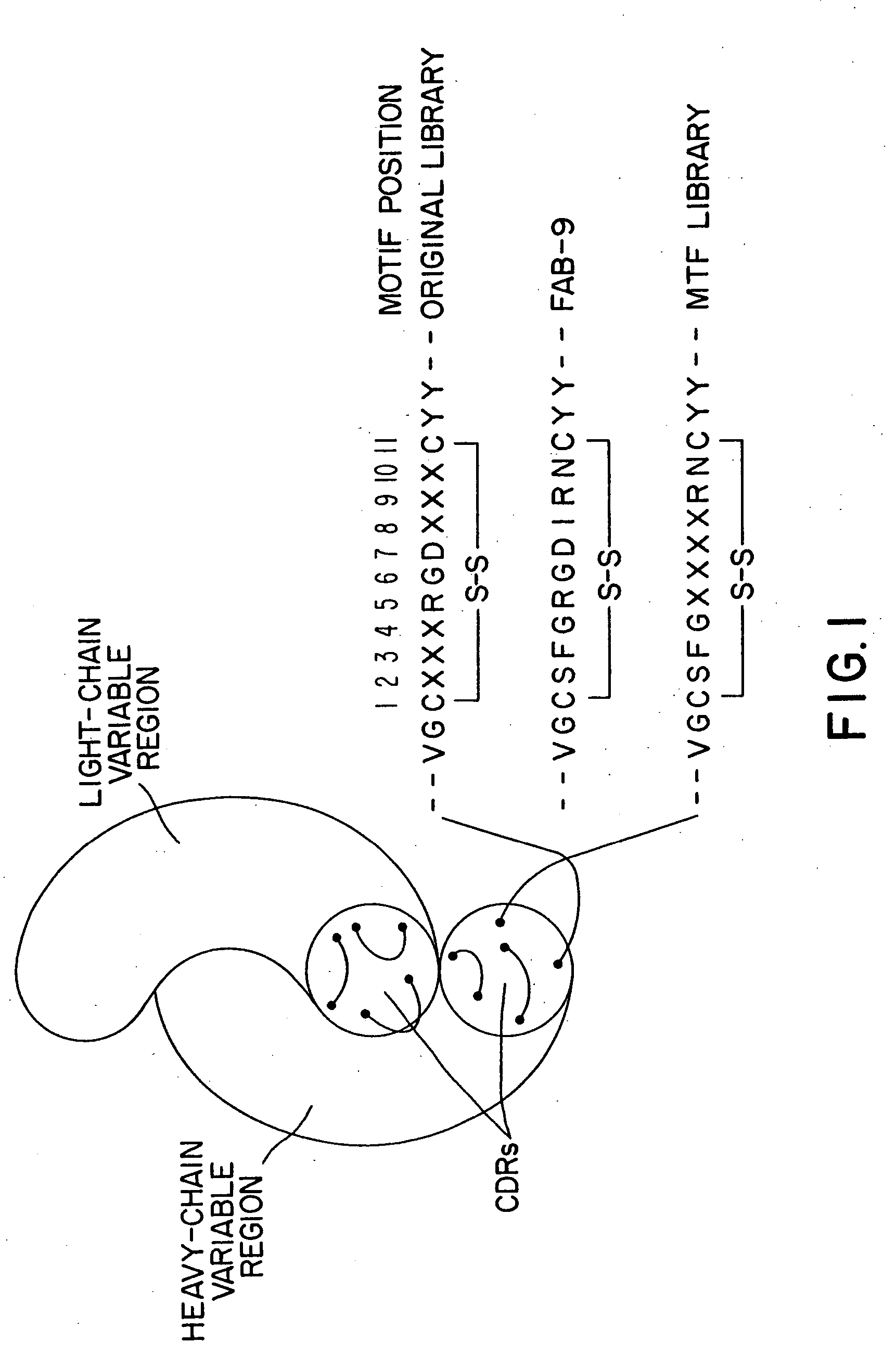
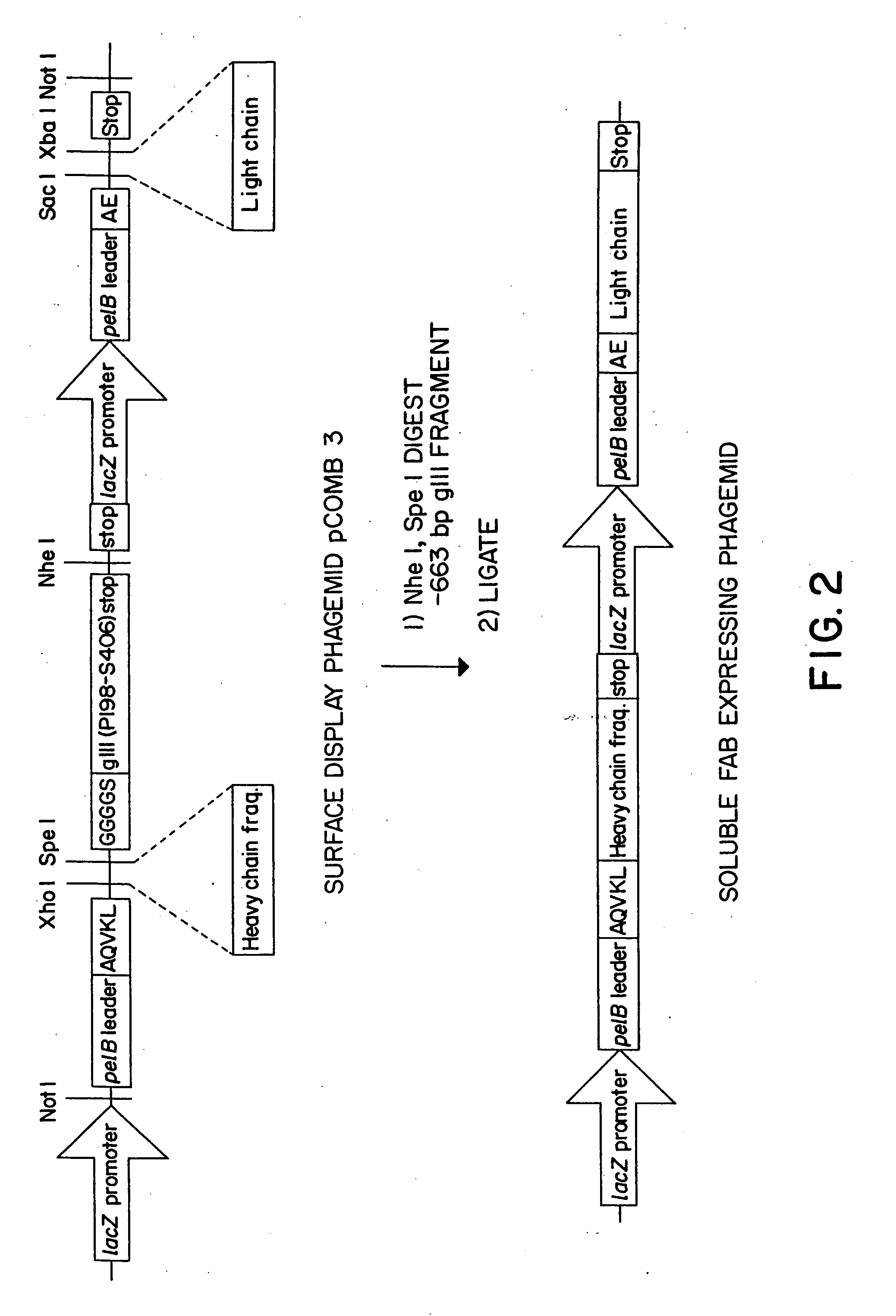
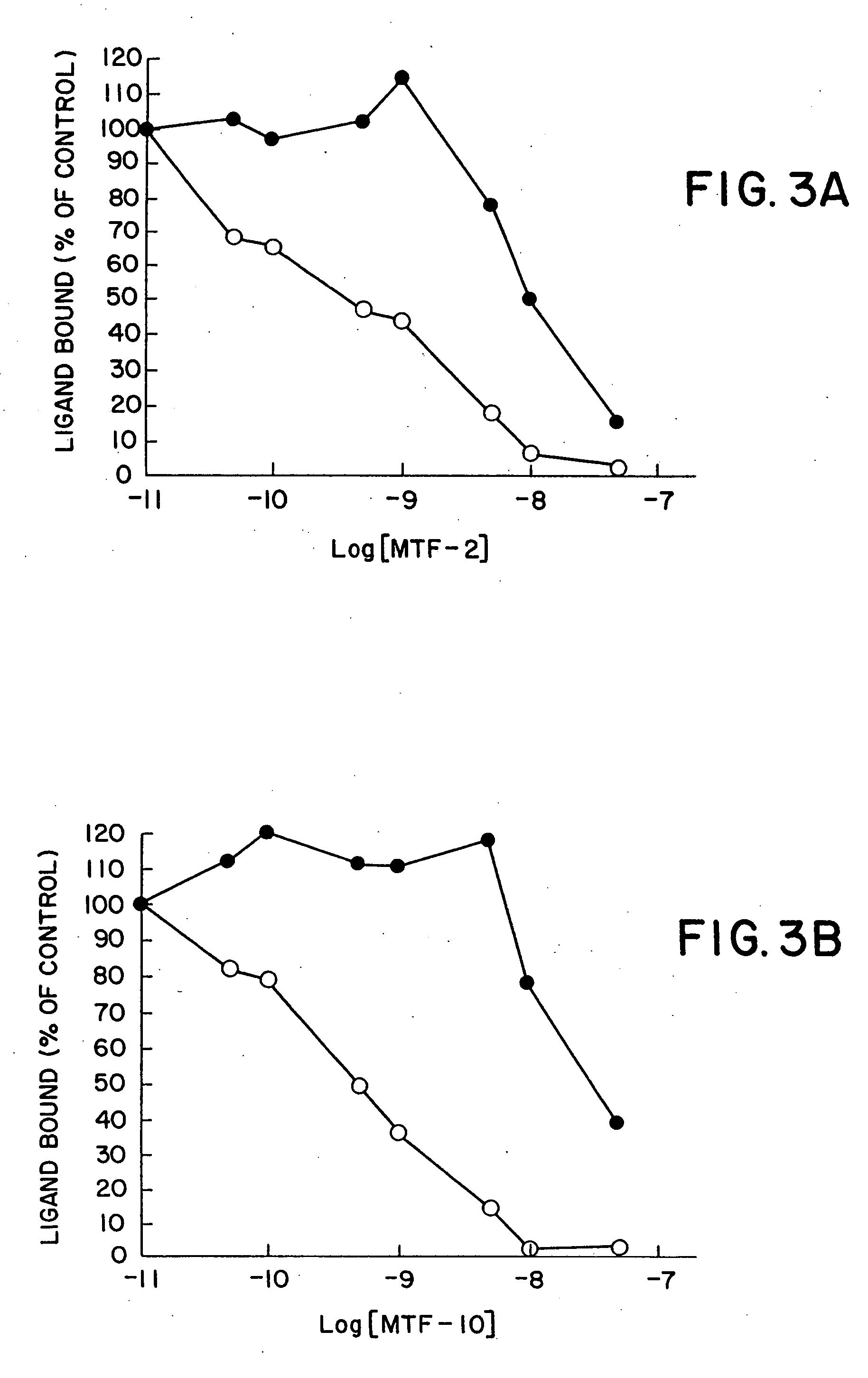
Methods for producing polypeptide binding sites, monoclonal antibodies and compositions thereof
a monoclonal antibody and polypeptide technology, applied in the field of protein biochemistry and immunology, to achieve the effects of increasing antibody binding specificity, reducing the specificity of ligands, and reducing the specificity of receptors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0313] The following examples relating to this invention are illustrative and should not, of course, be construed as specifically limiting the invention. Moreover, such variations of the invention, now known or later developed, which would be within the purview of one skilled in the art are to be considered to fall within the scope of the present invention hereinafter claimed.
1. Preparation of Synthetic Binding Sites Within the Heavy Chain CDR3 Domain of a Phagemid Fab Display Protein Produced by a Dicistronic Expression Vector
[0314] A. Preparation of Nucleotide Sequences for Encoding Synthetic Binding Sites Containing the Peptide, Arginine-Glycine-Aspartic Acid (RGD)
[0315] The immunoglobulin gene phagemid expression vector, pMT12, containing the heavy and light chain sequences for expressing the soluble form of an antibody was used to prepare the synthetic binding site proteins containing the peptides, arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD), of this invention as described below i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com