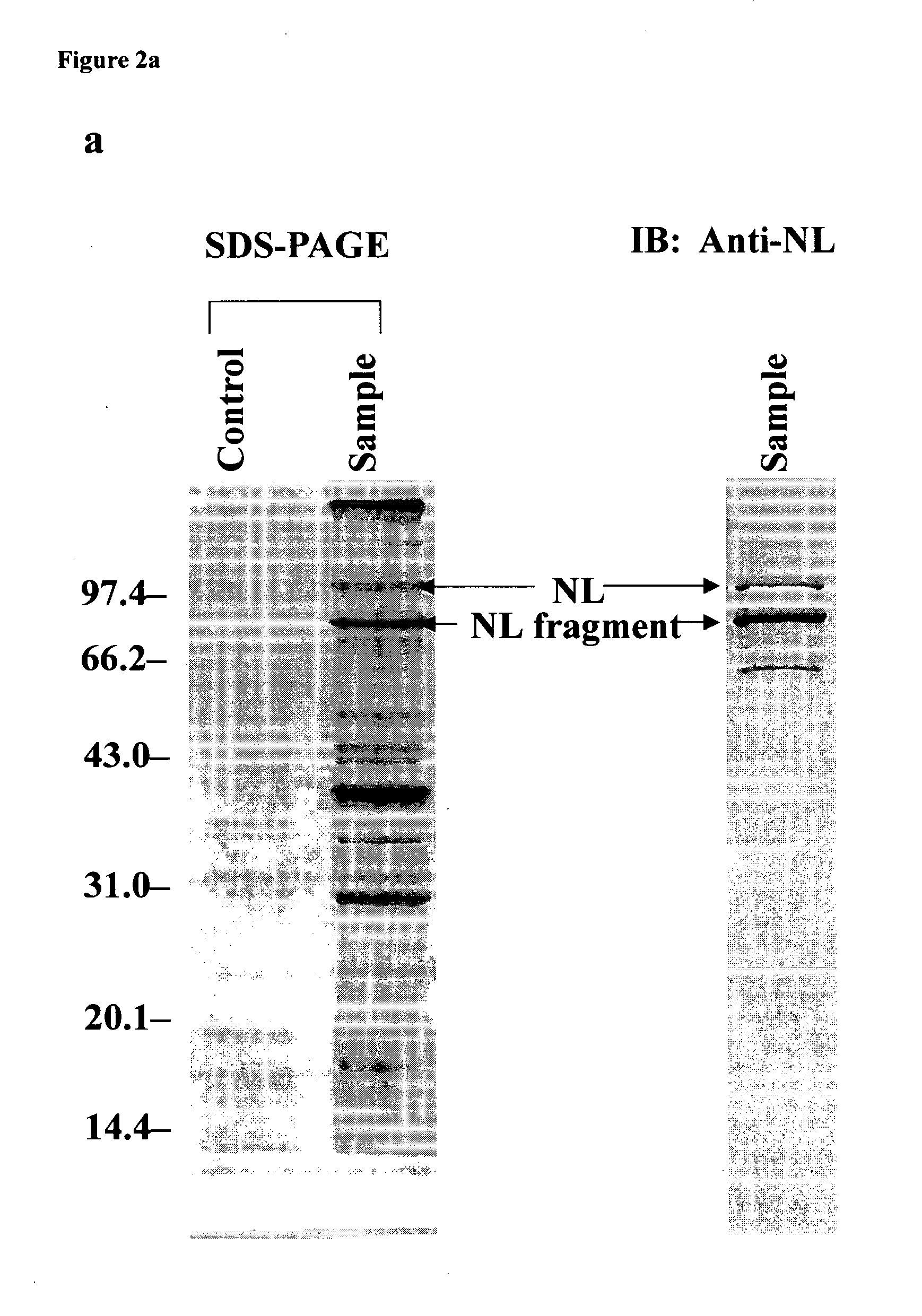
[0084] To investigate the mechanism of action of ES, we isolated ES-binding proteins directly from the membrane proteins of human microvascular endothelial cells (HMECs) with immobilized ES. Nucleolin was identified as a critical member in the ES signaling network, and is the most interesting one in the network. Here we describe that NL serves as a novel receptor for ES, and mediates the activity of ES in antiangiogenesis.
[0085] Methodology:
[0086] Methods that are used in the study of NL and ES interactions are generally known in the art. Descriptions of these methods are provided as follows:
[0088] Endothelial cells (HMECs or HUVECs, 2×104 per well) were seeded into the upper chamber of Transwell™ filter (8 μm pores, Costar) with DMEM medium containing 0.5% FCS and 10 ng / ml VEGF (PeproTech EC). ES (from Protgen) with indicated concentrations and other reagents (NL and Anti-NL) were added in both upper c...
example two
[0103] Nucleolin is a Novel Receptor for Endostatin
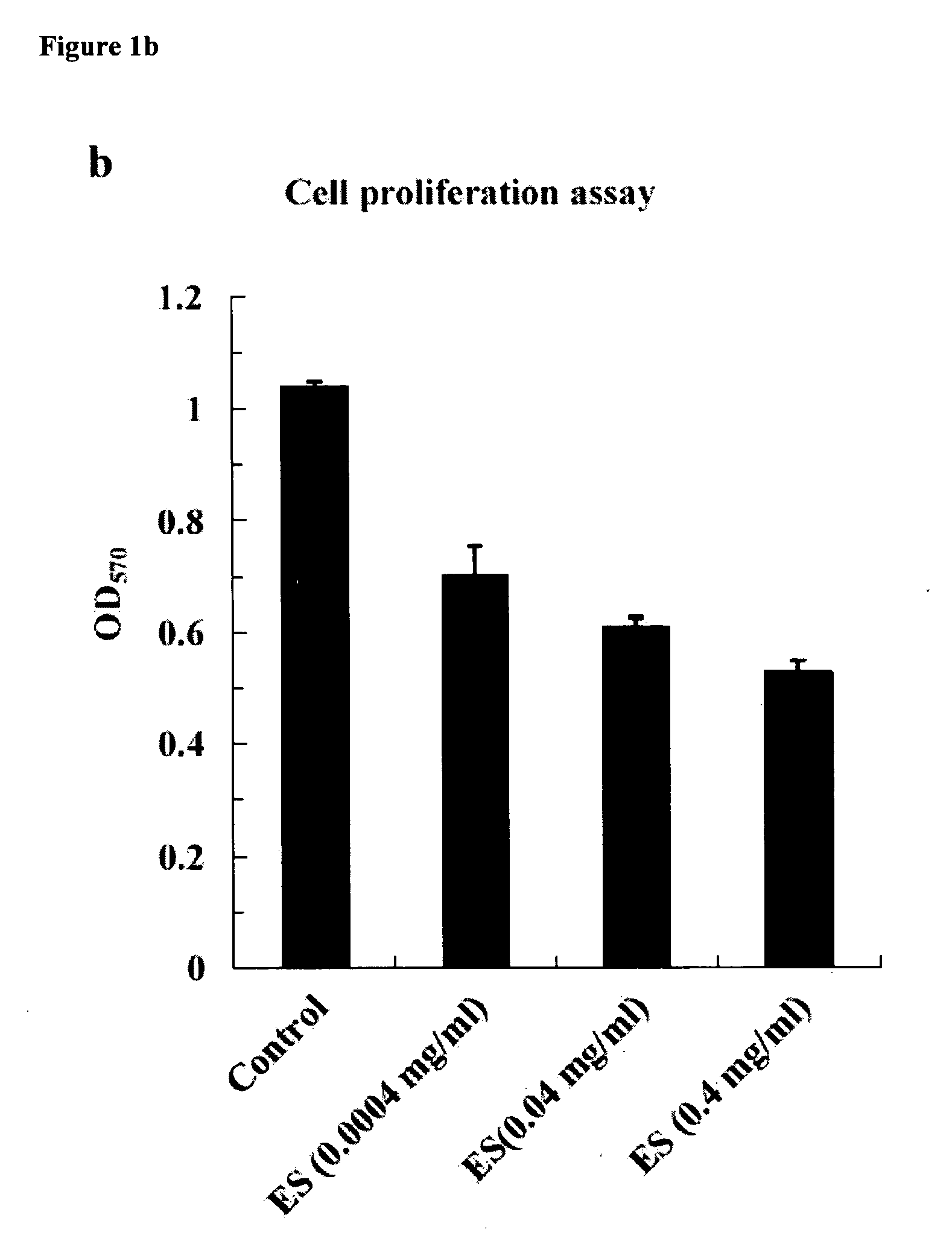
[0104] If NL is a receptor for ES, it should mediate the activities of ES in antiangiogenesis such as inhibiting the migration, proliferation, and adhesion of endothelial cells. To characterize the role of NL during the process of mediating ES activities, competitive cell migration and proliferation assays were therefore performed with ES, recombinant NL, and polyclonal antibodies against NL, respectively. Since NL was isolated from HMECs as a potential receptor for ES in antiangiogenesis, whether or not NL plays similar roles in other widely accepted endothelial cells should be demonstrated. To this end, human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC), isolated directly from umbilical veins, were subjected to competitive cell migration and proliferation assays. This kind of endothelial cells can migrate through a microporous (8 μm) membrane under stimulation of VEGF, and ES inhibits such migration. Recombinant NL lifted the inhibiti...
example three
[0106] Nucleolin Mediates Endostatin Signal Pathway
[0107] To unravel the exact role of NL in the signal transduction pathways of ES, we then investigated the down stream events. Retrospect that the amount of ES-NL complex varied when incubating ES with HMECs, and reached the maximal level around 2 h (FIG. 2e). ES may be internalized by HMECs via cell surface NL, and some of the internalized ES is degraded by HMECs subsequently. It seems that there is a balance between ES internalization and degradation (FIG. 2e).
[0108] To confirm that the internalization of ES is via cell surface NL, immunofluorescence localization was carried out with biotinylated ES. HMECs were incubated with biotinylated ES for different periods of time, and the process of internalization of ES was observed under fluorescence microscope after biotinylated ES was stained with TRITC-labeled streptavidin (FIG. 4a-f). Upon 30 min of incubation, most of the internalized ES distributed in cytoplasm but the amount was...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| MW | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| MW | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com