Grinding method of crank pin and grinding machine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
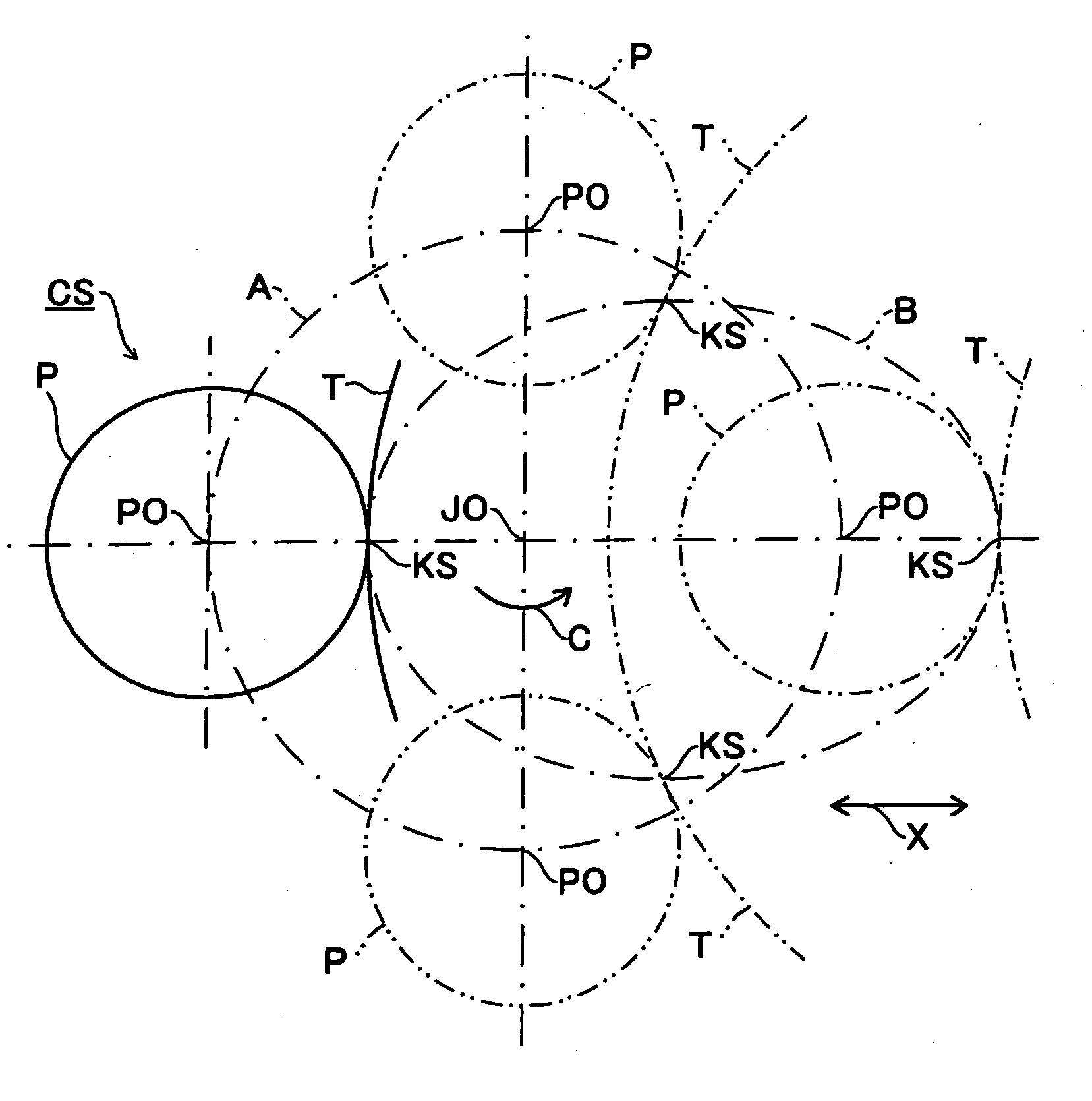
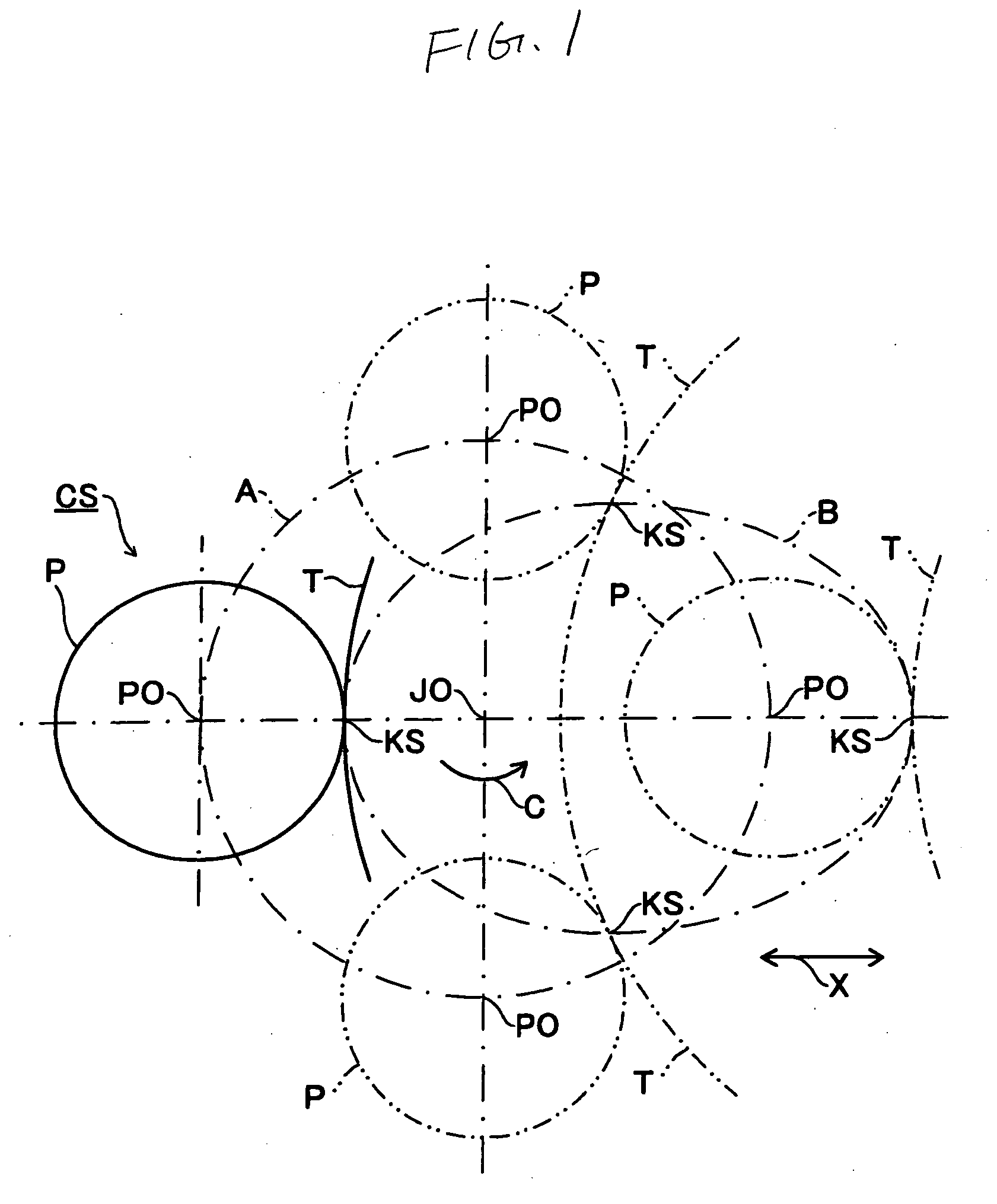
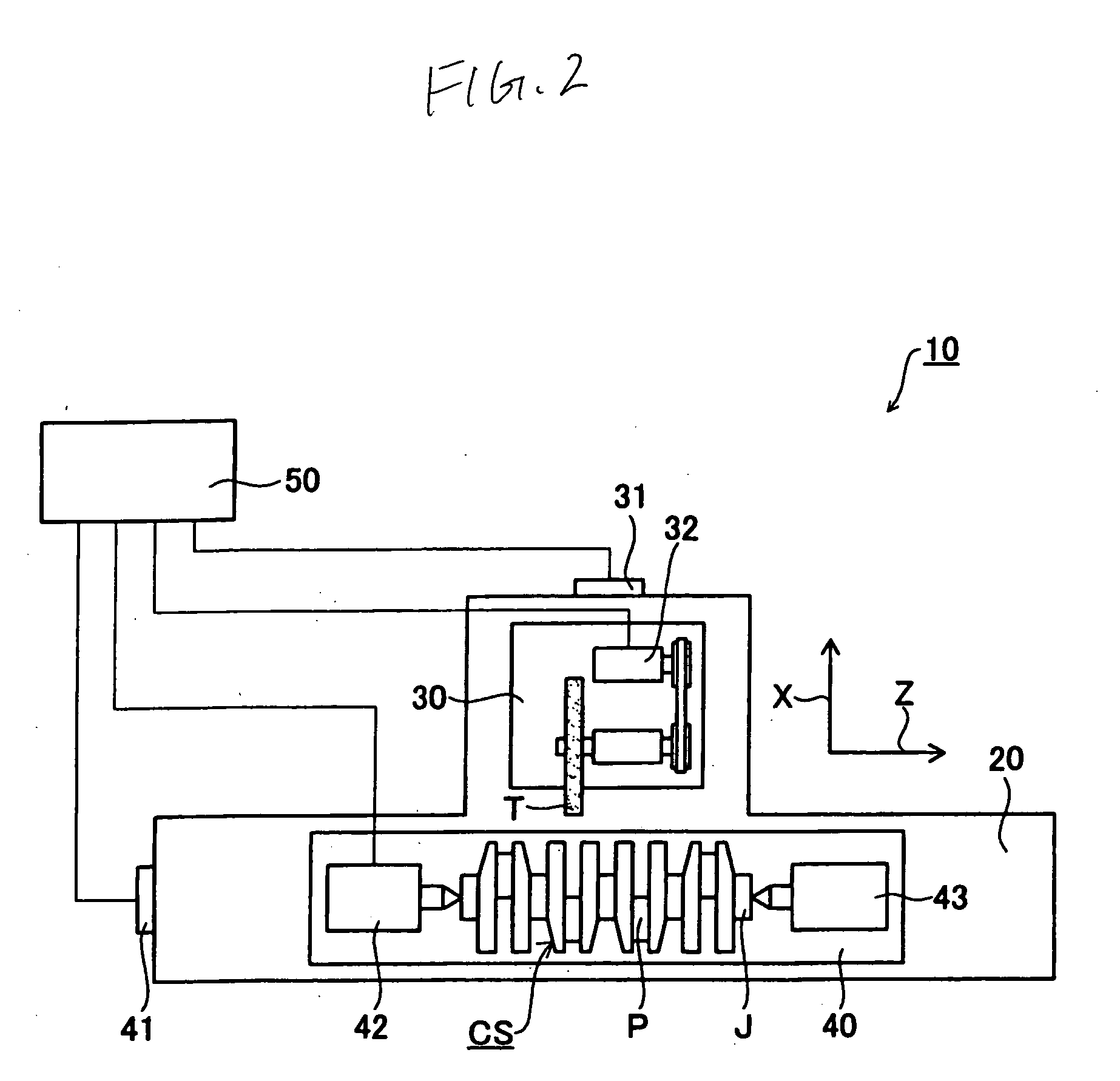
[0022] At grinding portions KS, at which the grinding wheel T comes into contact with the crank pin P, the rotation number of the crankshaft CS is changed according to a rotation phase angle of the crankshaft CS in order to make constant the relative speed between an outer circumferential surface of the grinding wheel T and an outer circumferential surface of the crank pin P or to make the change in the relative speed between the outer circumferential surface of the grinding wheel T and the outer circumferential surface of the crank pin P small comparing with the constant rotation number of the crankshaft CS, that is, to make the relative speed almost constant.
[0023] For example, the rotation number of the crankshaft CS by the rotation phase angle of the crankshaft CS is extracted from fixed values defined by the shapes of the crankshaft CS or the grinding wheel T such as “the diameter of the crank pin P”, “the distance between a journal center JO and a center axis of the crank pin...
embodiment 2
[0027] In one revolution of the crankshaft CS, since the grinding portions KS deviate vertically from the surface connecting the journal center JO and the rotation center of the grinding wheel T, the position of the crank pin P with respect to the grinding wheel T is changed. Therefore, the grinding efficiency and abrasive grain load are affected by the change in the position of the crank pin P as well as the change in the grinding speed. Therefore, the rotation number of the crankshaft CS is changed according to the rotation phase angle of the crankshaft CS in order to make constant the relevant indices such as grinding efficiency, abrasive grain load or the like on the basis of fixed values such as “the diameter of the crank pin P”, “the eccentric amount of the crank pin P”, “the diameter of the grinding wheel T” or the like; theoretical values extracted from fixed values or the like such as “grinding-removal allowance”; or estimated values extracted while some fixed values are om...
embodiment 3
[0029] When the crankshaft CS is revolved at a constant rotation number, there can be portions having superior surface roughness than required value and portions capable of enduring severer grinding conditions, for example, portions without grinding burn even at a higher grinding speed, throughout the outer circumferential surface of the crank pin P. Therefore, the rotation phase angles at the above portions are extracted as the theoretical values extracted from the various fixed values described above or values measured after an actual process, and then the rotation number of the crankshaft CS is changed to make the rotation number fast at the rotation phase angles.
[0030] Then, the process time can be shortened.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Speed | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com